Abstract
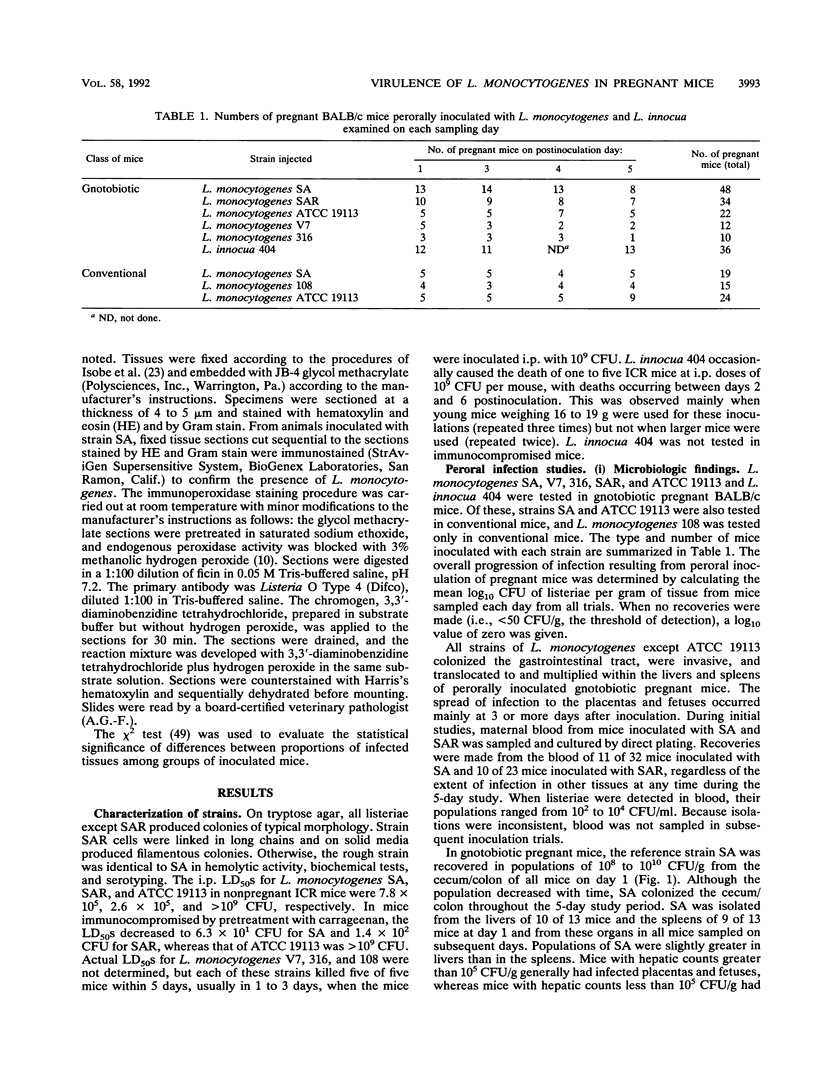
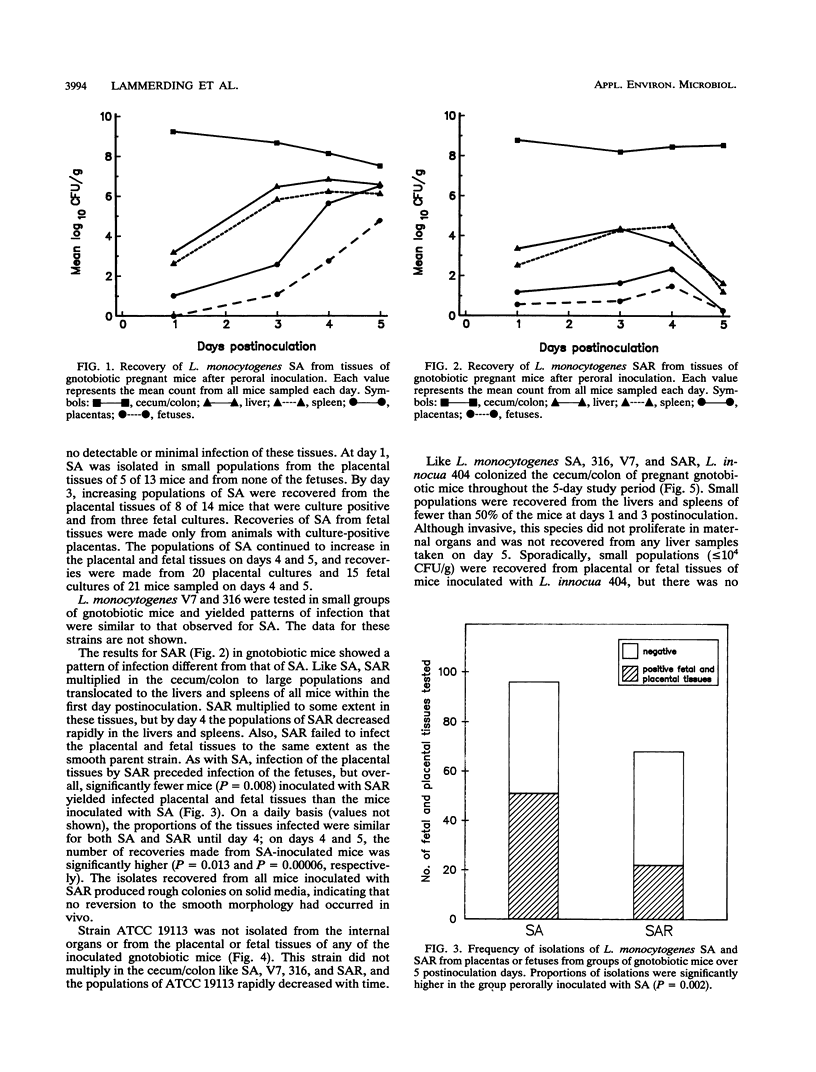
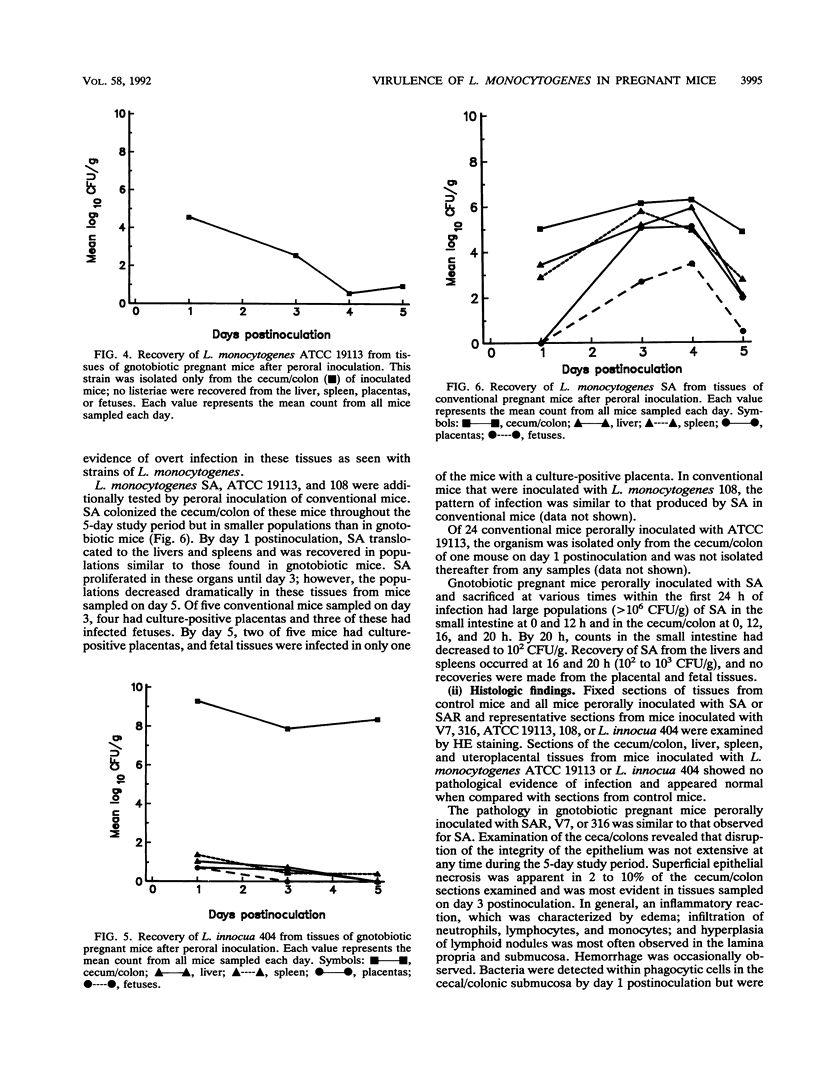
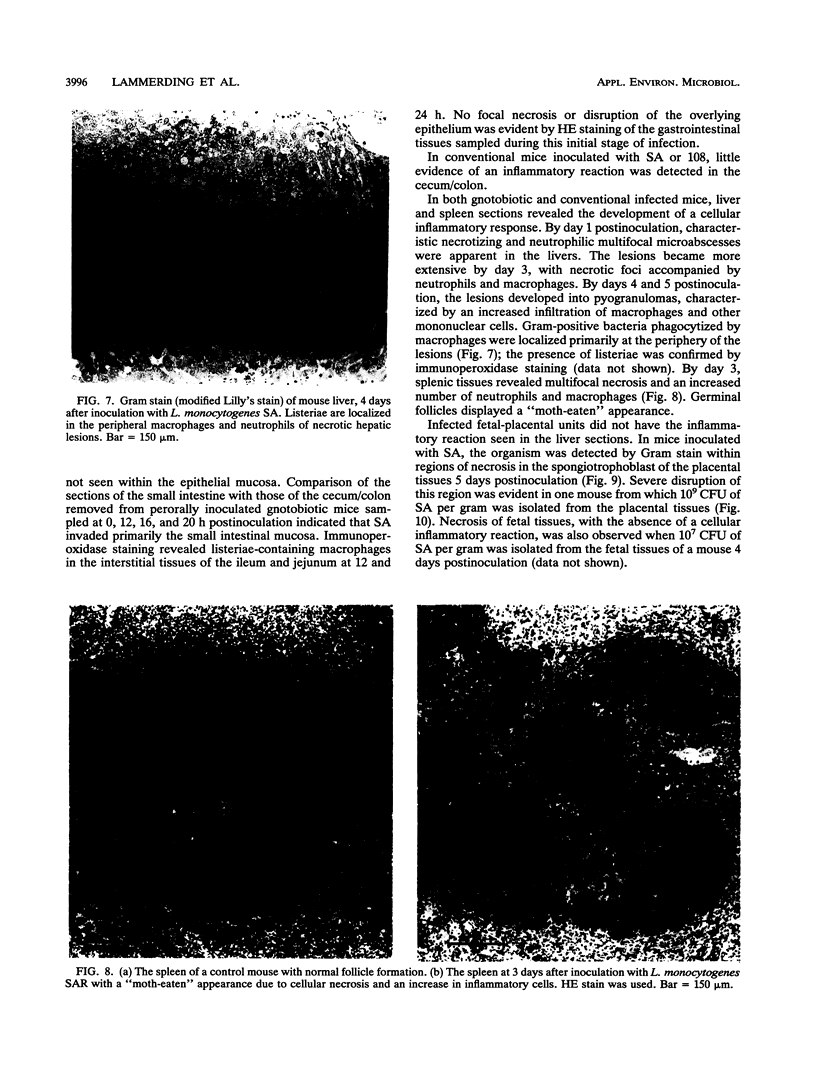
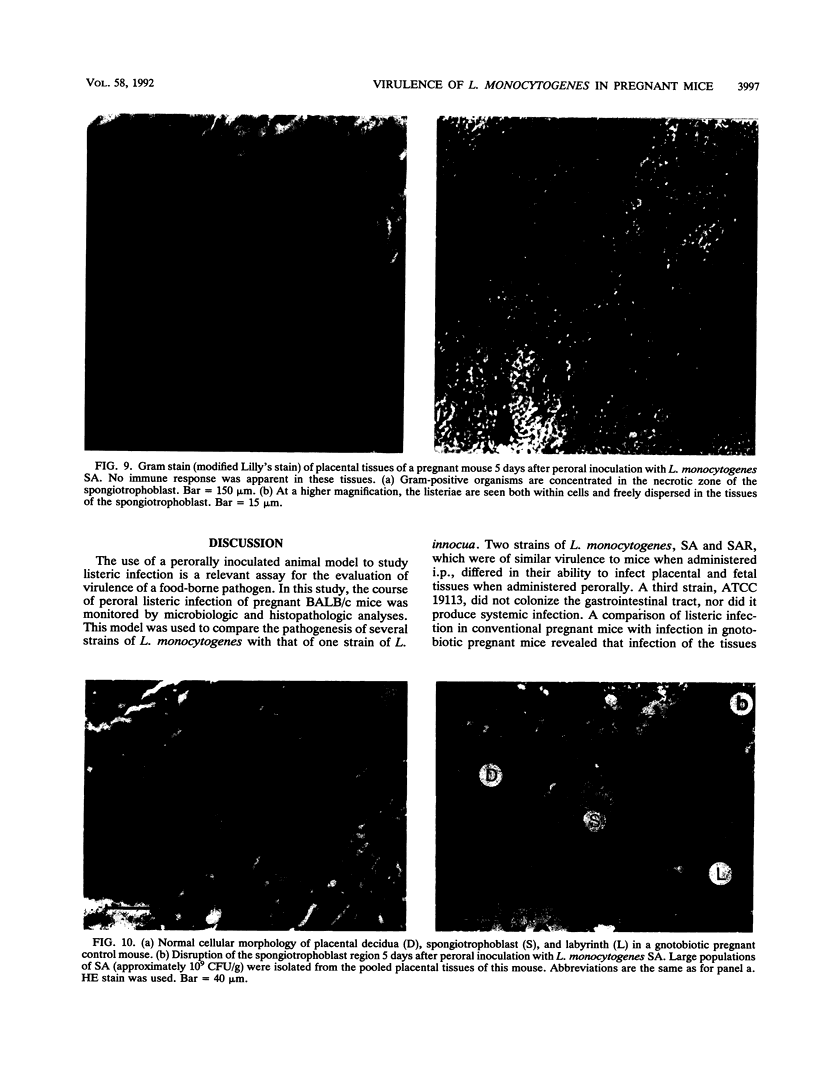
A pregnant mouse model was developed to follow the course of infection after peroral inoculation with six different strains of Listeria monocytogenes and one strain of Listeria innocua. Tissues were sampled and analyzed by microbiologic and histologic methods for 5 days postinoculation. In gnotobiotic pregnant BALB/c mice, L. monocytogenes Scott A (SA), serotype 4b, colonized the gastrointestinal tract, translocated to the livers and spleens of mice by day 1 postinoculation, and multiplied in these tissues until day 4. Infection of the placental tissues occurred by days 3 and 4 and was followed by infection of the fetuses. Little damage of colonic and cecal tissues was evident by histologic examination. Livers and spleens showed a cellular immune response; a similar immune response was not detected in the placentas or fetuses. A rough variant of L. monocytogenes SA which was as virulent as the parent strain in mice when injected intraperitoneally was less virulent perorally and did not consistently infect the fetuses. L. monocytogenes ATCC 19113, serotype 3a, did not colonize the gastrointestinal tract, nor was it isolated from any internal tissue. L. monocytogenes strains of serotypes 1/2a and 1/2b behaved like the SA strain in this mouse model. L. innocua colonized the gastrointestinal tract and translocated to the livers and spleens but did not survive in these organs and rapidly disappeared without infecting placental and fetal tissues. In comparison with gnotobiotic mice, conventional pregnant mice inoculated with L. monocytogenes strains showed less consistent infection. These results suggest that the gnotobiotic pregnant mouse is a useful model for detecting differences in virulence relating to colonization, invasiveness, and uteroplacental infection which cannot be detected by intraperitoneal inoculation of mice.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong B. A., Sword C. P. Electron microscopy of Listeria monocytogenes-infected mouse spleen. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1346–1355. