Abstract
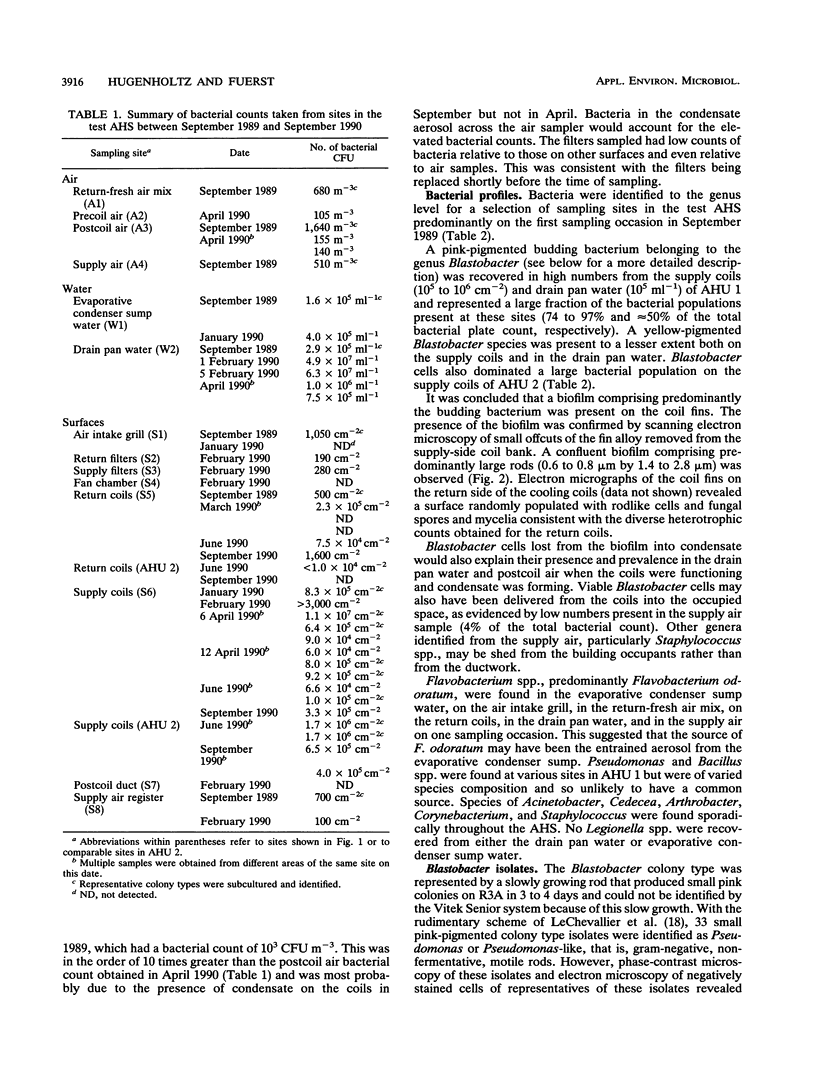
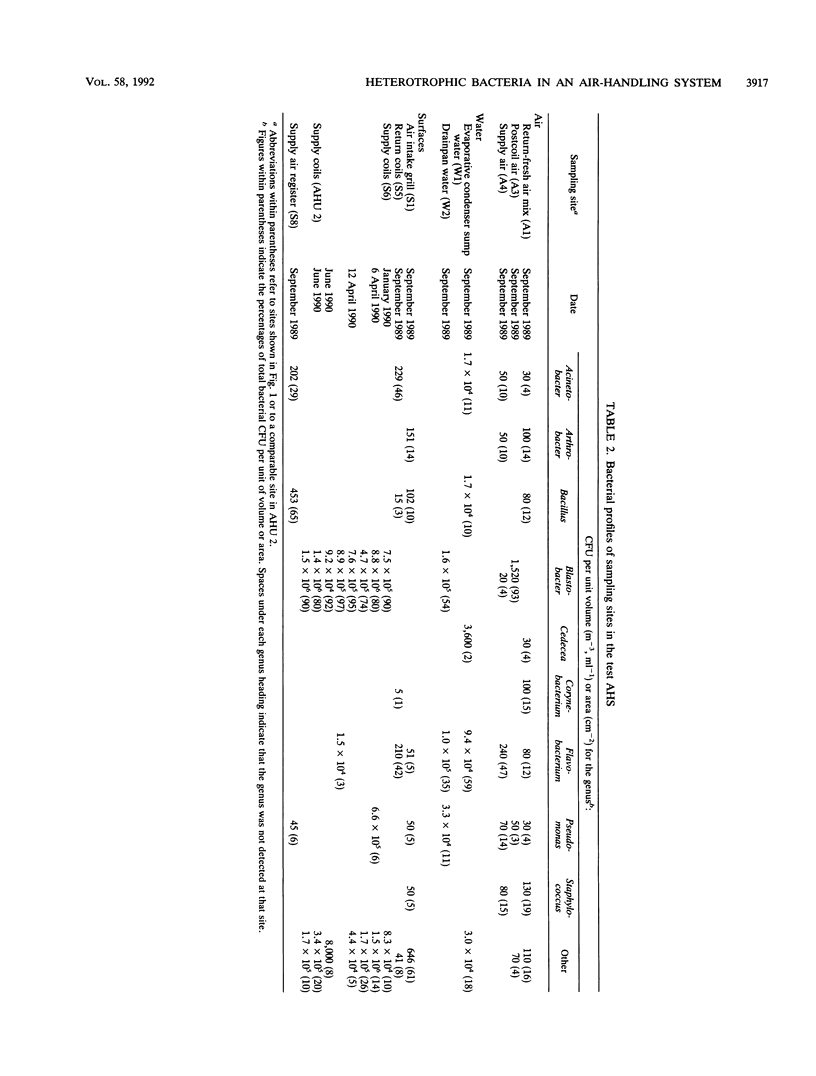
Heterotrophic bacteria from structural surfaces, drain pan water, and the airstream of a well-maintained air-handling system with no reported building-related illness were enumerated. Visually the system appeared clean, but large populations of bacteria were found on the fin surface of the supply-side cooling coils (10(5) to 10(6) CFU cm-2), in drain pan water (10(5) to 10(7) CFU ml-1), and in the sump water of the evaporative condenser (10(5) CFU ml-1). Representative bacterial colony types recovered from heterotrophic plate count cultures on R2A medium were identified to the genus level. Budding bacteria belonging to the genus Blastobacter dominated the supply surface of the coil fins, the drain pan water, and the postcoil air. These data and independent scanning electron microscopy indicated that a resident population of predominantly Blastobacter bacteria was present as a biofilm on the supply-side cooling coil fins.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnow P. M., Fink J. N., Schlueter D. P., Barboriak J. J., Mallison G., Said S. I., Martin S., Unger G. F., Scanlon G. T., Kurup V. P. Early detection of hypersensitivity pneumonitis in office workers. Am J Med. 1978 Feb;64(2):236–242. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banaszak E. F., Thiede W. H., Fink J. N. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis due to contamination of an air conditioner. N Engl J Med. 1970 Aug 6;283(6):271–276. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197008062830601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S., Rylander R., Larsson L. Airborne bacteria, endotoxin and fungi in dust in poultry and swine confinement buildings. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1983 Jul;44(7):537–541. doi: 10.1080/15298668391405265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H. Improved semiselective medium for isolation of Legionella pneumophila from contaminated clinical and environmental specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):298–303. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.298-303.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Gorman G. W., Langford N. C., Rasheed J. K., Mackel D. C., Baine W. B. Charcoal-yeast extract agar: primary isolation medium for Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):437–441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.437-441.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink J. N., Banaszak E. F., Thiede W. H., Barboriak J. J. Interstitial pneumonitis due to hypersensitivity to an organism contaminating a heating system. