Abstract
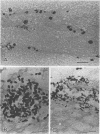
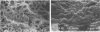
St. Nectaire cheese is a semisoft cheese of French origin that, along with Brie and Camembert cheeses, belongs to the class of surface mold-ripened cheese. The surface microorganisms that develop on the cheese rind during ripening impart a distinctive aroma and flavor to this class of cheese. We have documented the sequential appearance of microorganisms on the cheese rind and in the curd over a 60-day ripening period. Scanning electron microscopy was used to visualize the development of surface fungi and bacteria. Light microscopy of stained paraffin sections was used to study cross sections through the rind. We also monitored the development of bacterial and yeast populations in and the pH of the curd and rind. The earliest stage of ripening (0 to 2 days) is dominated by the lactic acid bacterium Streptococcus cremoris and multilateral budding yeasts, primarily Debaryomyces and Torulopsis species. Geotrichum candidum follows closely, and then zygomycetes of the genus Mucor develop at day 4 of ripening. At day 20, the deuteromycete Trichothecium roseum appears. From day 20 until the end of the ripening process, coryneforms of the genera Brevibacterium and Arthrobacter can be seen near the surface of the cheese rind among fungal hyphae and yeast cells.
Full text
PDF