Abstract
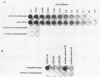
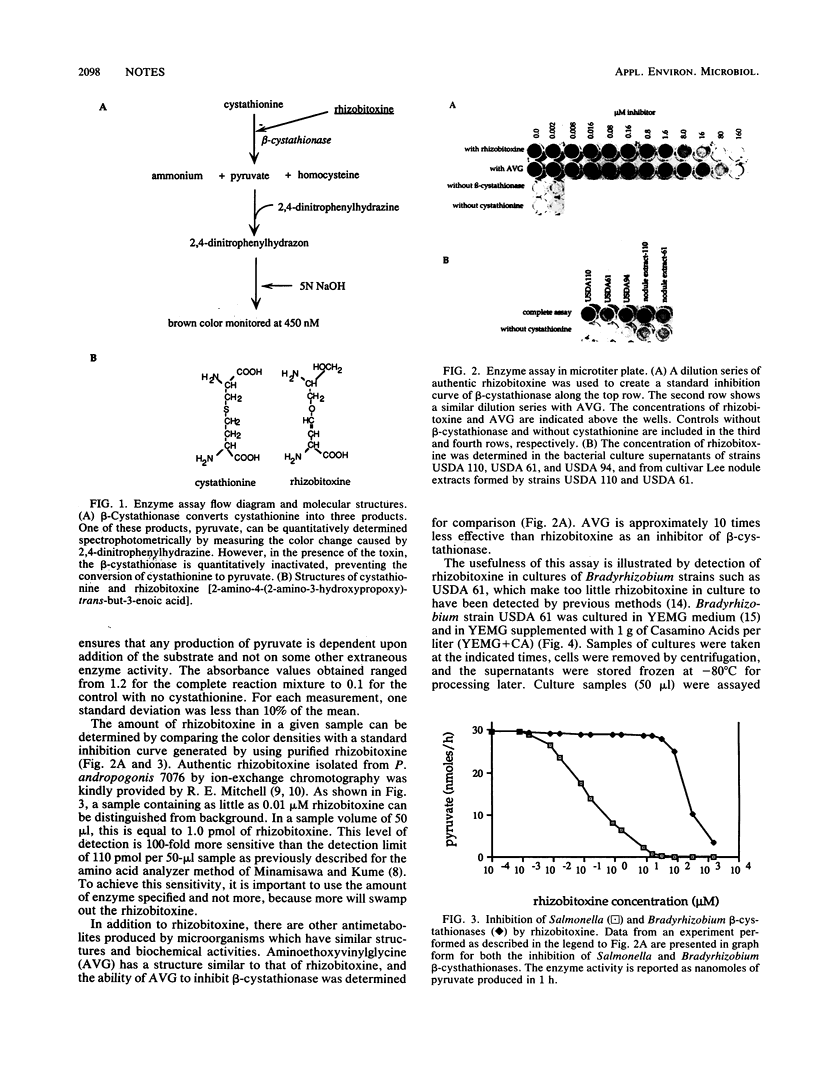
Rhizobitoxine is a phytotoxin synthesized by some strains of the legume symbiont genus Bradyrhizobium and the plant pathogen Pseudomonas andropogonis. We demonstrate here a new enzymatic assay which is 100-fold more sensitive than previous assays and can detect as little as 1.0 pmol of rhizobitoxine. The assay is based on the inhibition of Salmonella typhimurium beta-cystathionase by rhizobitoxine. Interestingly, beta-cystathionase from Bradyrhizobium japonicum is insensitive to rhizobitoxine at concentrations lower than 75 microM.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fuhrmann J. Symbiotic effectiveness of indigenous soybean bradyrhizobia as related to serological, morphological, rhizobitoxine, and hydrogenase phenotypes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jan;56(1):224–229. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.1.224-229.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanelli J., Owens L. D., Mudd S. H. Mechanism of inhibition of spinach beta-cystathionase by rhizobitoxine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 10;227(3):671–684. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. M., Flavin M. Cystathionine gamma-synthetase of Salmonella. Structural properties of a new enzyme in bacterial methionine biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 25;241(24):5781–5789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens L. D., Guggenheim S., Hilton J. L. Rhizobium-synthesized phytototoxin: an inhibitor of beta-cystathionase in Salmonella typhimurium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 May;158(2):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90134-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens L. D., Wright D. A. Production of the Soybean-Chlorosis Toxin by Rhizobium japonicum in Pure Culture. Plant Physiol. 1965 Sep;40(5):931–933. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.5.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens L. D., Wright D. A. Rhizobial-Induced Chlorosis in Soybeans: Isolation, Production in Nodules, and Varietal Specificity of the Toxin. Plant Physiol. 1965 Sep;40(5):927–930. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.5.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters N. K., Crist-Estes D. K. Nodule formation is stimulated by the ethylene inhibitor aminoethoxyvinylglycine. Plant Physiol. 1989 Oct;91(2):690–693. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.2.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]