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1346-1355.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audurier A., Pardon P., Marly J., Lantier F. Experimental infection of mice with Listeria monocytogenes and L. innocua. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1980 Jul-Aug;131B(1):47–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. D., Garlington A. W. Translocation of certain indigenous bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract to the mesenteric lymph nodes and other organs in a gnotobiotic mouse model. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):403–411. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.403-411.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernáth S., Pitron M. Haemolysin producing capacity and mouse-pathogenicity of Listeria monocytogenes. Acta Microbiol Hung. 1989;36(4):373–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb W. F., Gellin B. G., Weaver R., Schwartz B., Plikaytis B. D., Reeves M. W., Pinner R. W., Broome C. V. Analysis of clinical and food-borne isolates of Listeria monocytogenes in the United States by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis and application of the method to epidemiologic investigations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jul;56(7):2133–2141. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.7.2133-2141.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielecki J., Youngman P., Connelly P., Portnoy D. A. Bacillus subtilis expressing a haemolysin gene from Listeria monocytogenes can grow in mammalian cells. Nature. 1990 May 10;345(6271):175–176. doi: 10.1038/345175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortolussi R., McGregor D. D., Kongshavn P. A., Galsworthy S., Albritton W., Davies J. W., Seeliger H. P. Host defense mechanisms to perinatal and neonatal Listeria monocytogenes infection. Surv Synth Pathol Res. 1984;3(4):311–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty T., Goebel W. Recent developments in the study of virulence in Listeria monocytogenes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;138:41–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cinquetti R. Histological changes in the chorioallantoic placenta of the mouse with increasing gestational age. Arch Ital Anat Embriol. 