Abstract
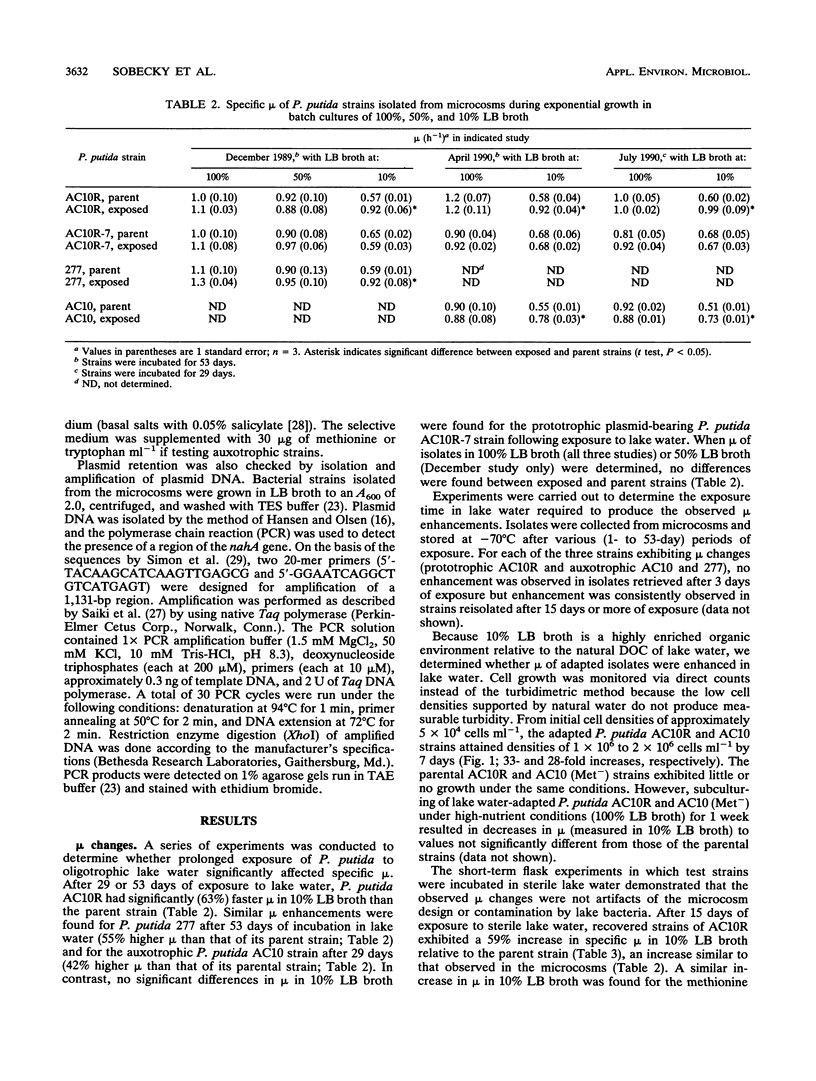
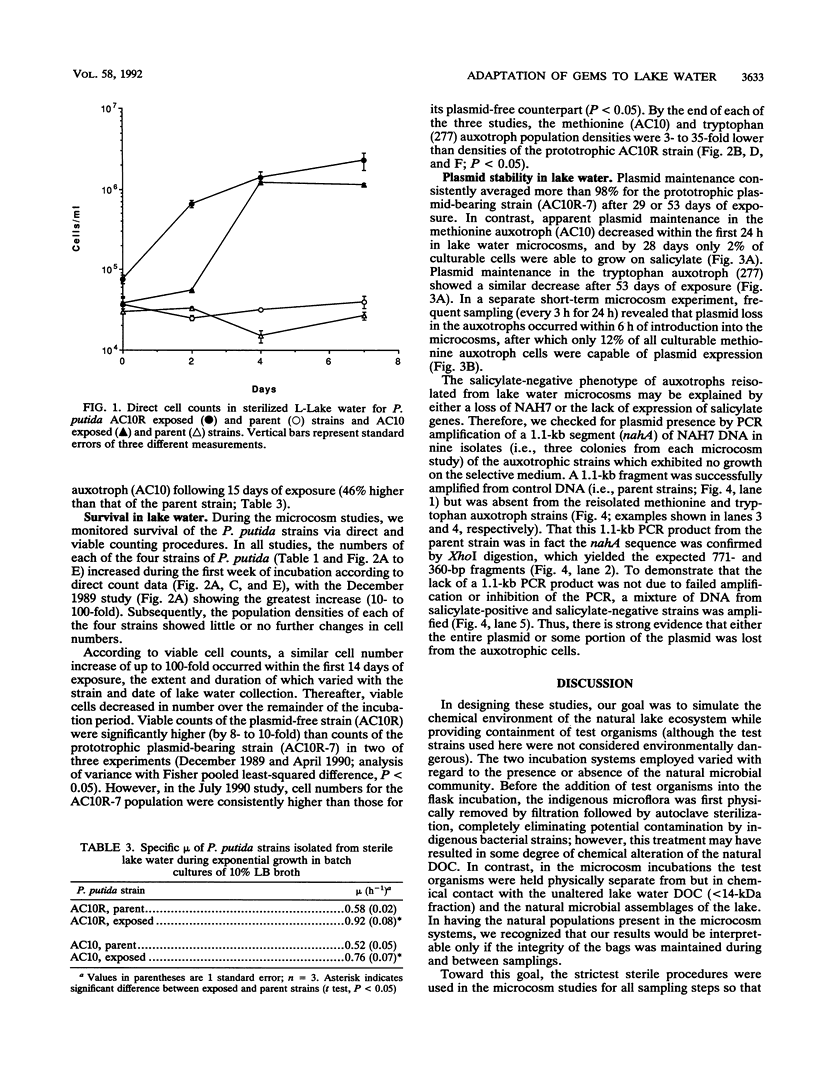
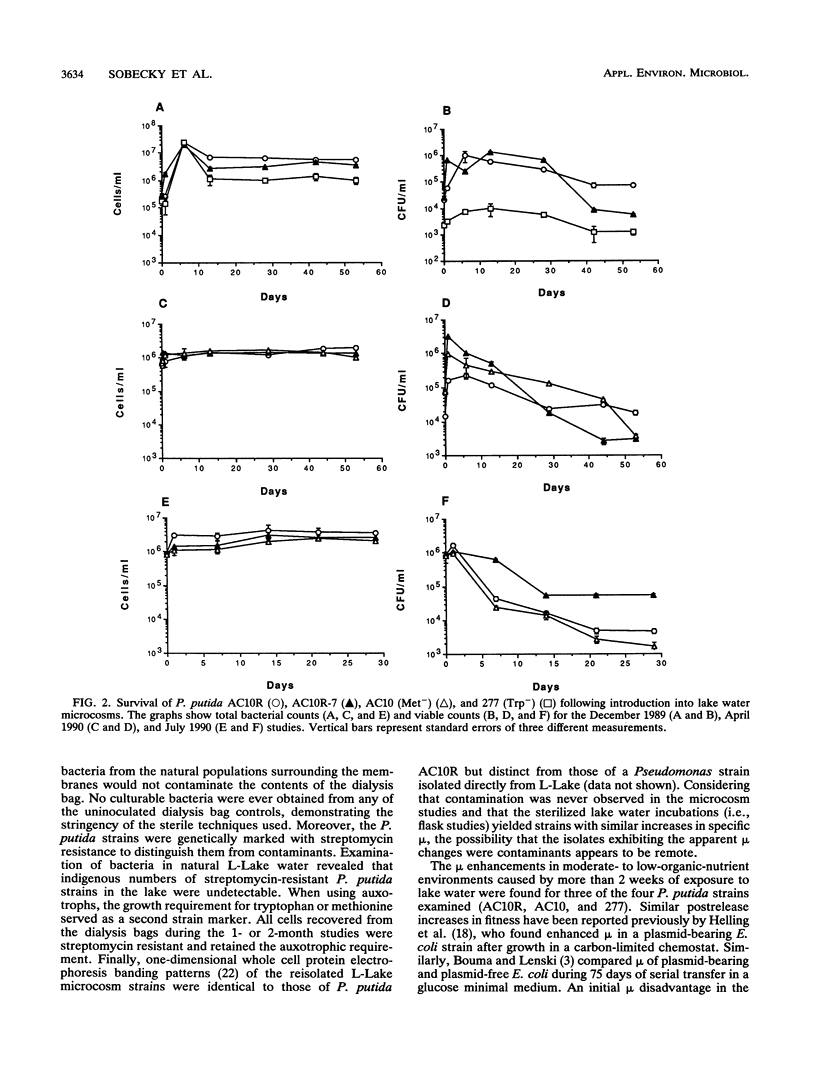
When a genetically engineered microorganism (GEM) is released into a natural ecosystem, its survival, and hence its potential environmental impact, depends on its genetic stability and potential for growth under highly oligotrophic conditions. In this study, we compared plasmid stability and potential for growth on low concentrations of organic nutrients of strains of Pseudomonas putida serving as model GEMs. Plasmid-free and plasmid-bearing (NAH7) prototrophic isogenic strains and two amino-acid auxotrophs, all containing antibiotic resistance markers, were held physically separate from but in chemical contact with lake water containing the natural bacterium-sized microbial populations. Cells were reisolated at intervals over a 2-month period to determine the percent retaining the plasmid and the specific growth rate on various media. Plasmid stability in lake water was strongly strain specific; the NAH7 plasmid was stably maintained by the prototrophic strain for the duration of the test but was lost within 24 h by both of the auxotrophs. Specific growth rates of reisolates, compared with those of the corresponding non-lake water-exposed strains (i.e., parental strains), were not different when measured in rich medium (Luria-Bertani broth). However, specific growth rates were 42, 55, and 63% higher in reisolates of auxotrophs and the plasmid-free prototroph, respectively, when measured in 10-fold-diluted medium after exposure of 15 days or longer to lake water. Moreover, lake water-exposed strains grew actively when reintroduced into sterile lake water (28- to 33-fold increase in numbers over 7 days), while the corresponding unadapted parental strains exhibited no growth over the same period.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P., Roth J. Spontaneous tandem genetic duplications in Salmonella typhimurium arise by unequal recombination between rRNA (rrn) cistrons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3113–3117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouma J. E., Lenski R. E. Evolution of a bacteria/plasmid association. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):351–352. doi: 10.1038/335351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill Winston J. Safety concerns and genetic engineering in agriculture. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):381–384. doi: 10.1126/science.11643810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrd J. J., Colwell R. R. Maintenance of plasmids pBR322 and pUC8 in nonculturable Escherichia coli in the marine environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jul;56(7):2104–2107. