Abstract
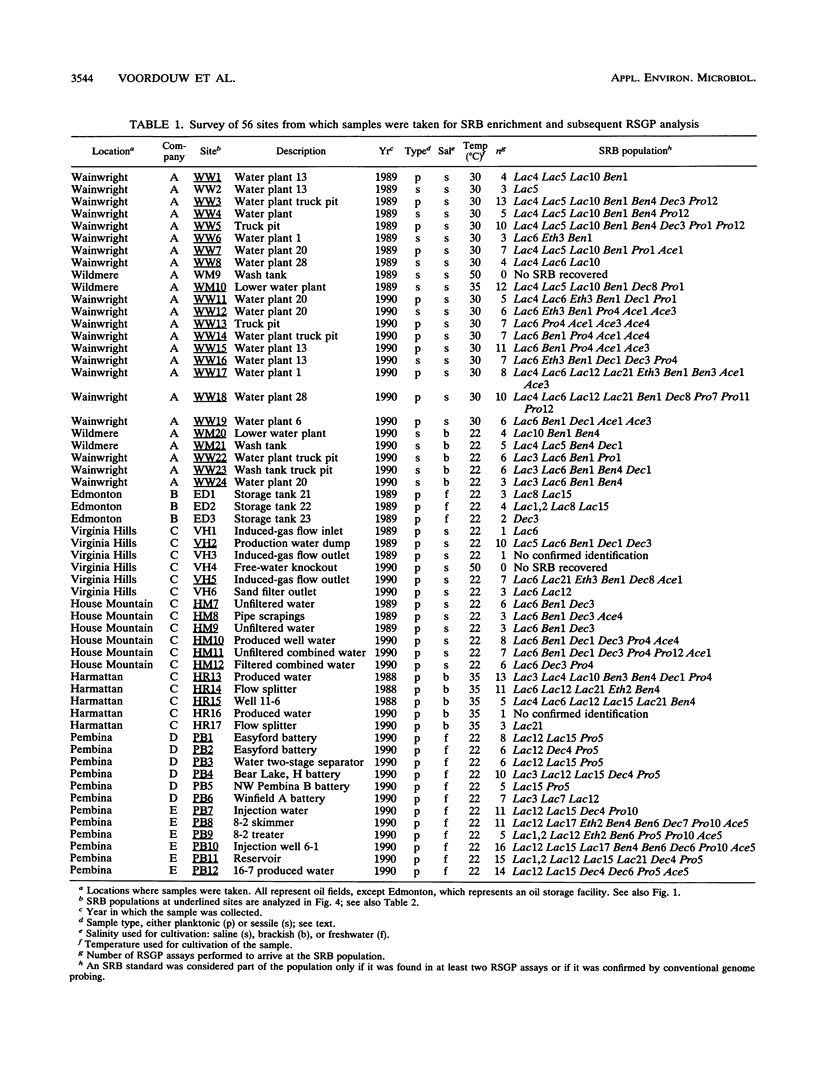
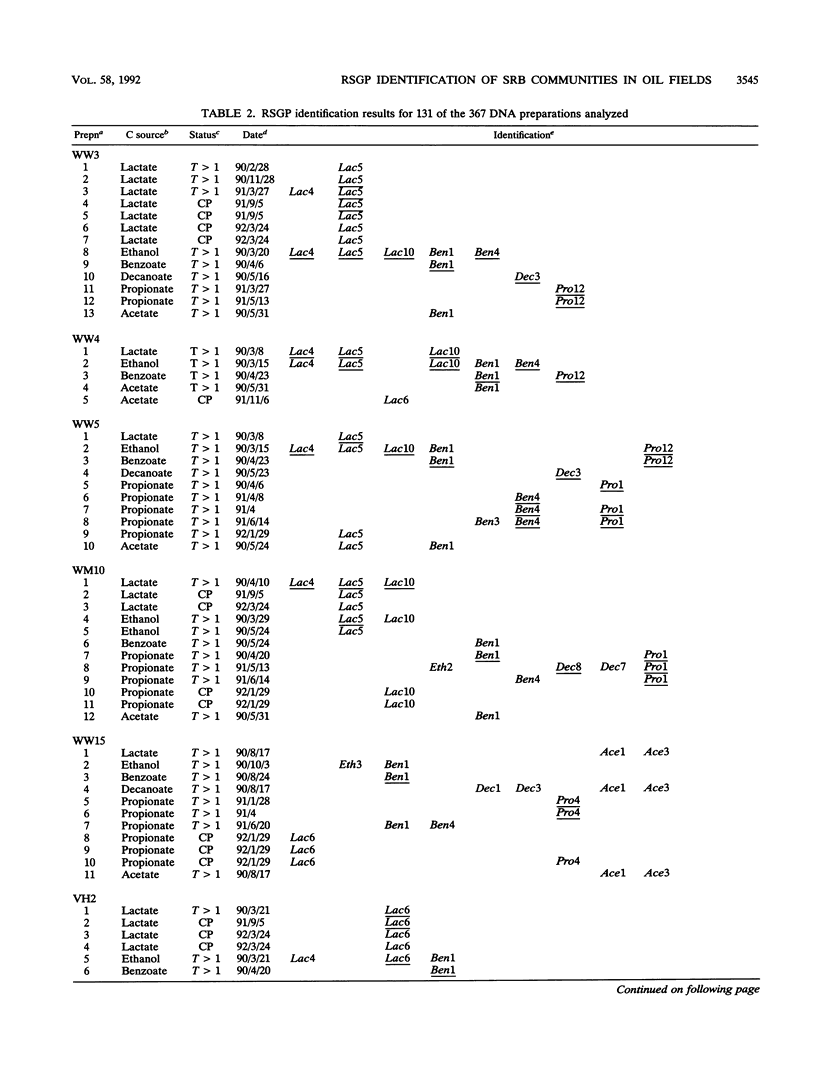
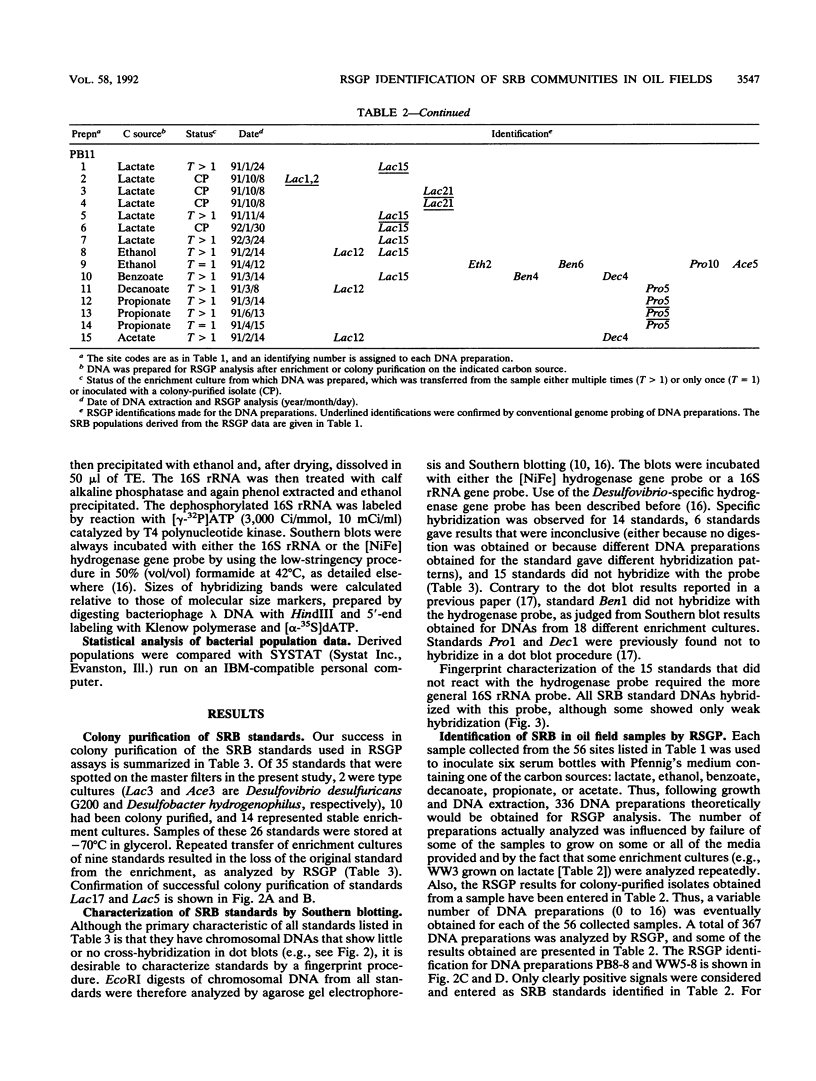
Thirty-five different standards of sulfate-reducing bacteria, identified by reverse sample genome probing and defined as bacteria with genomes showing little or no cross-hybridization, were in part characterized by Southern blotting, using 16S rRNA and hydrogenase gene probes. Samples from 56 sites in seven different western Canadian oil field locations were collected and enriched for sulfate-reducing bacteria by using different liquid media containing one of the following carbon sources: lactate, ethanol, benzoate, decanoate, propionate, or acetate. DNA was isolated from the enrichments and probed by reverse sample genome probing using master filters containing denatured chromosomal DNAs from the 35 sulfate-reducing bacterial standards. Statistical analysis of the microbial compositions at 44 of the 56 sites indicated the presence of two distinct communities of sulfate-reducing bacteria. The discriminating factor between the two communities was the salt concentration of the production waters, which were either fresh water or saline. Of 34 standards detected, 10 were unique to the fresh water and 18 were unique to the saline oil field environment, while only 6 organisms were cultured from both communities.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amann R. I., Stromley J., Devereux R., Key R., Stahl D. A. Molecular and microscopic identification of sulfate-reducing bacteria in multispecies biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Feb;58(2):614–623. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.2.614-623.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkay T., Liebert C., Gillman M. Hybridization of DNA probes with whole-community genome for detection of genes that encode microbial responses to pollutants: mer genes and Hg2+ resistance. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1574–1577. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1574-1577.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux R., Delaney M., Widdel F., Stahl D. A. Natural relationships among sulfate-reducing eubacteria. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6689–6695. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6689-6695.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux R., He S. H., Doyle C. L., Orkland S., Stahl D. A., LeGall J., Whitman W. B. Diversity and origin of Desulfovibrio species: phylogenetic definition of a family. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3609–3619. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3609-3619.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Nakazawa A. Cyclic AMP-dependent initiation and rho-dependent termination of colicin E1 gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7072–7078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holben William E., Jansson Janet K., Chelm Barry K., Tiedje James M. DNA Probe Method for the Detection of Specific Microorganisms in the Soil Bacterial Community. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Mar;54(3):703–711. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.3.703-711.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odom J. M., Jessie K., Knodel E., Emptage M. Immunological cross-reactivities of adenosine-5'-phosphosulfate reductases from sulfate-reducing and sulfide-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Mar;57(3):727–733. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.3.727-733.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerville C. C., Knight I. T., Straube W. L., Colwell R. R. Simple, rapid method for direct isolation of nucleic acids from aquatic environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Mar;55(3):548–554. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.3.548-554.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voordouw G., Niviere V., Ferris F. G., Fedorak P. M., Westlake D. W. Distribution of Hydrogenase Genes in Desulfovibrio spp. and Their Use in Identification of Species from the Oil Field Environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Dec;56(12):3748–3754. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.12.3748-3754.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voordouw G., Voordouw J. K., Karkhoff-Schweizer R. R., Fedorak P. M., Westlake D. W. Reverse sample genome probing, a new technique for identification of bacteria in environmental samples by DNA hybridization, and its application to the identification of sulfate-reducing bacteria in oil field samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Nov;57(11):3070–3078. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.11.3070-3078.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]