Abstract
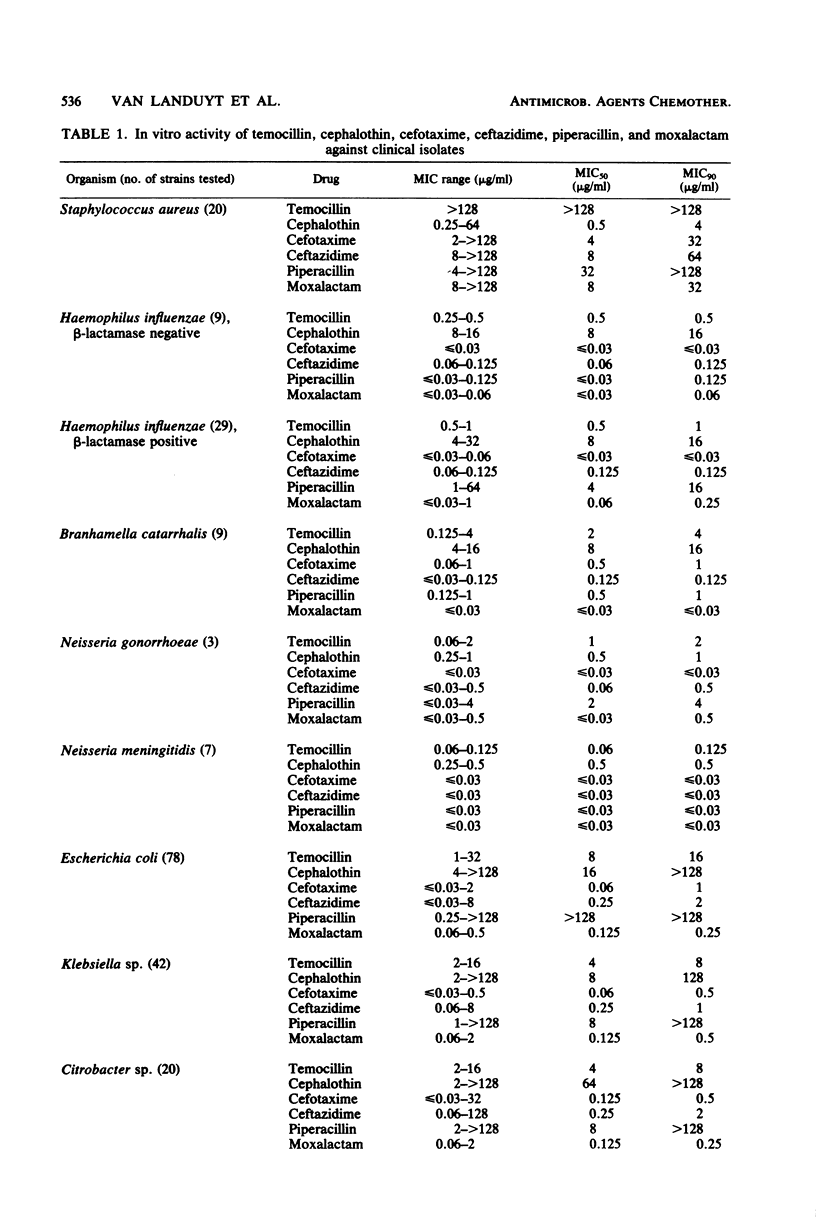
The minimal inhibitory concentration of temocillin (BRL 17421) against 476 clinical isolates was determined by an agar dilution method. Temocillin was active against most of the Enterobacteriaceae, Haemophilus, and Neisseria strains tested. The compound showed low activity or was inactive against Bacteroides, Campylobacter, Acinetobacter, Pseudomonas, and Staphylococcus aureus strains. Within each species, individual strains showed a high degree of uniformity in their susceptibility to temocillin; the drug concentrations that inhibited the growth of 90% of organisms were the same or close to those which inhibited the growth of 50% of organisms. In contrast, the same strains showed a very wide range of susceptibility to the other antibiotics tested, including third-generation cephalosporins. Against strains of Enterobacteriaceae highly susceptible to third-generation cephalosporins, temocillin was considerably less active than cefotaxime, ceftazidime, and moxalactam, although it was more active than cefazolin and piperacillin. Against certain strains of Enterobacter and Citrobacter resistant to third-generation cephalosporins, temocillin was more active than cefotaxime and ceftazidime. An increase in the inoculum size did not alter the activity of temocillin, indicating that the compound has high stability to beta-lactamases. The minimal lethal concentration was also very similar to the minimal inhibitory concentration when an inoculum of 10(5) colony-forming units was used.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolivar R., Weaver S. S., Bodey G. P. Comparative in vitro study of temocillin (BRL 17421), a new penicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Apr;21(4):641–645. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.4.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piot P., Van Dyck E. In vitro activity of BRL 17421 against Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Branhamella catarrhalis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jan;21(1):166–167. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.1.166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slocombe B., Basker M. J., Bentley P. H., Clayton J. P., Cole M., Comber K. R., Dixon R. A., Edmondson R. A., Jackson D., Merrikin D. J. BRL 17421, a novel beta-lactam antibiotic, highly resistant to beta-lactamases, giving high and prolonged serum levels in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jul;20(1):38–46. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


