Abstract
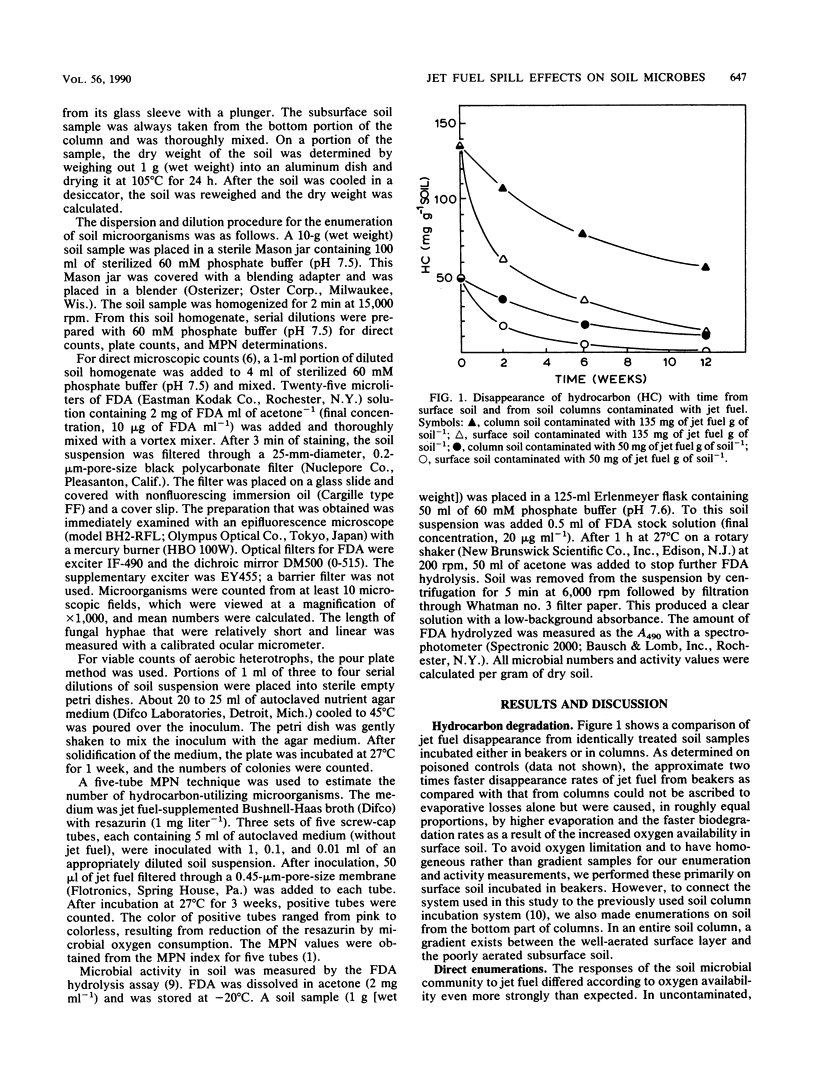
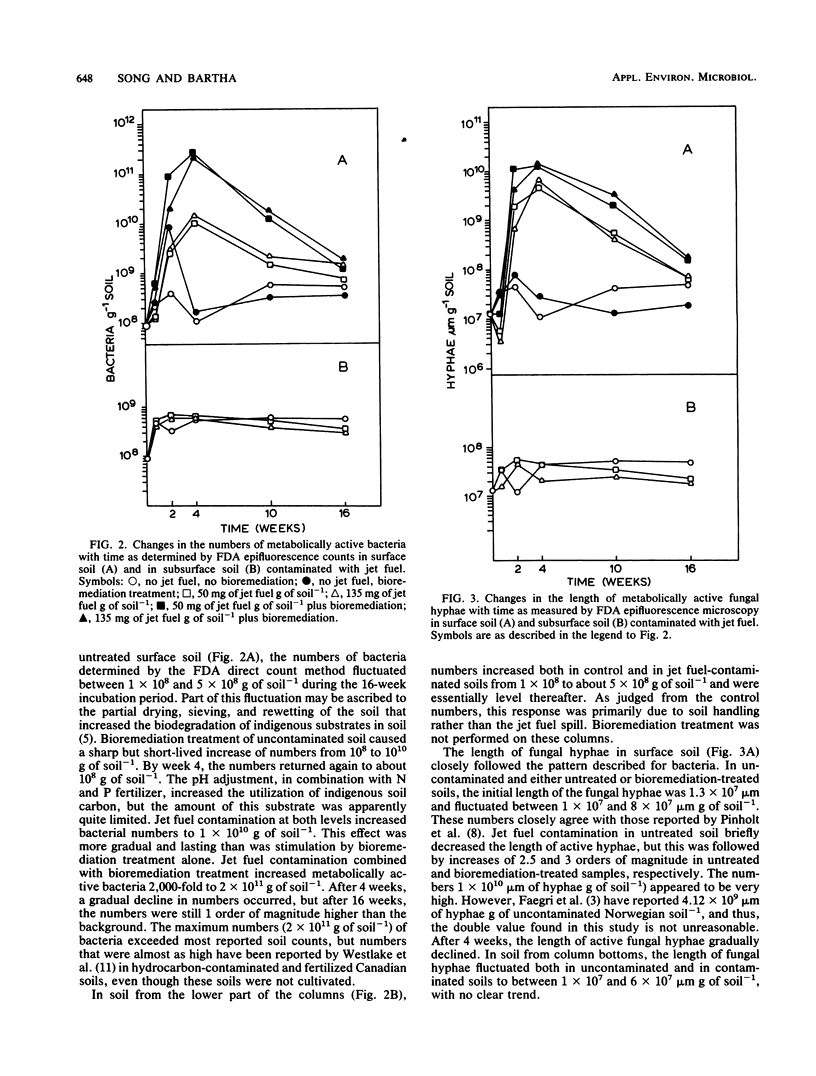
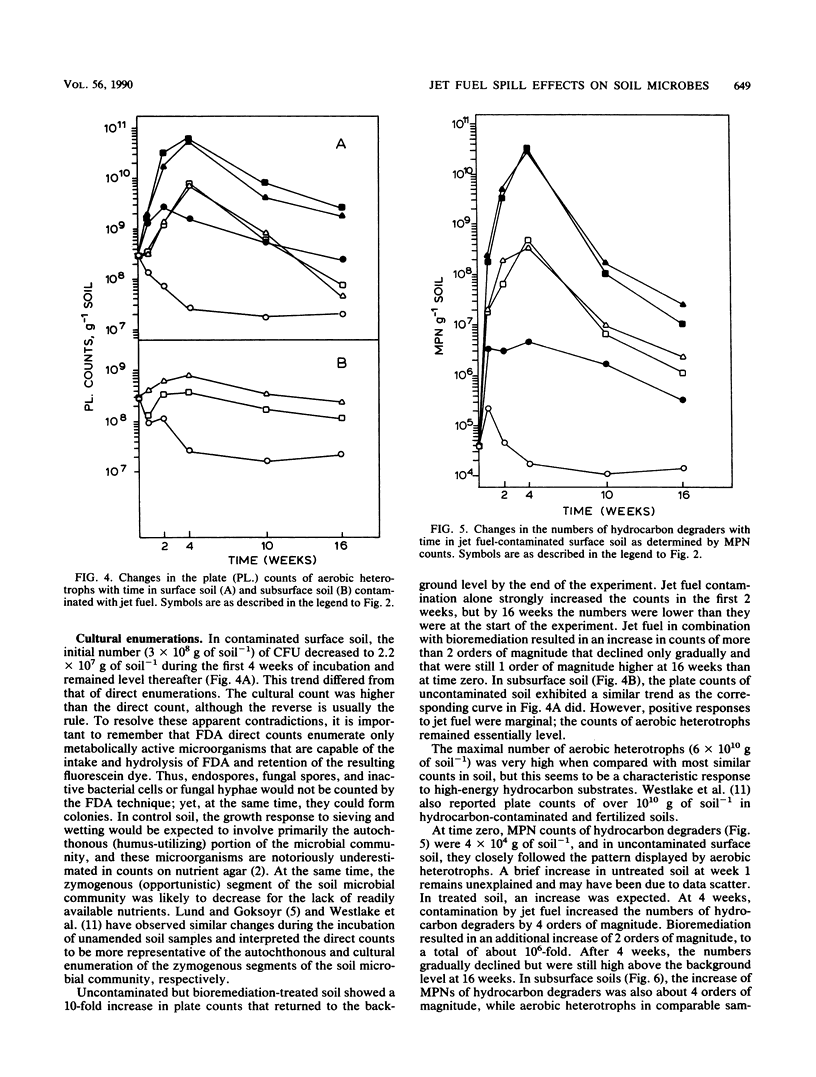
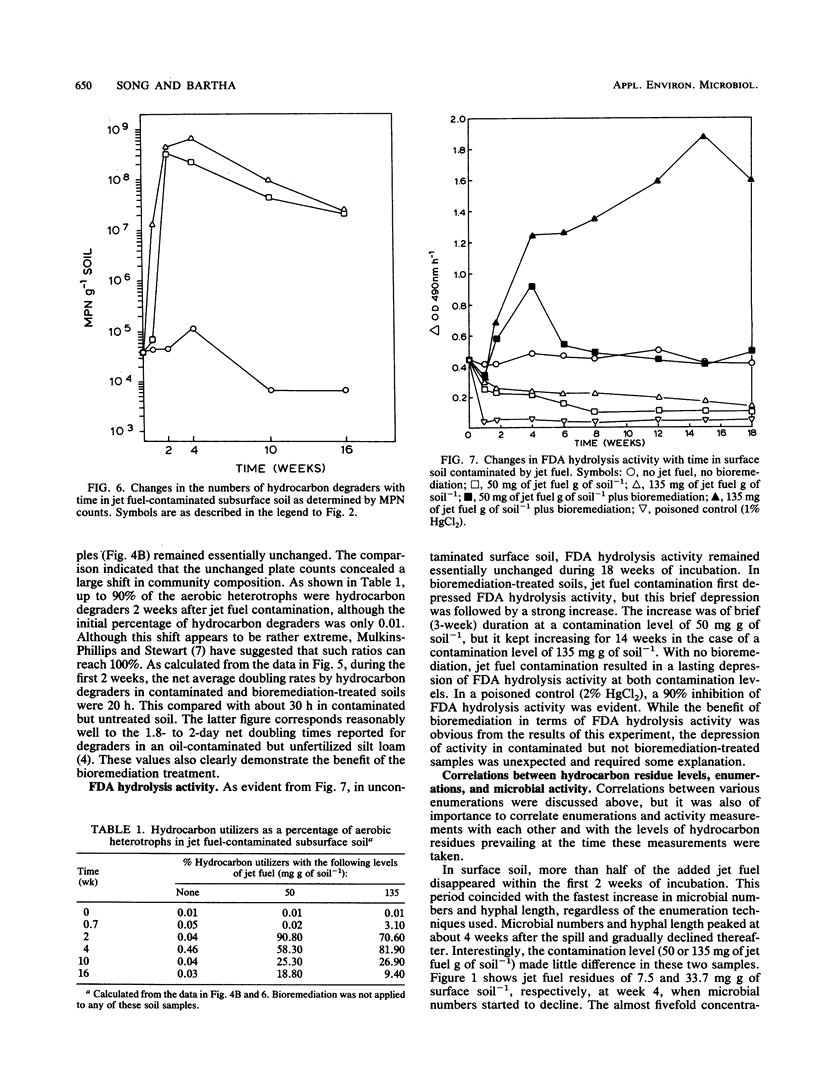
Hydrocarbon residues, microbial numbers, and microbial activity were measured and correlated in loam soil contaminated by jet fuel spills resulting in 50 and 135 mg of hydrocarbon g of soil−1. Contaminated soil was incubated at 27°C either as well-aerated surface soil or as poorly aerated subsurface soil. In the former case, the effects of bioremediation treatment on residues, microbial numbers, and microbial activity were also assessed. Hydrocarbon residues were measured by quantitative gas chromatography. Enumerations included direct counts of metabolically active bacteria, measurement of mycelial length, plate counts of aerobic heterotrophs, and most probable numbers of hydrocarbon degraders. Activity was assessed by fluorescein diacetate (FDA) hydrolysis. Jet fuel disappeared much more rapidly from surface soil than it did from subsurface