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.7.2104-2107.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell B. A., Ye C., Griffiths R. P., Moyer C. L., Morita R. Y. Plasmid expression and maintenance during long-term starvation-survival of bacteria in well water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Aug;55(8):1860–1864. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.8.1860-1864.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caulcott C. A., Dunn A., Robertson H. A., Cooper N. S., Brown M. E., Rhodes P. M. Investigation of the effect of growth environment on the stability of low-copy-number plasmids in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jul;133(7):1881–1889. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-7-1881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Cruz N. E., Toranzos G. A., Ahearn D. G., Hazen T. C. In situ survival of plasmid-bearing and plasmidless Pseudomonas aeruginosa in pristine tropical waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Oct;54(10):2574–2577. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.10.2574-2577.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss R., 3rd Genetic manipulation of microorganisms: potential benefits and biohazards. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1976;30:507–533. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.30.100176.002451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godwin D., Slater J. H. The influence of the growth environment on the stability of a drug resistance plasmid in Escherichia coli K12. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Mar;111(1):201–210. doi: 10.1099/00221287-111-1-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. B., Olsen R. H. Isolation of large bacterial plasmids and characterization of the P2 incompatibility group plasmids pMG1 and pMG5. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):227–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.227-238.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helling R. B., Kinney T., Adams J. The maintenance of Plasmid-containing organisms in populations of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Mar;123(1):129–141. doi: 10.1099/00221287-123-1-129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helling R. B., Vargas C. N., Adams J. Evolution of Escherichia coli during growth in a constant environment. Genetics. 1987 Jul;116(3):349–358. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.3.