Abstract
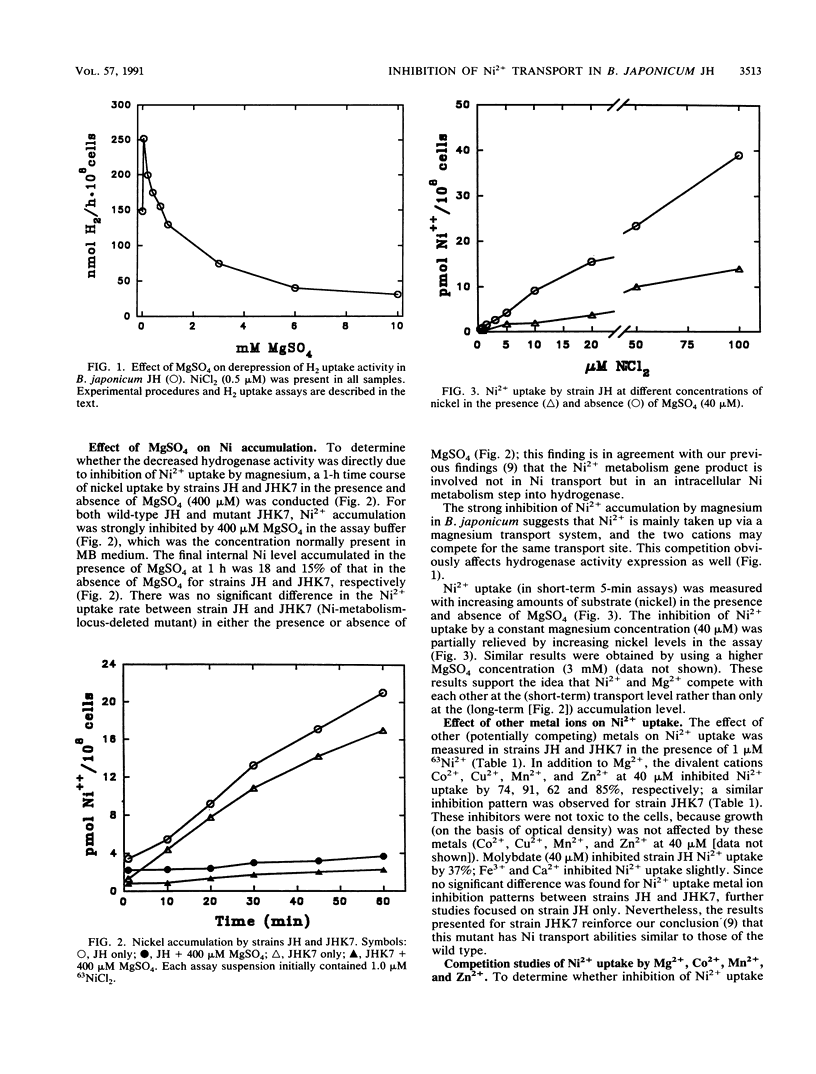
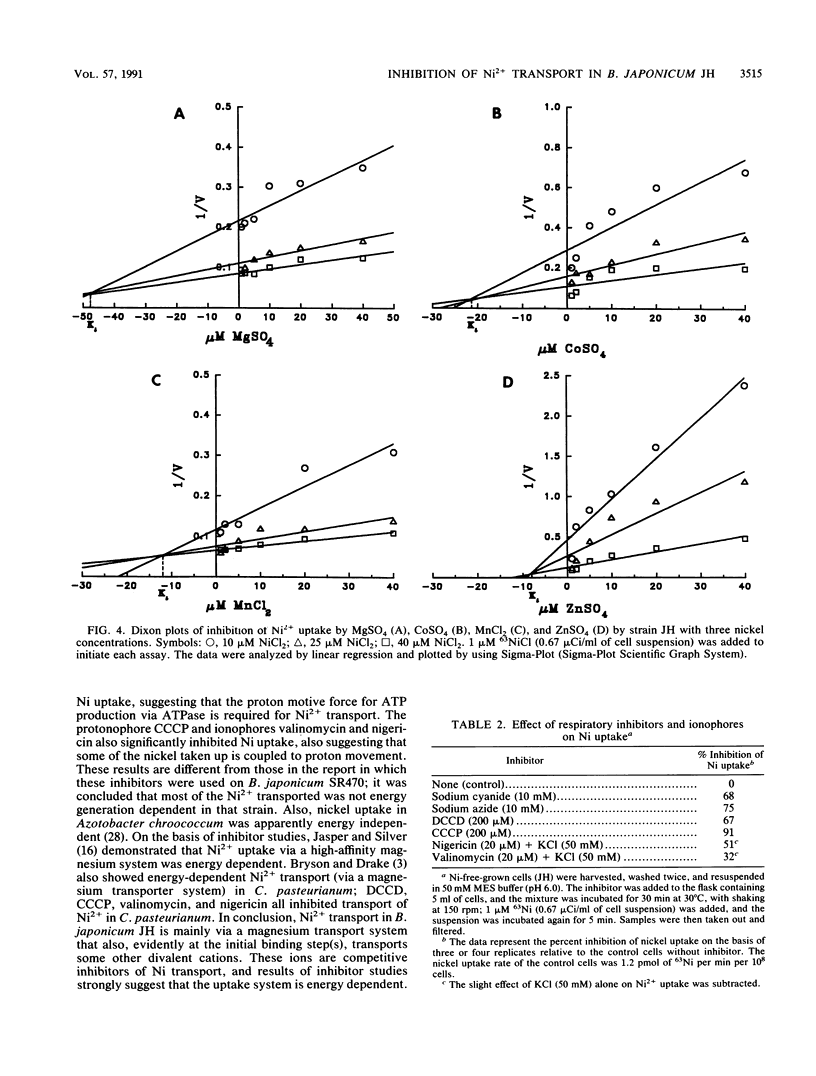
Both nickel-specific transport and nickel transport by a magnesium transporter have been described previously for a variety of nickel-utilizing bacteria. The derepression of hydrogenase activity in Bradyzhizobium japonicum JH and in a gene-directed mutant of strain JH (in an intracellular Ni metabolism locus), strain JHK7, was inhibited by MgSO4. For both strains, Ni2+ uptake was also markedly inhibited by Mg2+, and the Mg(2+)-mediated inhibition could be overcome by high levels of Ni2+ provided in the assay buffer. The results indicate that both B. japonicum strains transport Ni2+ via a high-affinity magnesium transport system. Dixon plots (1/V versus inhibitor) showed that the divalent cations Co2+, Mn2+, and Zn2+, like Mg2+, were competitive inhibitors of Ni2+ uptake. The KiS for nickel uptake inhibition by Mg2+, Co2+, Mn2+, and Zn2+ were 48, 22, 12, and 8 microM, respectively. Cu2+ strongly inhibited Ni2+ uptake, and molybdate inhibited it slightly. Respiratory inhibitors cyanide and azide, the uncoupler carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone, the ATPase inhibitor N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, and ionophores nigericin and valinomycin significantly inhibited short-term (5 min) Ni2+ uptake, showing that Ni2+ uptake in strain JH is energy dependent. Most of these conclusions are quite different from those reported previously for a different B. japonicum strain belonging to a different serogroup.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arp D. J. Rhizobium japonicum hydrogenase: purification to homogeneity from soybean nodules, and molecular characterization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Mar;237(2):504–512. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90303-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. E., Guevara J. G., Engelke J. A., Evans H. J. Relation between Glutamine Synthetase and Nitrogenase Activities in the Symbiotic Association between Rhizobium japonicum and Glycine max. Plant Physiol. 1976 Apr;57(4):542–546. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.4.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryson M. F., Drake H. L. Energy-dependent transport of nickel by Clostridium pasteurianum. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):234–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.234-238.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell P. M., Smith G. D. Transport and accumulation of nickel ions in the cyanobacterium Anabaena cylindrica. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Feb 1;244(2):470–477. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90615-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberz G., Eitinger T., Friedrich B. Genetic determinants of a nickel-specific transport system are part of the plasmid-encoded hydrogenase gene cluster in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1340–1345. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1340-1345.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eitinger T., Friedrich B. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and heterologous expression of a high-affinity nickel transport gene from Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3222–3227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eskew D. L., Welch R. M., Cary E. E. A simple plant nutrient solution purification method for effective removal of trace metals using controlled pore glass-8-hydroxyquinoline chelation column chromatography. Plant Physiol. 1984 Sep;76(1):103–105. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu C. L., Maier R. J. Identification of a locus within the hydrogenase gene cluster involved in intracellular nickel metabolism in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Dec;57(12):3502–3510. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.12.3502-3510.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker A. R., Xu L. S., Hanus F. J., Evans H. J. Some properties of the nickel-containing hydrogenase of chemolithotrophically grown Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):850–856. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.850-856.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausinger R. P. Nickel utilization by microorganisms. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):22–42. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.22-42.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hom S. S., Uratsu S. L., Hoang F. Transposon Tn5-induced mutagenesis of Rhizobium japonicum yielding a wide variety of mutants. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):335–340. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.335-340.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrell K. F., Sprott G. D. Nickel transport in Methanobacterium bryantii. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1195–1203. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1195-1203.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H., Maier R. J. Transcriptional regulation of hydrogenase synthesis by nickel in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18729–18732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H., Yu C., Maier R. J. Common cis-acting region responsible for transcriptional regulation of Bradyrhizobium japonicum hydrogenase by nickel, oxygen, and hydrogen. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(13):3993–3999. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.13.3993-3999.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundie L. L., Jr, Yang H. C., Heinonen J. K., Dean S. I., Drake H. L. Energy-dependent, high-affinity transport of nickel by the acetogen Clostridium thermoaceticum. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5705–5708. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5705-5708.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R. J., Hanus F. J., Evans H. J. Regulation of hydrogenase in Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):825–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.825-829.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R. J., Pihl T. D., Stults L., Sray W. Nickel accumulation and storage in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1905–1911. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1905-1911.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon N. K., Robbins J., Wendt J. C., Shanmugam K. T., Przybyla A. E. Mutational analysis and characterization of the Escherichia coli hya operon, which encodes [NiFe] hydrogenase 1. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4851–4861. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4851-4861.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merberg D., O'Hara E. B., Maier R. J. Regulation of hydrogenase in Rhizobium japonicum: analysis of mutants altered in regulation by carbon substrates and oxygen. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1236–1242. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1236-1242.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge C. D., Yates M. G. Effect of chelating agents on hydrogenase in Azotobacter chroococcum. Evidence that nickel is required for hydrogenase synthesis. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):339–344. doi: 10.1042/bj2040339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stults L. W., Mallick S., Maier R. J. Nickel uptake in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1398–1402. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1398-1402.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stults L. W., O'Hara E. B., Maier R. J. Nickel is a component of hydrogenase in Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):153–158. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.153-158.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. C., Daniel S. L., Hsu T. D., Drake H. L. Nickel transport by the thermophilic acetogen Acetogenium kivui. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 May;55(5):1078–1081. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.5.1078-1081.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