1983 Jul-Sep;88(3):267–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossart P., Vicente M. F., Mengaud J., Baquero F., Perez-Diaz J. C., Berche P. Listeriolysin O is essential for virulence of Listeria monocytogenes: direct evidence obtained by gene complementation. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3629–3636. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3629-3636.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coune A. Liposomes as drug delivery system in the treatment of infectious diseases. Potential applications and clinical experience. Infection. 1988 May-Jun;16(3):141–147. doi: 10.1007/BF01644088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Balish E. Pathogenesis of Listeria monocytogenes for gnotobiotic rats. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):323–331. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.323-331.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. M., Peterkin P. I. Listeria monocytogenes, a food-borne pathogen. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):476–511. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.476-511.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming D. W., Cochi S. L., MacDonald K. L., Brondum J., Hayes P. S., Plikaytis B. D., Holmes M. B., Audurier A., Broome C. V., Reingold A. L. Pasteurized milk as a vehicle of infection in an outbreak of listeriosis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 14;312(7):404–407. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502143120704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kathariou S., Rocourt J., Hof H., Goebel W. Levels of Listeria monocytogenes hemolysin are not directly proportional to virulence in experimental infections of mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):534–536. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.534-536.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H. Immunity against intracellular bacteria: biological effector functions and antigen specificity of T lymphocytes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;138:141–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kongshavn P. A. Genetic control of resistance to Listeria infection. