Abstract
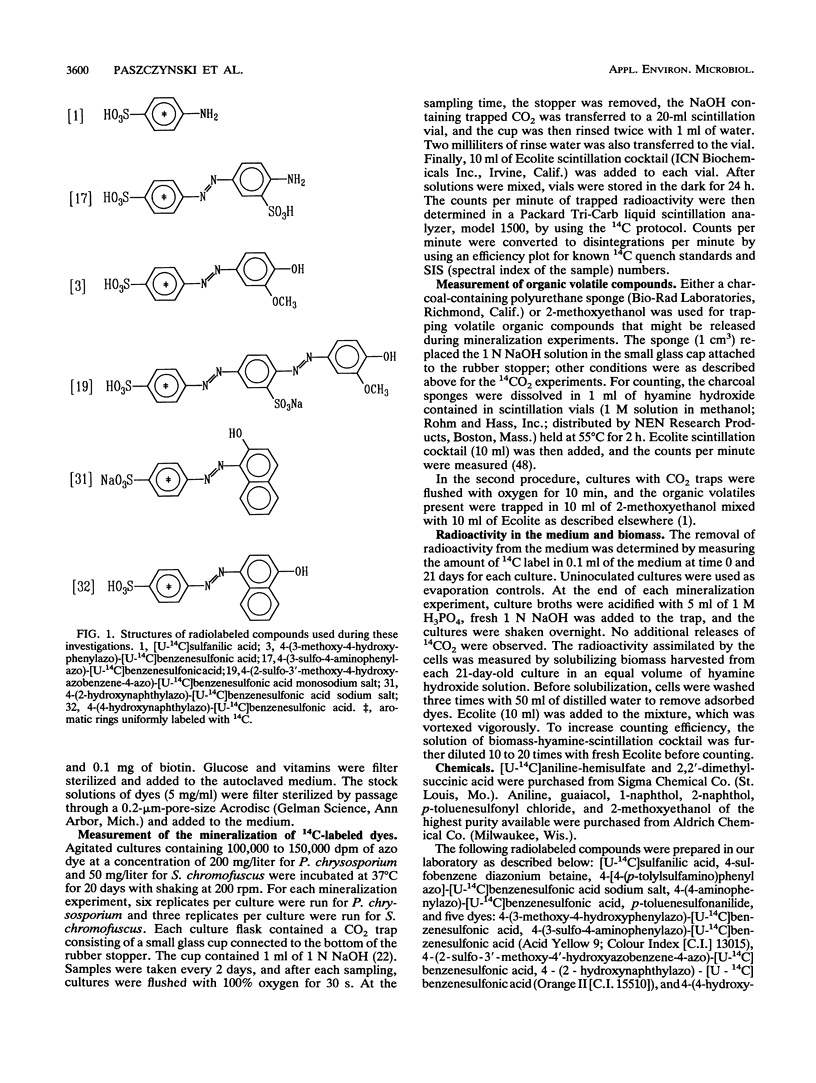
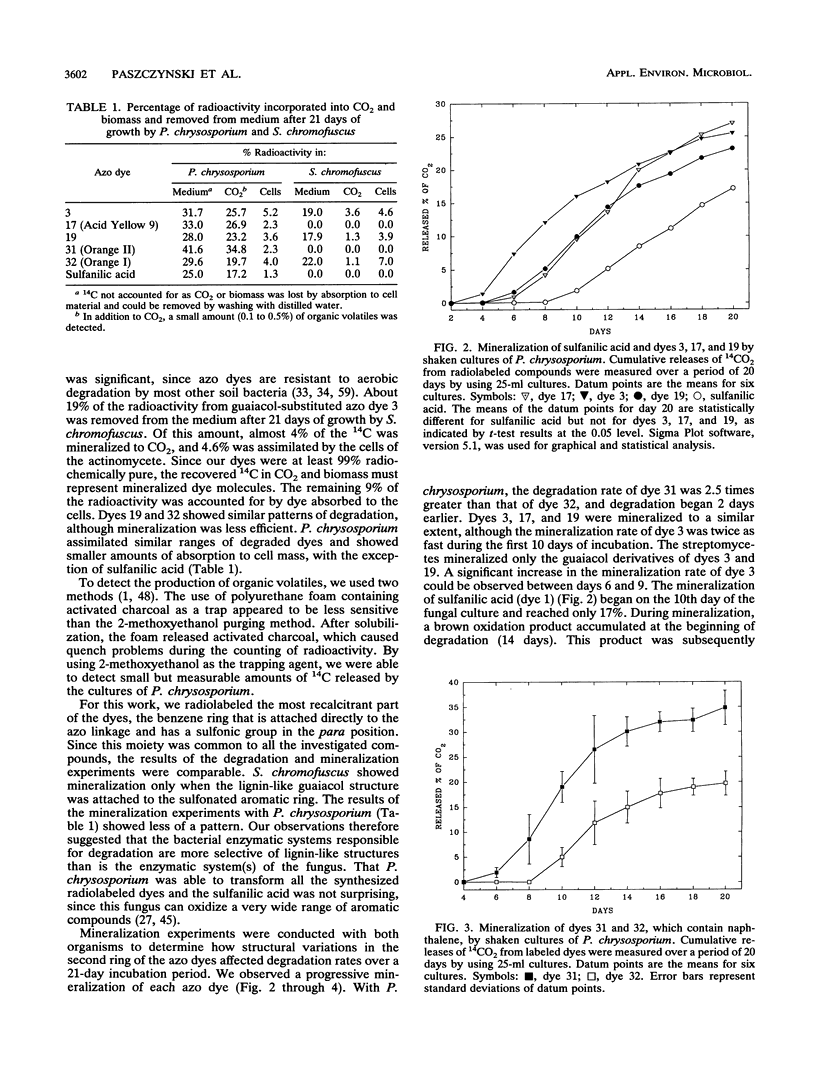
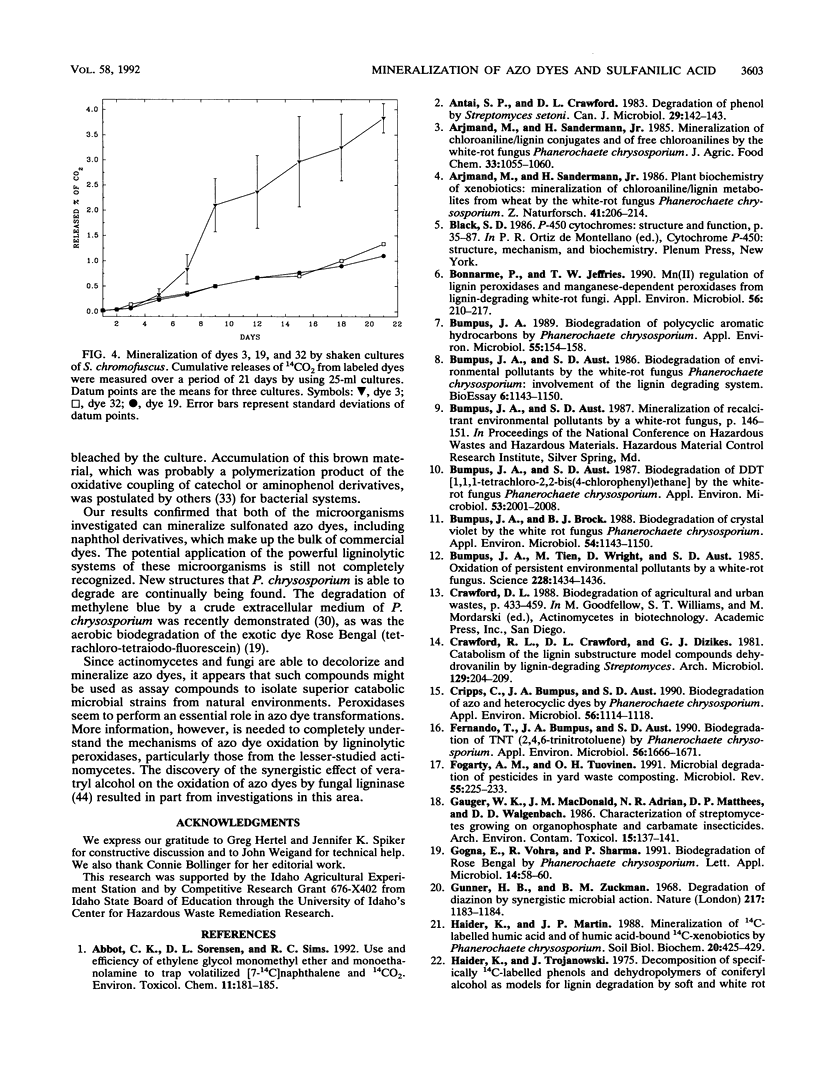
Five 14C-radiolabeled azo dyes and sulfanilic acid were synthesized and used to examine the relationship between dye substitution patterns and biodegradability (mineralization to CO2) by a white-rot fungus and an actinomycete. 4-Amino-[U-14C]benzenesulfonic acid and 4-(3-sulfo-4-aminophenylazo)-[U-14C]benzenesulfonic acid were used as representative compounds having sulfo groups or both sulfo and azo groups. Such compounds are not known to be present in the biosphere as natural products. The introduction of lignin-like fragments into the molecules of 4-amino-[U-14C]benzenesulfonic acid and 4-(3-sulfo-4-aminophenylazo)-[U-14C]benzenesulfonic acid by coupling reactions with guaiacol (2-methoxyphenol) resulted in the formation of the dyes 4-(3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylazo)-[U-14C]benzenesulfonic acid and 4-(2-sulfo-3'-methoxy-4'-hydroxy-azobenzene-4-azo)-[U-14C]benzenesulf oni c acid, respectively. The synthesis of acid azo dyes 4-(2-hydroxy-1-naphthylazo)-[U-14C]benzenesulfonic acid and 4-(4-hydroxy-1-naphthylazo)-[U-14C]benzenesulfonic acid also allowed the abilities of these microorganisms to mineralize these commercially important compounds to be evaluated. Phanerochaete chrysosporium mineralized all of the sulfonated azo dyes, and the substitution pattern did not significantly influence the susceptibility of the dyes to degradation. In contrast, Streptomyces chromofuscus was unable to mineralize aromatics with sulfo groups and both sulfo and azo groups. However, it mediated the mineralization of modified dyes containing lignin-like substitution patterns. This work showed that lignocellulolytic fungi and bacteria can be used for the biodegradation of anionic azo dyes, which thus far have been considered among the xenobiotic compounds most resistant to biodegradation.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonnarme P., Jeffries T. W. Mn(II) Regulation of Lignin Peroxidases and Manganese-Dependent Peroxidases from Lignin-Degrading White Rot Fungi. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jan;56(1):210–217. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.1.210-217.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bumpus J. A., Aust S. D. Biodegradation of DDT [1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane] by the white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Sep;53(9):2001–2008. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.9.2001-2008.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bumpus J. A. Biodegradation of polycyclic hydrocarbons by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jan;55(1):154–158. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.1.154-158.