Abstract
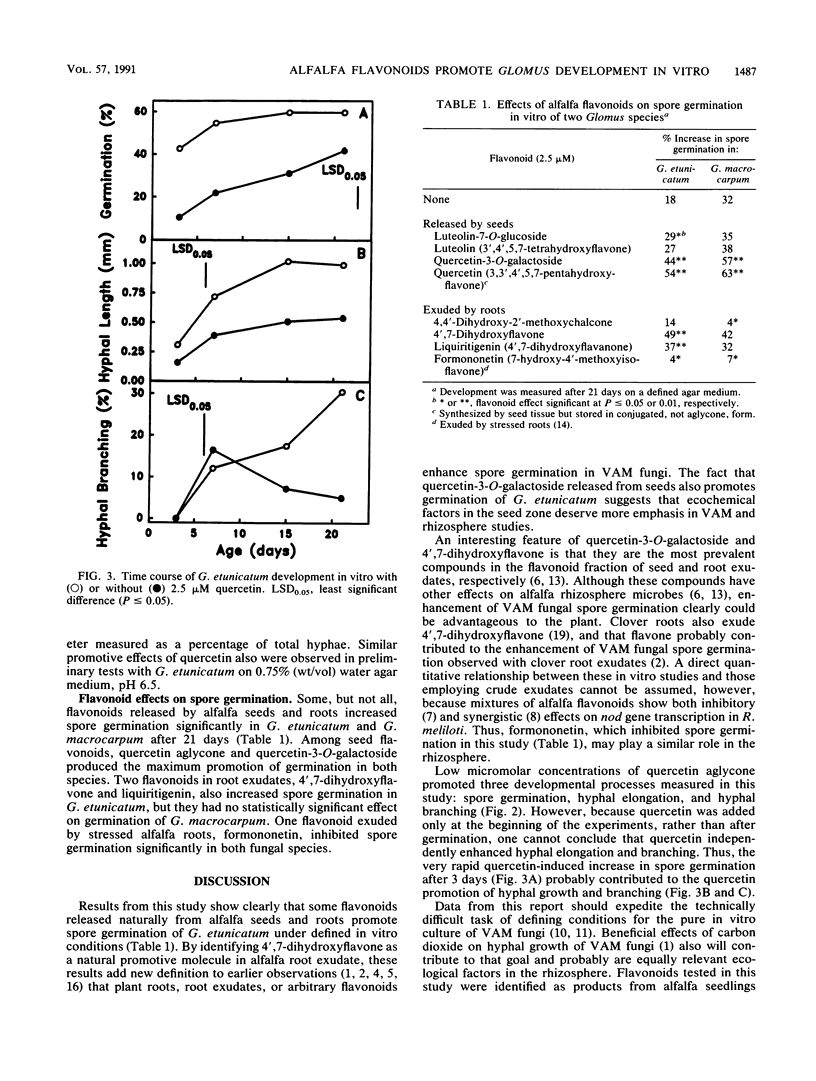
Because flavonoids from legumes induce transcription of nodulation genes in symbiotic rhizobial bacteria, it is reasonable to test whether these compounds alter the development of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal (VAM) fungi that infect those plants. Quercetin-3-O-galactoside, the dominant flavonoid released naturally from alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) seeds, promoted spore germination of Glomus etunicatum and Glomus macrocarpum in vitro. Quercetin produced the maximum increases in spore germination, hyphal elongation, and hyphal branching in G. etunicatum at 1 to 2.5 μM concentrations. Two flavonoids exuded from alfalfa roots, 4′,7-dihydroxyflavone and 4′,7-dihydroxyflavanone, also enhanced spore germination of this fungal species. Formononetin, an isoflavone that is released from stressed alfalfa roots, inhibited germination of both Glomus species. These in vitro results suggest that plant flavonoids may facilitate or regulate the development of VAM symbioses and offer new hope for developing pure, plant-free cultures of VAM fungi.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bécard G., Piché Y. Fungal Growth Stimulation by CO(2) and Root Exudates in Vesicular-Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Symbiosis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Sep;55(9):2320–2325. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.9.2320-2325.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias K. S., Safir G. R. Hyphal Elongation of Glomus fasciculatus in Response to Root Exudates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Aug;53(8):1928–1933. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.8.1928-1933.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig U. A., Joseph C. M., Phillips D. A. Flavonoids Released Naturally from Alfalfa Seeds Enhance Growth Rate of Rhizobium meliloti. Plant Physiol. 1991 Mar;95(3):797–803. doi: 10.1104/pp.95.3.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig U. A., Maxwell C. A., Joseph C. M., Phillips D. A. Chrysoeriol and Luteolin Released from Alfalfa Seeds Induce nod Genes in Rhizobium meliloti. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jan;92(1):116–122. doi: 10.1104/pp.92.1.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig U. A., Maxwell C. A., Joseph C. M., Phillips D. A. Effects of alfalfa nod gene-inducing flavonoids on nodABC transcription in Rhizobium meliloti strains containing different nodD genes. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2769–2773. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2769-2773.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig U. A., Maxwell C. A., Joseph C. M., Phillips D. A. Interactions among Flavonoid nod Gene Inducers Released from Alfalfa Seeds and Roots. Plant Physiol. 1989 Nov;91(3):1138–1142. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.3.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. R. Rhizobium-legume nodulation: life together in the underground. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):203–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90893-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell C. A., Hartwig U. A., Joseph C. M., Phillips D. A. A Chalcone and Two Related Flavonoids Released from Alfalfa Roots Induce nod Genes of Rhizobium meliloti. Plant Physiol. 1989 Nov;91(3):842–847. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.3.842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell C. A., Phillips D. A. Concurrent Synthesis and Release of nod-Gene-Inducing Flavonoids from Alfalfa Roots. Plant Physiol. 1990 Aug;93(4):1552–1558. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.4.1552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters N. K., Frost J. W., Long S. R. A plant flavone, luteolin, induces expression of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3738520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters N. K., Verma D. P. Phenolic compounds as regulators of gene expression in plant-microbe relations. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1990 Jan-Feb;3(1):4–8. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-3-004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