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;124:67–85. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70986-9_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn M., Goebel W. Identification of an extracellular protein of Listeria monocytogenes possibly involved in intracellular uptake by mammalian cells. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):55–61. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.55-61.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler S., Bubert A., Vogel M., Goebel W. Expression of the iap gene coding for protein p60 of Listeria monocytogenes is controlled on the posttranscriptional level. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4668–4674. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4668-4674.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., McClain D. Improved Listeria monocytogenes selective agar. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Nov;52(5):1215–1217. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.5.1215-1217.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft B. J., Remington J. S. Effect of pregnancy on resistance to Listeria monocytogenes and Toxoplasma gondii infections in mice. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1164–1171. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1164-1171.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald T. T., Carter P. B. Cell-mediated immunity to intestinal infection. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):516–523. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.516-523.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainou-Fowler T., MacGowan A. P., Postlethwaite R. Virulence of Listeria spp.: course of infection in resistant and susceptible mice. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Oct;27(2):131–140. doi: 10.1099/00222615-27-2-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlin J. Distribution of serovars of Listeria monocytogenes isolated from different categories of patients with listeriosis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Mar;9(3):210–213. doi: 10.1007/BF01963840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlin J. Human listeriosis in Britain, 1967-85, a summary of 722 cases. 1. Listeriosis during pregnancy and in the newborn. Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Apr;104(2):181–189. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800059343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. K., Burns J. Histopathology of Listeria monocytogenes after oral feeding to mice. Appl Microbiol. 1970 May;19(5):772–775. doi: 10.1128/am.19.5.772-775.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mues B., Langer D., Zwadlo G., Sorg C. Phenotypic characterization of macrophages in human term placenta. Immunology. 1989 Jul;67(3):303–307. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piffaretti J. C., Kressebuch H., Aeschbacher M., Bille J., Bannerman E., Musser J. M., Selander R. K., Rocourt J. Genetic characterization of clones of the bacterium Listeria monocytogenes causing epidemic disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3818–3822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinner R. W., Schuchat A., Swaminathan B., Hayes P. S., Deaver K. A., Weaver R. E., Plikaytis B. D., Reeves M., Broome C. V., Wenger J. D. Role of foods in sporadic listeriosis. II. Microbiologic and epidemiologic investigation. The Listeria Study Group. JAMA. 1992 Apr 15;267(15):2046–2050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redline R. W., Lu C. Y. Role of local immunosuppression in murine fetoplacental listeriosis. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1234–1241. doi: 10.1172/JCI112942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redline R. W., Lu C. Y. Specific defects in the anti-listerial immune response in discrete regions of the murine uterus and placenta account for susceptibility to infection. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3947–3955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocourt J., Espaze E. P., Minck R., Catimel B., Hubert B., Courtieu A. L. Cluster of listeriosis isolates with different serovar and phagovar characteristics. Lancet. 1989 Nov 18;2(8673):1217–1218. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91823-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rácz P., Tenner K., Mérö E. Experimental Listeria enteritis. I. An electron microscopic study of the epithelial phase in experimental listeria infection. Lab Invest. 