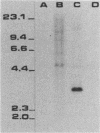
Abstract
The acetogens, although phylogenetically diverse, can be characterized by their possession of the acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) pathway for autotrophic CO2 fixation. The gene encoding formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase, a key enzyme of the acetyl-CoA pathway, was previously cloned from the thermophilic acetogen Clostridium thermoaceticum and has now been tested as a group-specific probe for acetogens. Stable hybrids were formed between the probe and single DNA fragments from eight known acetogens representing six genera. A hybrid was also formed between the probe and a DNA fragment from one sulfate reducer known to be capable of both autotrophic CO2 fixation and acetate catabolism. No such hybrid was formed between the probe and DNA from a homoacetate fermenter not known to use the acetyl-CoA pathway, with two known formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase-producing purine fermenters, or with DNA from 27 other species representing 16 genera of organisms that do not use the acetyl-CoA pathway. DNA purified from cells extracted from horse manure was also screened with the acetogen probe. Six hybrids, indicating at least six detectable acetogen "strains," were observed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braun K., Gottschalk G. Effect of molecular hydrogen and carbon dioxide on chemo-organotrophic growth of Acetobacterium woodii and Clostridium aceticum. Arch Microbiol. 1981 Jan;128(3):294–298. doi: 10.1007/BF00422533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun M., Mayer F., Gottschalk G. Clostridium aceticum (Wieringa), a microorganism producing acetic acid from molecular hydrogen and carbon dioxide. Arch Microbiol. 1981 Jan;128(3):288–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00422532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun M., Schoberth S., Gottschalk G. Enumeration of bacteria forming acetate from H2 and CO2 in anaerobic habitats. Arch Microbiol. 1979 Mar 12;120(3):201–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00423066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breznak J. A., Switzer J. M. Acetate Synthesis from H(2) plus CO(2) by Termite Gut Microbes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):623–630. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.623-630.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. M., Dilworth M. J. Ammonia assimilation by rhizobium cultures and bacteroids. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jan;86(1):39–48. doi: 10.1099/00221287-86-1-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahle A. B., Laake M. Diversity dynamics of marine bacteria studied by immunofluorescent staining on membrane filters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):169–176. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.169-176.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLong E. F., Wickham G. S., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic stains: ribosomal RNA-based probes for the identification of single cells. Science. 1989 Mar 10;243(4896):1360–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.2466341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dev I. K., Harvey R. J. A complex of N5,N10-methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase and N5,N10-methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase in Escherichia coli. Purification, subunit structure, and allosteric inhibition by N10-formyltetrahydrofolate. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4245–4253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genthner B. R., Davis C. L., Bryant M. P. Features of rumen and sewage sludge strains of Eubacterium limosum, a methanol- and H2-CO2-utilizing species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jul;42(1):12–19. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.1.12-19.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannoni S. J., DeLong E. F., Olsen G. J., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic group-specific oligodeoxynucleotide probes for identification of single microbial cells. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):720–726. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.720-726.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greening R. C., Leedle J. A. Enrichment and isolation of Acetitomaculum ruminis, gen. nov., sp. nov.: acetogenic bacteria from the bovine rumen. Arch Microbiol. 1989;151(5):399–406. doi: 10.1007/BF00416597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holben William E., Jansson Janet K., Chelm Barry K., Tiedje James M. DNA Probe Method for the Detection of Specific Microorganisms in the Soil Bacterial Community. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Mar;54(3):703–711. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.3.703-711.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungdahl L. G., Andreesen J. R. Formate dehydrogenase, a selenium--tungsten enzyme from Clostridium thermoaceticum. Methods Enzymol. 1978;53:360–372. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)53042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungdahl L. G. The autotrophic pathway of acetate synthesis in acetogenic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:415–450. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.002215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovell C. R., Przybyla A., Ljungdahl L. G. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the Clostridium thermoaceticum gene encoding thermostable formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase. Arch Microbiol. 1988;149(4):280–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00411642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovell C. R., Przybyla A., Ljungdahl L. G. Primary structure of the thermostable formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase from Clostridium thermoaceticum. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 19;29(24):5687–5694. doi: 10.1021/bi00476a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON J. W., WILSON P. W., BURRIS R. H. Direct demonstration of ammonia as an intermediate in nitrogen fixation by Azotobacter. J Biol Chem. 1953 Sep;204(1):445–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'brien W. E., Brewer J. M., Ljungdahl L. G. Chemical, physical and enzymatic comparisons of formyltetrahydrofolate synthetases from thermo- and mesophilic Clostridia. Experientia Suppl. 1976;26:249–262. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7675-9_21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps T. J., Zeikus J. G. Influence of pH on Terminal Carbon Metabolism in Anoxic Sediments from a Mildly Acidic Lake. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Dec;48(6):1088–1095. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.6.1088-1095.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayler G. S., Layton A. C. Environmental application of nucleic acid hybridization. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:625–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. L., Klug M. J. Electron donors utilized by sulfate-reducing bacteria in eutrophic lake sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jul;42(1):116–121. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.1.116-121.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl D. A., Flesher B., Mansfield H. R., Montgomery L. Use of phylogenetically based hybridization probes for studies of ruminal microbial ecology. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 May;54(5):1079–1084. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.5.1079-1084.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl D. A., Lane D. J., Olsen G. J., Pace N. R. Characterization of a Yellowstone hot spring microbial community by 5S rRNA sequences. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1379–1384. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1379-1384.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staley J. T., Konopka A. Measurement of in situ activities of nonphotosynthetic microorganisms in aquatic and terrestrial habitats. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:321–346. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffan R. J., Goksøyr J., Bej A. K., Atlas R. M. Recovery of DNA from soils and sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Dec;54(12):2908–2915. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.12.2908-2915.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuncan E. U., Martin S. E. Lysostaphin lysis procedure for detection of Staphylococcus aureus by the firefly bioluminescent ATP method. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jan;53(1):88–91. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.1.88-91.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead T. R., Park M., Rabinowitz J. C. Distribution of 10-formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase in eubacteria. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):995–997. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.995-997.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead T. R., Rabinowitz J. C. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene for 10-formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase from Clostridium acidiurici ("Clostridium acidi-urici"). J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):205–209. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.205-209.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead T. R., Rabinowitz J. C. Nucleotide sequence of the Clostridium acidiurici ("Clostridium acidi-urici") gene for 10-formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase shows extensive amino acid homology with the trifunctional enzyme C1-tetrahydrofolate synthase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3255–3261. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3255-3261.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G. The biology of methanogenic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):514–541. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.514-541.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]