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbie J. E., Daley R. J., Jasper S. Use of nuclepore filters for counting bacteria by fluorescence microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1225–1228. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1225-1228.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanaka T., Aiba S. A perspective on the application of genetic engineering: stability of recombinant plasmid. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;369:1–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb14172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain R. K., Sayler G. S., Wilson J. T., Houston L., Pacia D. Maintenance and stability of introduced genotypes in groundwater aquifer material. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):996–1002. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.996-1002.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. A., Winstanley C., Pickup R. W., Jones J. G., Saunders J. R. Direct phenotypic and genotypic detection of a recombinant pseudomonad population released into lake water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2537–2544. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2537-2544.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
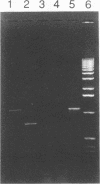
- Schell M. A. Transcriptional control of the nah and sal hydrocarbon-degradation operons by the nahR gene product. Gene. 1985;36(3):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90185-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. R., Farrell E., Dunican K. Survival of R+ Escherichia coli in sea water. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):983–984. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.983-984.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonti R. V., Roth J. R. Role of gene duplications in the adaptation of Salmonella typhimurium to growth on limiting carbon sources. Genetics. 1989 Sep;123(1):19–28. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung K. H., Schell M. A., Hartel P. G. Growth of genetically engineered Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas putida in soil and rhizosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Dec;55(12):3243–3246. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.12.3243-3246.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zünd P., Lebek G. Generation time-prolonging R plasmids: correlation between increases in the generation time of Escherichia coli caused by R plasmids and their molecular size. Plasmid. 1980 Jan;3(1):65–69. doi: 10.1016/s0147-619x(80)90034-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]