Abstract
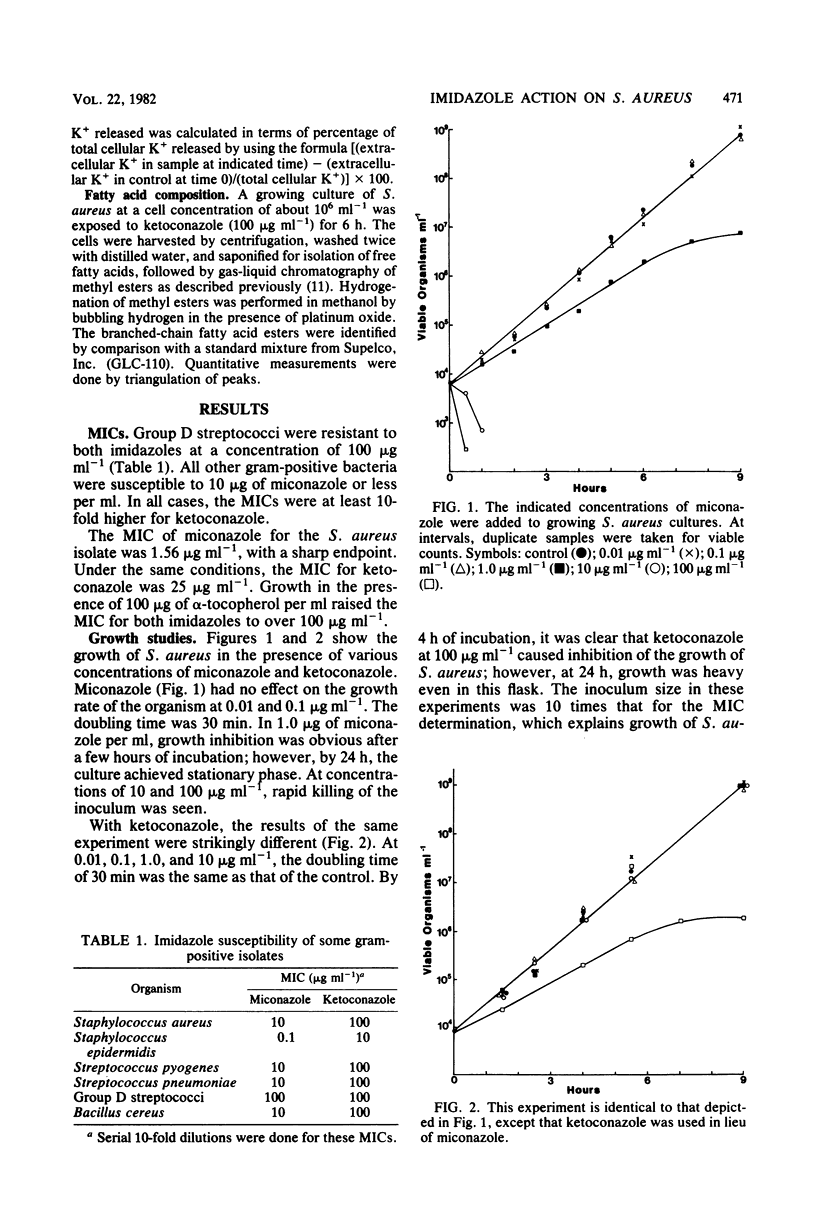
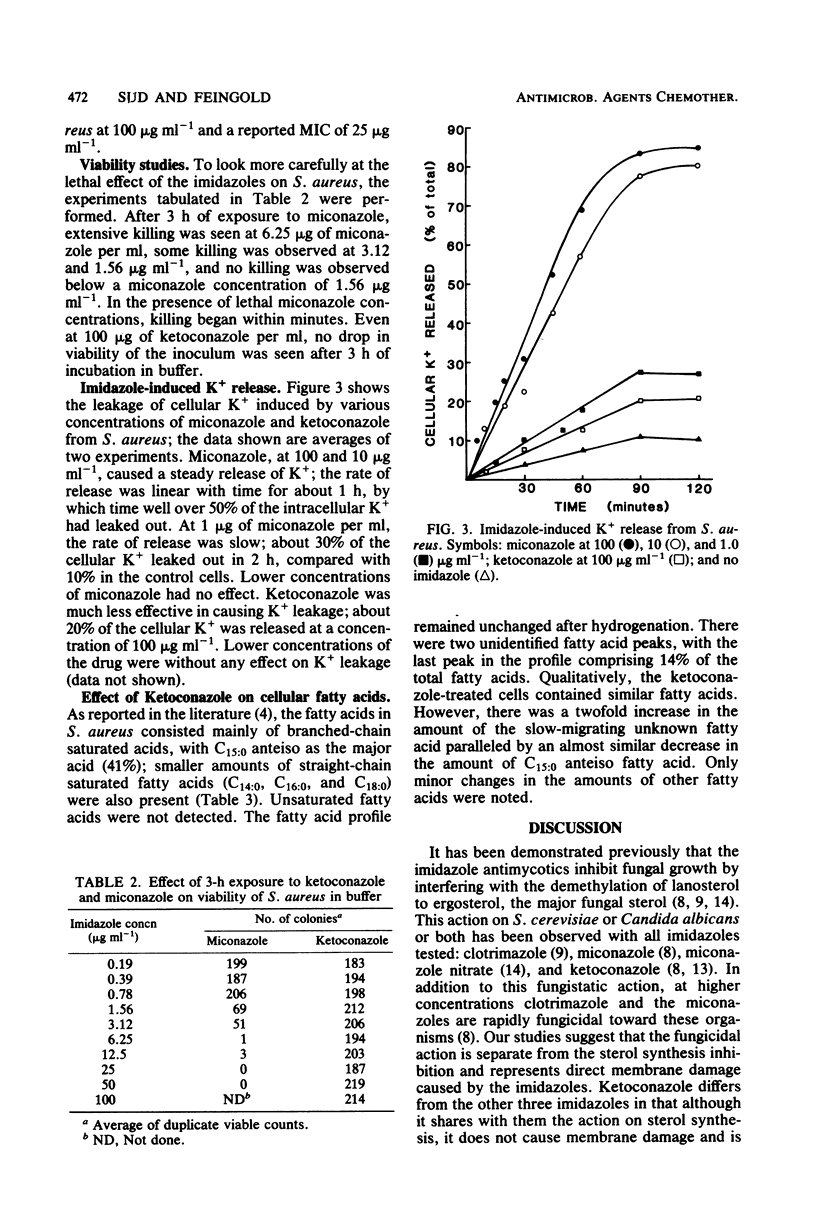
In Staphylococcus aureus, using the imidazoles miconazole and ketoconazole, detailed studies of minimal inhibitory concentrations, kinetics of growth, viability, and release of intracellular K+ confirm that the two imidazoles work differently in this bacterium. Miconazole is bactericidal at low concentrations and causes release of cellular K+. Ketoconazole has no bactericidal effect at any tested concentration and has little effect on K+ permeability of S. aureus; it slows growth at high concentration. This is reflected in a low minimal inhibitory concentration for miconazole and a high one for ketoconazole. The probable mechanisms of the bacteriostatic and bactericidal effects of the imidazoles are discussed in light of these results and the previously described antifungal mechanisms of the drugs. alpha-Tocopherol blocks the action of both imidazoles.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen W. C., Sud I. J., Chou D. L., Feingold D. S. Selective toxicity of the polyene antibiotics and their methyl ester derivatives. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):480–487. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90329-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cope J. E. Mode of action of miconazole on Candida albicans: effect on growth, viability and K+ release. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Jul;119(1):245–251. doi: 10.1099/00221287-119-1-245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Nollin S., Van Belle H., Goossens F., Thone F., Borgers M. Cytochemical and biochemical studies of yeasts after in vitro exposure to miconazole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Mar;11(3):500–513. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.3.500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates M. Bacterial lipids. Adv Lipid Res. 1964;2:17–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda S., Uno J., Arai T. Target substances of some antifungal agents in the cell membrane. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):454–459. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schär G., Kayser F. H., Dupont M. C. Antimicrobial activity of econazole and miconazole in vitro and in experimental candidiasis and aspergillosis. Chemotherapy. 