soil. In surface soil, microbial numbers and mycelial length were increased by 2 to 2.5 orders of magnitude as a result of jet fuel contamination alone and by 3 to 4 orders of magnitude as a result of the combination of jet fuel contamination and bioremediation. FDA hydrolysis was stimulated by jet fuel and bioremediation, but was inhibited by jet fuel alone. The latter was traced to an inhibition of the FDA assay by jet fuel biodegradation products. In subsurface soil, oxygen limitation strongly attenuated microbial responses to jet fuel. An increase in the most probable numbers of hydrocarbon degraders was accompanied by a decline in other aerobic heterotrophs, so that total plate counts changed little. The correlations between hydrocarbon residues, microbial numbers, and microbial activity help in elucidating microbial contributions to jet fuel elimination from soil.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Mulkins-Phillips G. J., Stewart J. E. Distribution of hydrocarbon-utilizing bacteria in Northwestern Atlantic waters and coastal sediments. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Jul;20(7):955–956. doi: 10.1139/m74-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnürer J., Rosswall T. Fluorescein diacetate hydrolysis as a measure of total microbial activity in soil and litter. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1256–1261. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1256-1261.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song H. G., Wang X., Bartha R. Bioremediation potential of terrestrial fuel spills. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Mar;56(3):652–656. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.3.652-656.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westlake D. W., Jobson A. M., Cook F. D. In situ degradation of oil in a soil of the boreal region of the Northwest Territories. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Mar;24(3):254–260. doi: 10.1139/m78-044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