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Jan;74(1):80–83. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-74-1-80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finnegan M. J., Pickering C. A. Building related illness. Clin Allergy. 1986 Sep;16(5):389–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1986.tb01974.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson A. R., Kilburn K. H., Halprin G. M., McKenzie W. N. Granulocyte recruitment to airways exposed to endotoxin aerosols. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Jan;115(1):89–95. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.115.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. T., O'Brien D. M. Evaluation of building ventilation systems. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1986 Apr;47(4):207–213. doi: 10.1080/15298668691389630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. L., Bernstein I. L., Gallagher J. S., Bonventre P. F., Brooks S. M. Familial hypersensitivity pneumonitis induced by Bacillus subtilis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Aug;122(2):339–348. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.2.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeChevallier M. W., Seidler R. J., Evans T. M. Enumeration and characterization of standard plate count bacteria in chlorinated and raw water supplies. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Nov;40(5):922–930. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.5.922-930.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reasoner D. J., Geldreich E. E. A new medium for the enumeration and subculture of bacteria from potable water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jan;49(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.1.1-7.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rylander R., Snella M. C. Endotoxins and the lung: cellular reactions and risk for disease. Prog Allergy. 1983;33:332–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rylander R., Snella M. C. Endotoxins and the lung: cellular reactions and risk for disease. Prog Allergy. 1983;33:332–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snella M. C., Rylander R. Lung cell reactions after inhalation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Respir Dis. 1982 Nov;63(6):550–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn W. C., Jr Legionnaires disease: historical perspective. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jan;1(1):60–81. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




