Abstract
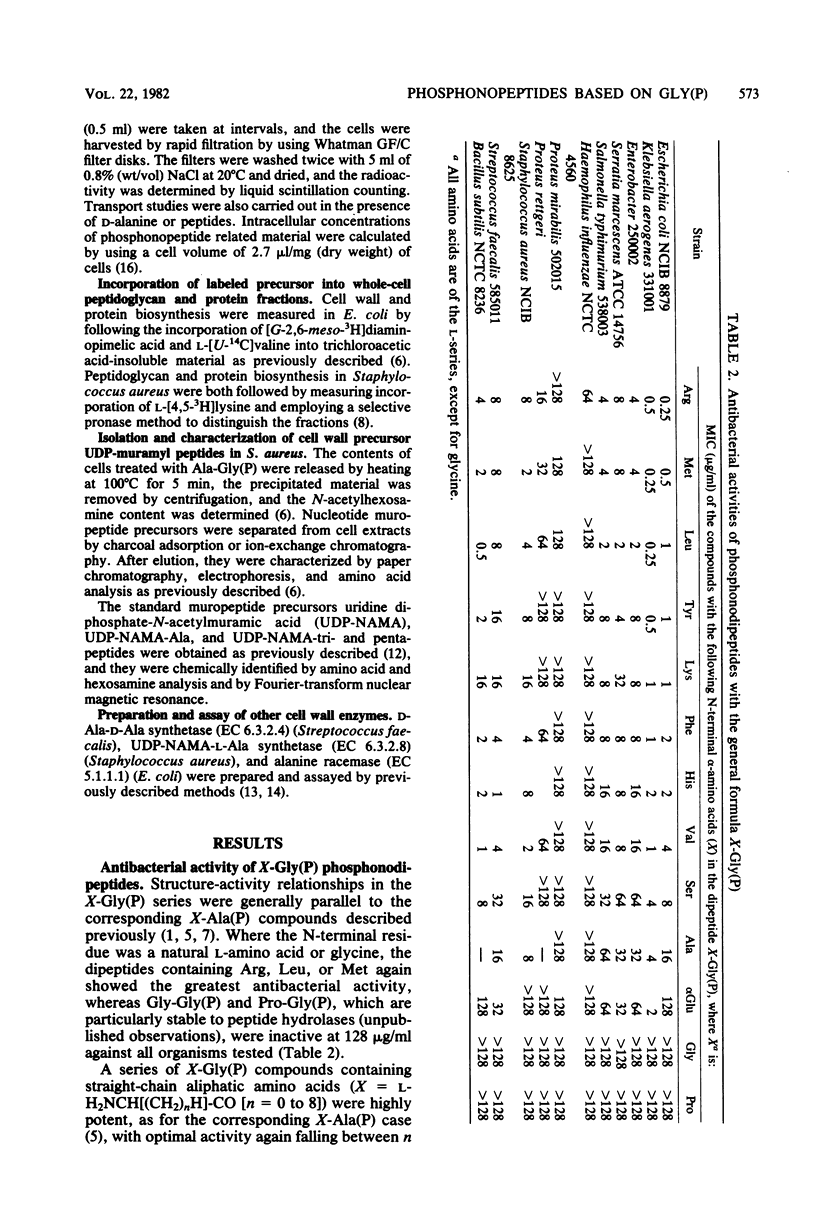
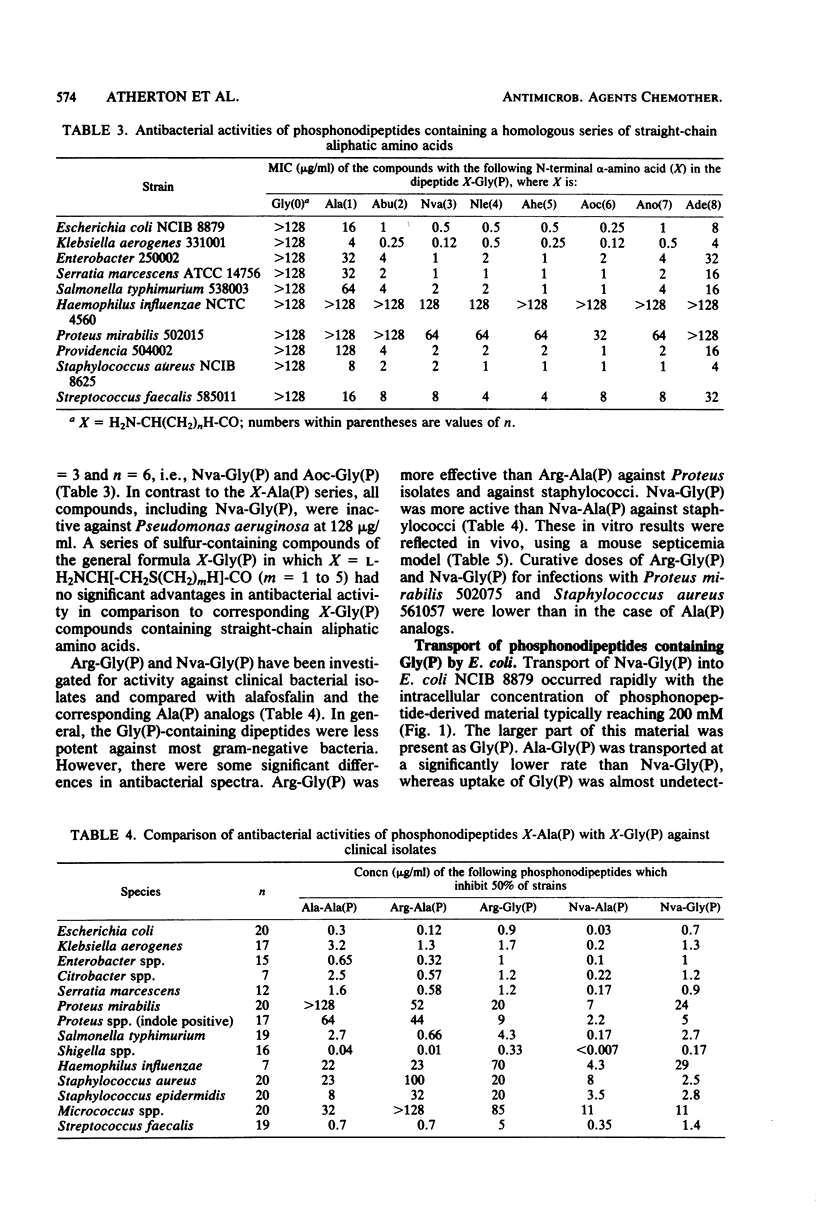
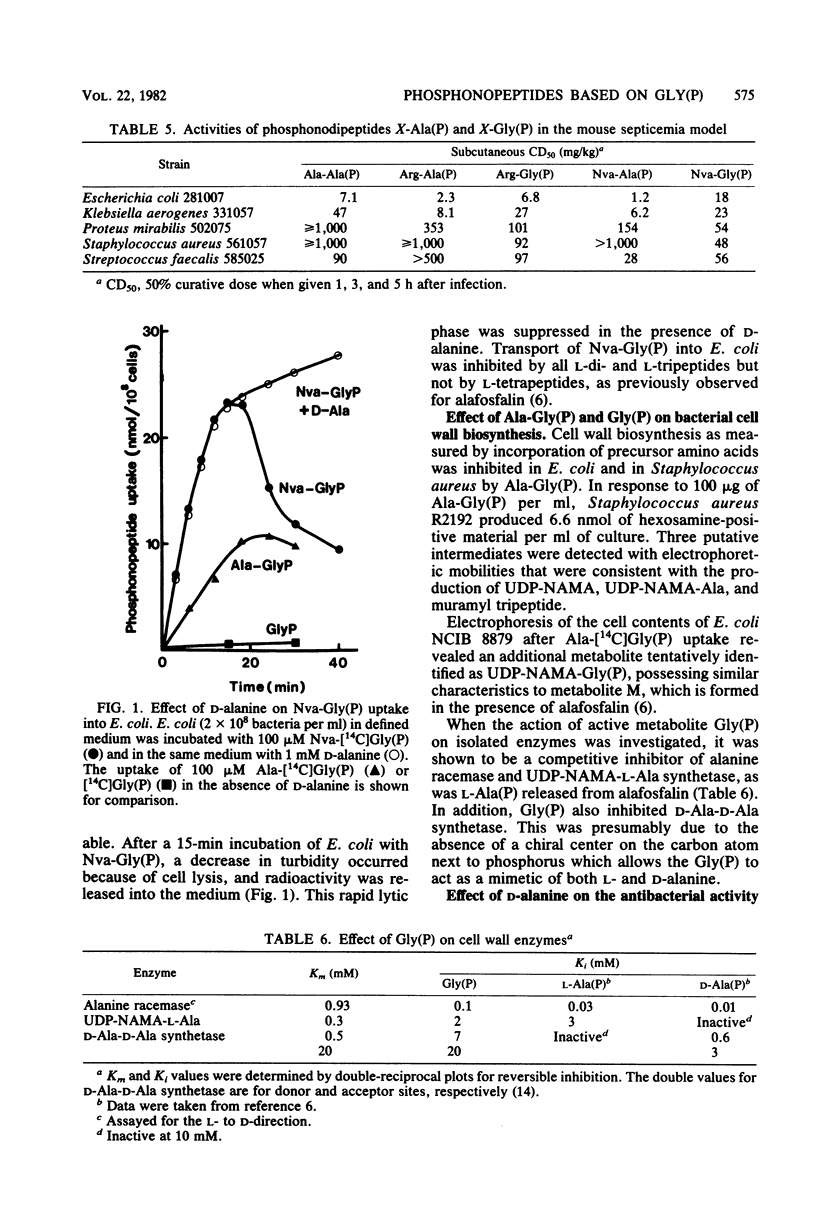
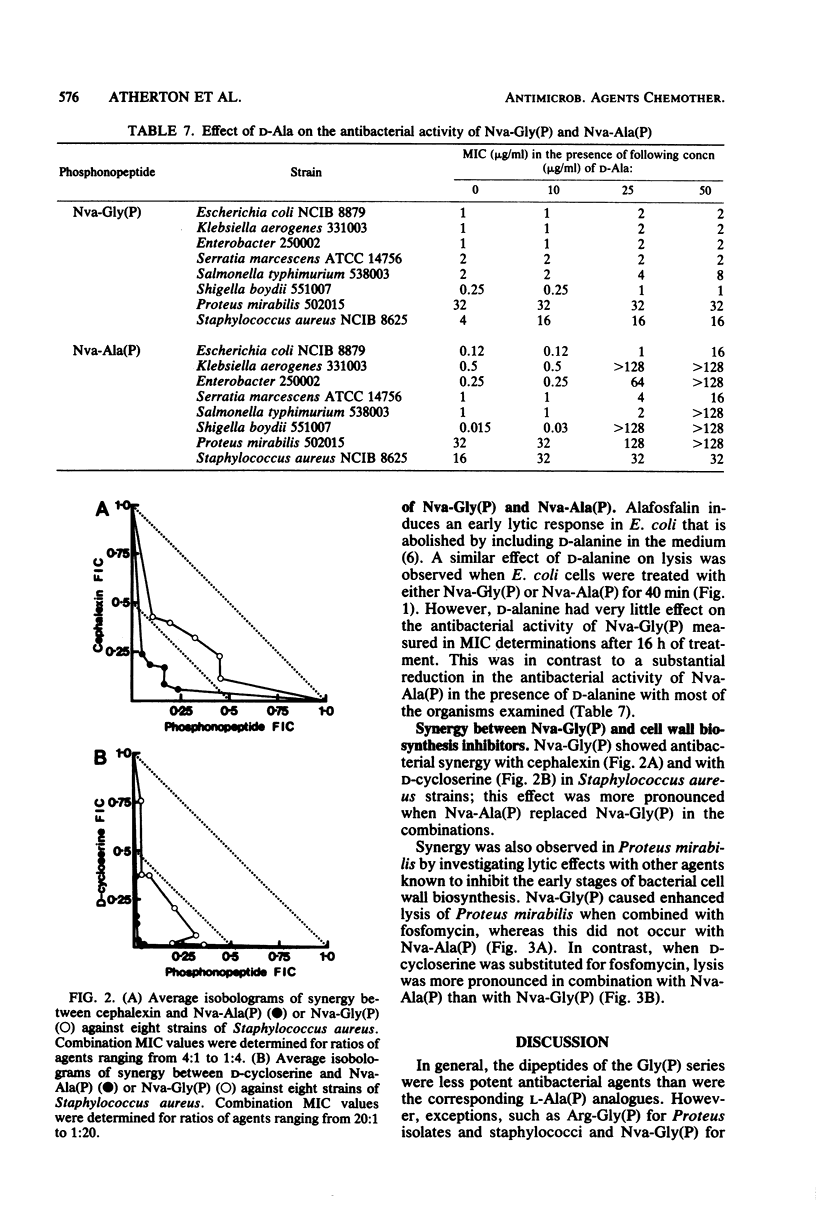
Phosphonopeptides based on aminomethylphosphonic acid as the C-terminal residue linked to L-amino acids possessed antibacterial activity in vitro and in vivo. Analogs in this series were generally less potent than corresponding compounds based on L-1-aminoethylphosphonic acid such as alafosfalin (L-alanyl-L-1-aminoethylphosphonic acid). Significant differences in antibacterial spectra were observed. The mechanism of action involved active transport of the peptide mimetics into the bacterial cells, followed by intracellular release of high concentrations of aminomethylphosphonic acid which inhibited bacterial cell wall biosynthesis. Aminomethylphosphonic acid behaved as a mimetic of both D- and L-alanine and inhibited D-Ala-D-Ala synthetase (EC 6.3.2.4.), alanine racemase (EC 5.1.1.1.), and UDP-N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanine synthetase (EC 6.3.2.8.). The minimal inhibitory concentration of L-norvalyl-aminomethylphosphonic acid was essentially unaffected by the presence of D-alanine, whereas the activity of the corresponding L-norvalyl derivative of L-1-aminoethylphosphonic acid was markedly decreased. Substantial