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bumpus J. A., Brock B. J. Biodegradation of crystal violet by the white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 May;54(5):1143–1150. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.5.1143-1150.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bumpus J. A., Tien M., Wright D., Aust S. D. Oxidation of persistent environmental pollutants by a white rot fungus. Science. 1985 Jun 21;228(4706):1434–1436. doi: 10.1126/science.3925550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cripps C., Bumpus J. A., Aust S. D. Biodegradation of azo and heterocyclic dyes by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Apr;56(4):1114–1118. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.4.1114-1118.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernando T., Bumpus J. A., Aust S. D. Biodegradation of TNT (2,4,6-trinitrotoluene) by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1666–1671. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1666-1671.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogarty A. M., Tuovinen O. H. Microbiological degradation of pesticides in yard waste composting. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jun;55(2):225–233. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.2.225-233.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauger W. K., MacDonald J. M., Adrian N. R., Matthees D. P., Walgenbach D. D. Characterization of a streptomycete growing on organophosphate and carbamate insecticides. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 1986 Feb;15(2):137–141. doi: 10.1007/BF01059962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunner H. B., Zuckerman B. M. Degradation of 'Diazinon' by synergistic microbial action. Nature. 1968 Mar 23;217(5134):1183–1184. doi: 10.1038/2171183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haemmerli S. D., Leisola M. S., Sanglard D., Fiechter A. Oxidation of benzo(a)pyrene by extracellular ligninases of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Veratryl alcohol and stability of ligninase. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):6900–6903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammel K. E., Kalyanaraman B., Kirk T. K. Oxidation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and dibenzo[p]-dioxins by Phanerochaete chrysosporium ligninase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):16948–16952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huynh V. B., Paszczyński A., Olson P., Crawford R. Transformations of arylpropane lignin model compounds by a lignin peroxidase of the white-rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Oct;250(1):186–196. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90716-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyser P., Kirk T. K., Zeikus J. G. Ligninolytic enzyme system of Phanaerochaete chrysosporium: synthesized in the absence of lignin in response to nitrogen starvation. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):790–797. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.790-797.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lackner R., Srebotnik E., Messner K. Oxidative degradation of high molecular weight chlorolignin by manganese peroxidase of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 15;178(3):1092–1098. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91004-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasti M. B., Pometto A. L., 3rd, Nuti M. P., Crawford D. L. Lignin-solubilizing ability of actinomycetes isolated from termite (Termitidae) gut. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jul;56(7):2213–2218. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.7.2213-2218.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paszczynski A., Crawford R. L. Degradation of azo compounds by ligninase from Phanerochaete chrysosporium: involvement of veratryl alcohol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 15;178(3):1056–1063. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90999-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paszczyński A., Huynh V. B., Crawford R. Comparison of ligninase-I and peroxidase-M2 from the white-rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Feb 1;244(2):750–765. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90644-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHATZ A., ISENBERG H. D., ANGRIST A. A., SCHATZ V. Microbiol metabolism of carbamates. I. Isolation of Streptomyces nitrificans, spec. nov., and other organisms which grow on urethan. J Bacteriol. 1954 Jul;68(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/jb.68.1.1-4.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland J. B., Crawford D. L., Pometto A. L. Catabolism of substituted benzoic acids by streptomyces species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):442–448. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.442-448.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valli K., Gold M. H. Degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol by the lignin-degrading fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):345–352. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.345-352.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter B., Fiechter A., Zimmermann W. Degradation of organochlorine compounds in spent sulfite bleach plant effluents by actinomycetes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Oct;57(10):2858–2863. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.10.2858-2863.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