1976;22(3-4):211–220. doi: 10.1159/000221928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sud I. J., Chou D. L., Feingold D. S. Effect of free fatty acids on liposome susceptibility to imidazole antifungals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Nov;16(5):660–663. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.5.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sud I. J., Feingold D. S. Heterogeneity of action of mechanisms among antimycotic imidazoles. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jul;20(1):71–74. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sud I. J., Feingold D. S. Lipid composition and sensitivity of Prototheca wickerhamii to membrane-active antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Oct;16(4):486–490. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.4.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sud I. J., Feingold D. S. Mechanisms of action of the antimycotic imidazoles. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Jun;76(6):438–441. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12521036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Cutsem J. M., Thienpont D. Miconazole, a broad-spectrum antimycotic agent with antibacterial activity. Chemotherapy. 1972;17(6):392–404. doi: 10.1159/000220875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Bossche H., Willemsens G., Cools W., Cornelissen F. Inhibition of ergosterol synthesis in Candida albicans by ketoconazole [proceedings]. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1979 Oct;87(4):849–851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H., Iwata K. Effect of fatty acyl group and sterol composition on sensitivity of lecithin liposomes to imidazole antimycotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 May;15(5):706–711. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.5.706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Bossche H., Willemsens G., Cools W., Lauwers W. F., Le Jeune L. Biochemical effects of miconazole on fungi. II. Inhibition of ergosterol biosynthesis in Candida albicans. Chem Biol Interact. 1978 Apr;21(1):59–78. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(78)90068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