differences in the inhibitory and lytic activity of the L-norvalyl derivatives of aminomethylphosphonic and L-1-aminoethylphosphonic acids were also observed when these agents were combined with other inhibitors of bacterial cell wall biosynthesis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. G., Atherton F. R., Hall M. J., Hassall C. H., Holmes S. W., Lambert R. W., Nisbet L. J., Ringrose P. S. Phosphonopeptides as antibacterial agents: alaphosphin and related phosphonopeptides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 May;15(5):684–695. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.5.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. G., Atherton F. R., Hall M. J., Hassall C. H., Holmes S. W., Lambert R. W., Nisbet L. J., Ringrose P. S. Phosphonopeptides, a new class of synthetic antibacterial agents. Nature. 1978 Mar 2;272(5648):56–58. doi: 10.1038/272056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. G., Lees L. J. Pharmacokinetics of alafosfalin, alone and in combination with cephalexin, in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):973–979. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton F. R., Hall M. J., Hassall C. H., Holmes S. W., Lambert R. W., Lloyd W. J., Nisbet L. J., Ringrose P. S., Westmacott D. Antibacterial properties of alafosfalin combined with cephalexin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Oct;20(4):470–476. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.4.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton F. R., Hall M. J., Hassall C. H., Holmes S. W., Lambert R. W., Lloyd W. J., Ringrose P. S. Phosphonopeptide antibacterial agents related to alafosfalin: design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationships. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Dec;18(6):897–905. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.6.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton F. R., Hall M. J., Hassall C. H., Lambert R. W., Lloyd W. J., Ringrose P. S. Phosphonopeptides as antibacterial agents: mechanism of action of alaphosphin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 May;15(5):696–705. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.5.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton F. R., Hall M. J., Hassall C. H., Lambert R. W., Ringrose P. S. Phosphonopeptides as antibacterial agents: rationale, chemistry, and structure-activity relationships. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 May;15(5):677–683. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.5.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boothby D., Daneo-Moore L., Shockman G. D. A rapid, guantitative, and selective estimation of radioactively labeled peptidoglycan in gram-positive bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1971 Dec;44(2):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90255-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELION G. B., SINGER S., HITCHINGS G. H. Antagonists of nucleic acid derivatives. VIII. Synergism in combinations of biochemically related antimetabolites. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jun;208(2):477–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M. P., Neuhaus F. C. Mechanism of D-cycloserine action: alanine racemase from Escherichia coli W. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):978–987. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.978-987.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEUHAUS F. C., LYNCH J. L. THE ENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS OF D-ALANYL-D-ALANINE. 3. ON THE INHIBITION OF D-ALANYL-D-ALANINE SYNTHETASE BY THE ANTIBIOTIC D-CYCLOSERINE. Biochemistry. 1964 Apr;3:471–480. doi: 10.1021/bi00892a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Wilson T. H. The role of energy coupling in the transport of beta-galactosides by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2200–2211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


