Abstract
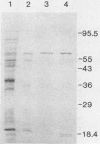
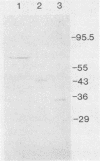
Three unique parathion hydrolases were purified from gram-negative bacterial isolates and characterized. All three purified enzymes had roughly comparable affinities for ethyl parathion and had broad temperature optima at ca. 40 degrees C. The membrane-bound hydrolase of Flavobacterium sp. strain ATCC 27551 was composed of a single subunit of approximately 35,000 daltons (Da) and was inhibited by sulfhydryl reagents such as dithiothreitol (DTT) and by metal salts such as CuCl2. The cytosolic hydrolase of strain B-1 was composed of a single subunit of approximately 43,000 Da and was stimulated by DTT and inhibited by CuCl2. The membrane-bound hydrolase of strain SC was composed of four identical subunits of 67,000 Da and was inhibited by DTT and stimulated by CuCl2. The substrate ranges of the three enzymes also differed, as evidenced by their relative affinities for parathion and the related organophosphate insecticide O-ethyl-O-4-nitrophenyl phenylphosphonothioate (EPN). The B-1 hydrolase displayed equal affinity for both compounds, the Flavobacterium enzyme showed twofold-lower affinity for EPN than for parathion, and the SC hydrolase displayed no activity toward EPN. The range in characteristics of these three enzymes can be exploited in different waste disposal strategies.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhry G. R., Ali A. N., Wheeler W. B. Isolation of a methyl parathion-degrading Pseudomonas sp. that possesses DNA homologous to the opd gene from a Flavobacterium sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):288–293. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.288-293.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Don R. H., Pemberton J. M. Properties of six pesticide degradation plasmids isolated from Alcaligenes paradoxus and Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):681–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.681-686.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb V. F., Jr, Bernlohr R. W. A new spectrophotometric assay for protein in cell extracts. Anal Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(2):362–371. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulbry W. W., Karns J. S., Kearney P. C., Nelson J. O., McDaniel C. S., Wild J. R. Identification of a plasmid-borne parathion hydrolase gene from Flavobacterium sp. by southern hybridization with opd from Pseudomonas diminuta. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):926–930. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.926-930.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulbry W. W., Kearney P. C., Nelson J. O., Karns J. S. Physical comparison of parathion hydrolase plasmids from Pseudomonas diminuta and Flavobacterium sp. Plasmid. 1987 Sep;18(2):173–177. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(87)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munnecke D. M. Enzymatic hydrolysis of organophosphate insecticides, a possible pesticide disposal method. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jul;32(1):7–13. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.1.7-13.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethunathan N., Yoshida T. A Flavobacterium sp. that degrades diazinon and parathion. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Jul;19(7):873–875. doi: 10.1139/m73-138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton D. R., Somich C. J. Isolation and characterization of coumaphos-metabolizing bacteria from cattle dip. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Oct;54(10):2566–2571. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.10.2566-2571.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]