1972 Jun;26(6):694–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuchat A., Deaver K. A., Wenger J. D., Plikaytis B. D., Mascola L., Pinner R. W., Reingold A. L., Broome C. V. Role of foods in sporadic listeriosis. I. Case-control study of dietary risk factors. The Listeria Study Group. JAMA. 1992 Apr 15;267(15):2041–2045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuchat A., Swaminathan B., Broome C. V. Epidemiology of human listeriosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Apr;4(2):169–183. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.2.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B., Hexter D., Broome C. V., Hightower A. W., Hirschhorn R. B., Porter J. D., Hayes P. S., Bibb W. F., Lorber B., Faris D. G. Investigation of an outbreak of listeriosis: new hypotheses for the etiology of epidemic Listeria monocytogenes infections. J Infect Dis. 1989 Apr;159(4):680–685. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.4.680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stelma G. N., Jr, Reyes A. L., Peeler J. T., Francis D. W., Hunt J. M., Spaulding P. L., Johnson C. H., Lovett J. Pathogenicity test for Listeria monocytogenes using immunocompromised mice. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2085–2089. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2085-2089.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Pregnancy-associated depression of cell-mediated immunity. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Nov-Dec;6(6):814–831. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.6.814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachar Z., Savage D. C. Microbial interference and colonization of the murine gastrointestinal tract by Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1979 Jan;23(1):168–174. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.1.168-174.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Koenig C. H., Heymer B., Hof H., Finger H. Course of infection and development of immunity in experimental infection of mice with Listeria serotypes. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1170–1177. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1170-1177.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]