Abstract
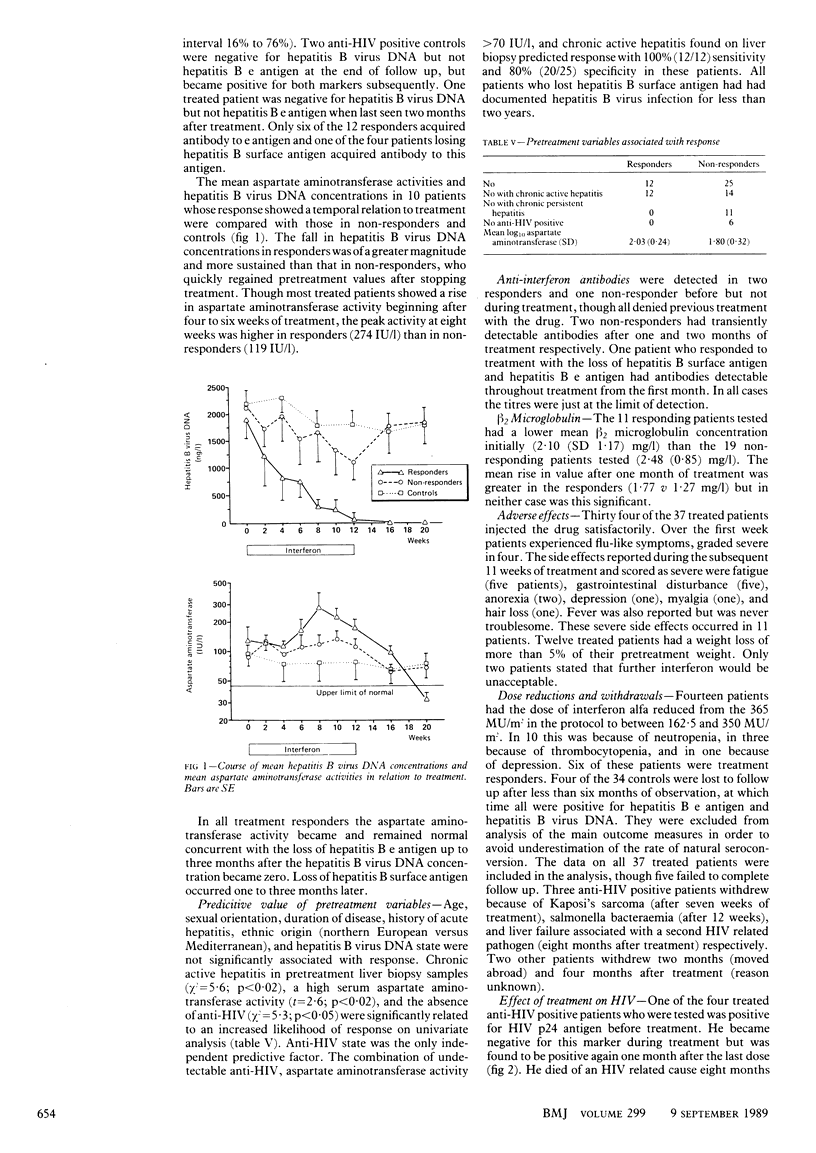
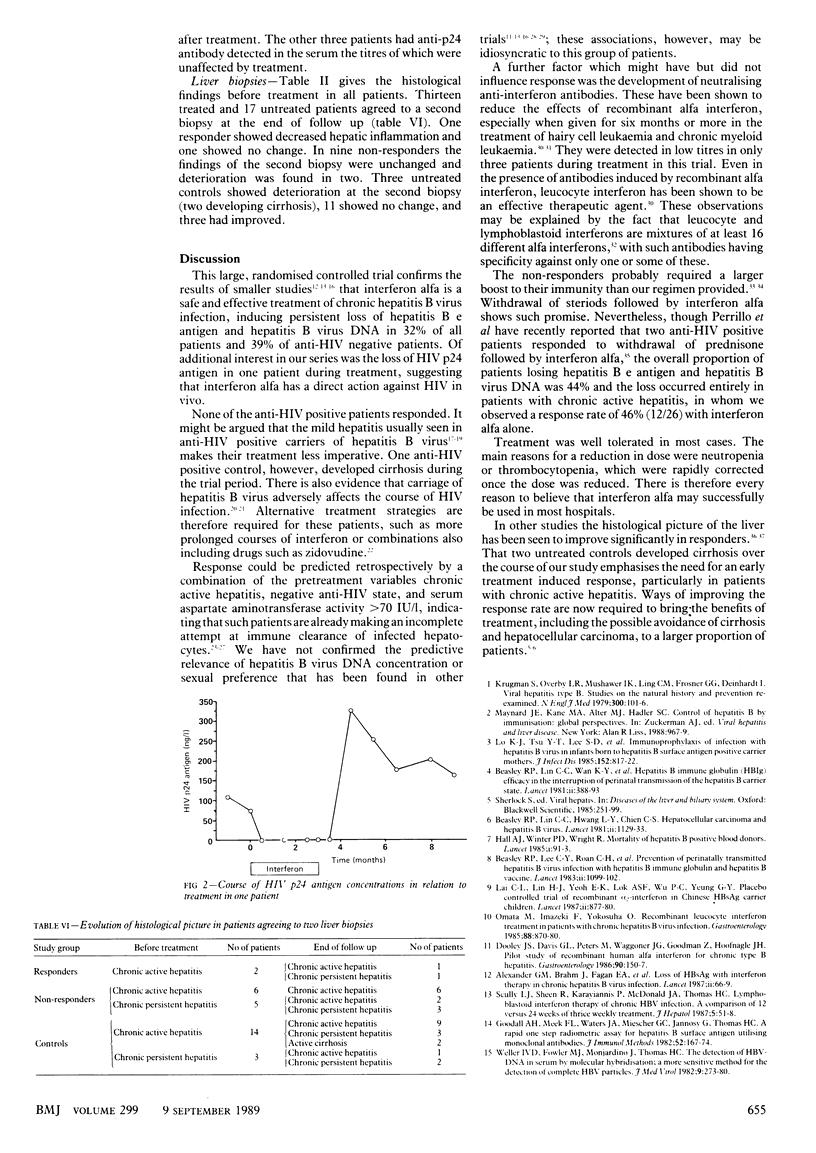
OBJECTIVE--To confirm the findings of pilot studies that interferon alfa is an effective treatment of Europid men with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. DESIGN--Randomised controlled trial of three months treatment with interferon alfa followed by 12 months of observation. SETTING--Outpatient clinic of a tertiary referral centre. PATIENTS--37 Treated men (six anti-HIV positive) and 34 untreated men (nine anti-HIV positive) who met the criteria for the trial. Four controls failed to complete follow up. INTERVENTIONS--The treated group received subcutaneous injections of 5-10 MU interferon alfa/m2 daily for five days, then 10 MU/m2 thrice weekly for 11 weeks. Follow up continued at monthly intervals for 12 months. Untreated controls were monitored over the same period. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURE--Hepatitis B e antigen and hepatitis B virus DNA state after 15 months of observation. RESULTS--12 Of the 37 treated patients cleared hepatitis B e antigen and hepatitis B virus DNA, whereas only one of 30 untreated controls seroconverted over the same period--an increased response rate of 29% (95% confidence interval 13% to 45%). The life table estimate of response at 15 months was 35% in treated patients, an increase of 32% above controls (95% confidence interval 16% to 48%). The response rates in groups by predictive pretreatment variables were 12 of 31 anti-HIV negative patients (excess response 34%; 95% confidence interval 14% to 54%), 12 of 26 with chronic active hepatitis before treatment (excess response 46%; 27% to 65%), and 12 of 21 with a pretreatment serum aspartate aminotransferase activity greater than 70 IU/l (excess response 46%; 16% to 76%). The combination of these factors predicted response with a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 80%. Four of the 12 responders, who had all been infected for less than two years, also lost hepatitis B surface antigen. Treatment was well tolerated. CONCLUSIONS--Interferon alfa is effective in the treatment of a proportion of Europid men with chronic hepatitis B virus infection, who might be identified before treatment. Additional strategies are required to improve the rate of response.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beasley R. P., Hwang L. Y., Lee G. C., Lan C. C., Roan C. H., Huang F. Y., Chen C. L. Prevention of perinatally transmitted hepatitis B virus infections with hepatitis B immune globulin and hepatitis B vaccine. Lancet. 1983 Nov 12;2(8359):1099–1102. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90624-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beasley R. P., Hwang L. Y., Lin C. C., Stevens C. E., Wang K. Y., Sun T. S., Hsieh F. J., Szmuness W. Hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG) efficacy in the interruption of perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus carrier state. Initial report of a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 1981 Aug 22;2(8243):388–393. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90832-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook M. G., Petrovic L., McDonald J. A., Scheuer P. J., Thomas H. C. Histological improvement after anti-viral treatment for chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 1989 Mar;8(2):218–225. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(89)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley J. S., Davis G. L., Peters M., Waggoner J. G., Goodman Z., Hoofnagle J. H. Pilot study of recombinant human alpha-interferon for chronic type B hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1986 Jan;90(1):150–157. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90087-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall A. H., Meek F. L., Waters J. A., Miescher G. C., Janossy G., Thomas H. C. A rapid one-step radiometric assay for hepatitis B surface antigen utilizing monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Jul 30;52(2):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90042-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman S. Z., Zucker M. L. Recombinant DNA related to hepatitis B and human immunodeficiency viruses in mononuclear cells of patients with AIDS. J Med Virol. 1988 Oct;26(2):145–152. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890260206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogsgaard K., Lindhardt B. O., Nielson J. O., Andersson P., Kryger P., Aldershvile J., Gerstoft J., Pedersen C. The influence of HTLV-III infection on the natural history of hepatitis B virus infection in male homosexual HBsAg carriers. Hepatology. 1987 Jan-Feb;7(1):37–41. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krugman S., Overby L. R., Mushahwar I. K., Ling C. M., Frösner G. G., Deinhardt F. Viral hepatitis, type B. Studies on natural history and prevention re-examined. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jan 18;300(3):101–106. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197901183000301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo K. J., Tsai Y. T., Lee S. D., Wu T. C., Wang J. Y., Chen G. H., Yeh C. L., Chiang B. N., Yeh S. H., Goudeau A. Immunoprophylaxis of infection with hepatitis B virus in infants born to hepatitis B surface antigen-positive carrier mothers. J Infect Dis. 1985 Oct;152(4):817–822. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.4.817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lok A. S., Novick D. M., Karayiannis P., Dunk A. A., Sherlock S., Thomas H. C. A randomized study of the effects of adenine arabinoside 5'-monophosphate (short or long courses) and lymphoblastoid interferon on hepatitis B virus replication. Hepatology. 1985 Nov-Dec;5(6):1132–1138. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. A., Harris S., Waters J. A., Thomas H. C. Effect of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection on chronic hepatitis B hepatic viral antigen display. J Hepatol. 1987 Jun;4(3):337–342. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(87)80543-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick D. M., Lok A. S., Thomas H. C. Diminished responsiveness of homosexual men to antiviral therapy for HBsAg-positive chronic liver disease. J Hepatol. 1985;1(1):29–35. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(85)80065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrillo R. P., Regenstein F. G., Peters M. G., DeSchryver-Kecskemeti K., Bodicky C. J., Campbell C. R., Kuhns M. C. Prednisone withdrawal followed by recombinant alpha interferon in the treatment of chronic type B hepatitis. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Jul 15;109(2):95–100. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-2-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignatelli M., Waters J., Lever A., Iwarson S., Gerety R., Thomas H. C. Cytotoxic T-cell responses to the nucleocapsid proteins of HBV in chronic hepatitis. Evidence that antibody modulation may cause protracted infection. J Hepatol. 1987 Feb;4(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(87)80004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Fischl M. A., Grieco M. H., Gottlieb M. S., Volberding P. A., Laskin O. L., Leedom J. M., Groopman J. E., Mildvan D., Hirsch M. S. The toxicity of azidothymidine (AZT) in the treatment of patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 23;317(4):192–197. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707233170402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scullard G. H., Andres L. L., Greenberg H. B., Smith J. L., Sawhney V. K., Neal E. A., Mahal A. S., Popper H., Merigan T. C., Robinson W. S. Antiviral treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: improvement in liver disease with interferon and adenine arabinoside. Hepatology. 1981 May-Jun;1(3):228–232. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steis R. G., Smith J. W., 2nd, Urba W. J., Clark J. W., Itri L. M., Evans L. M., Schoenberger C., Longo D. L. Resistance to recombinant interferon alfa-2a in hairy-cell leukemia associated with neutralizing anti-interferon antibodies. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 2;318(22):1409–1413. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806023182201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vento S., Hegarty J. E., Alberti A., O'Brien C. J., Alexander G. J., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. T lymphocyte sensitization to HBcAg and T cell-mediated unresponsiveness to HBsAg in hepatitis B virus-related chronic liver disease. Hepatology. 1985 Mar-Apr;5(2):192–197. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters J. A., Pignatelli M., Brown D., O'Rourke S., Lever A., Thomas H. C. The immune response to hepatitis B virus. Postgrad Med J. 1987;63 (Suppl 2):51–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller I. V., Fowler M. J., Monjardino J., Thomas H. C. The detection of HBV-DNA in serum by molecular hybridisation: a more sensitive method for the detection of complete HBV particles. J Med Virol. 1982;9(4):273–280. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890090405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Wussow P., Hartmann F., Freund M., Poliwoda H., Deicher H. Leucocyte-derived interferon-alpha in patients with antibodies to recombinant IFN-alpha 2b. Lancet. 1988 Apr 16;1(8590):882–883. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91628-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


