Abstract
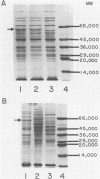
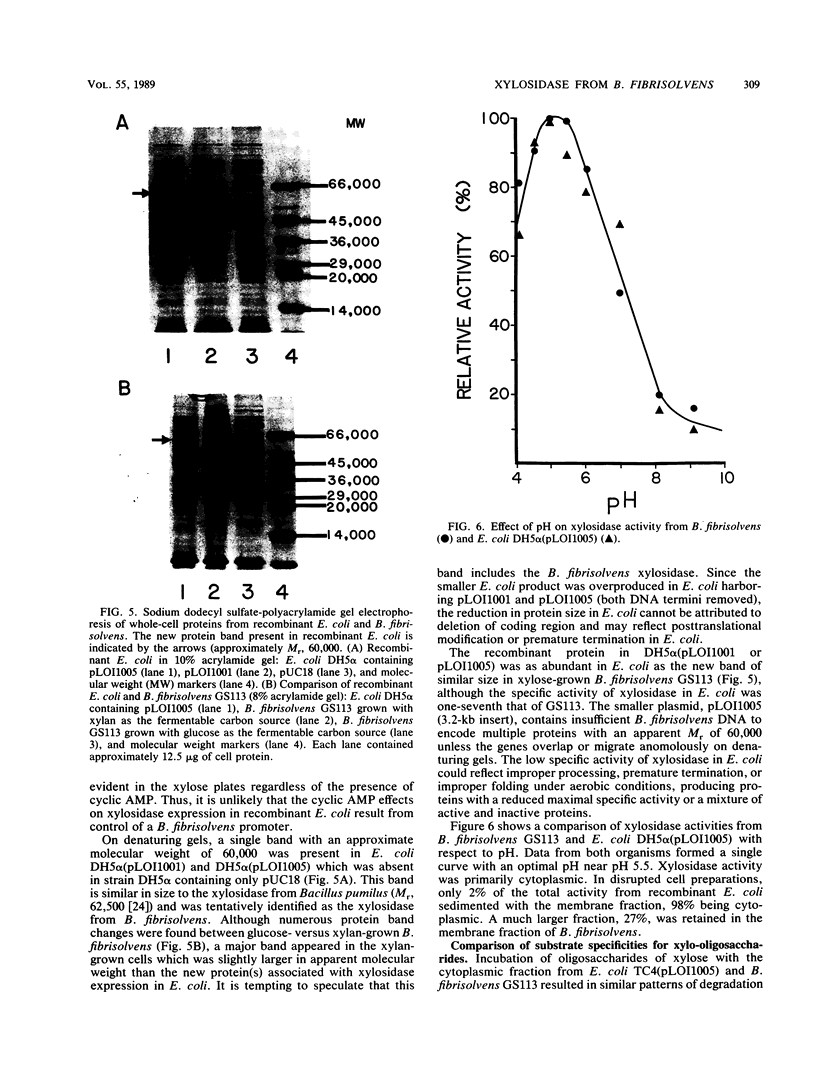
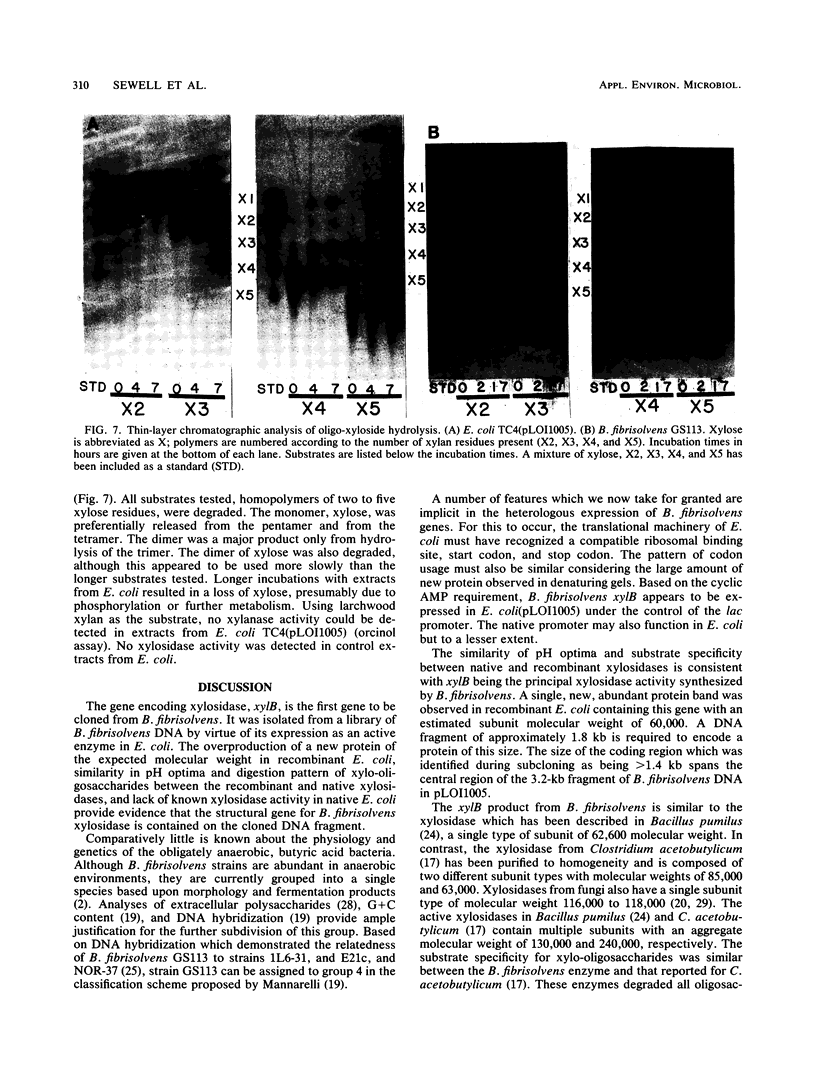
The gene encoding the principal Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens xylosidase (xylB) has been cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli under the control of the lac promoter. The coding region for this gene was localized within a 3.2-kilobase B. fibrisolvens DNA fragment in pUC18. A new protein band was observed in recombinant E. coli containing xylB. This protein (approximately 60,000 molecular weight) was presumed to be the xylosidase monomer. The optimal pH (5.5) and substrate range for the recombinant and native xylosidases appeared identical. Both enzymes hydrolyzed xylo-oligosaccharides with chain lengths of 2 to 5 and both were inactive on xylan.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bounias M. N-(1-naphthyl)ethylenediamine dihydrochloride as a new reagent for nanomole quantification of sugars on thin-layer plates by a mathematical calibration process. Anal Biochem. 1980 Aug;106(2):291–295. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90523-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Curtiss J. E., Jacobs W. R., Docherty M. A., Ritchie L. R., Curtiss R., 3rd Molecular analysis of DNA and construction of genomic libraries of Mycobacterium leprae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1093–1102. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1093-1102.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway T., Osman Y. A., Konnan J. I., Hoffmann E. M., Ingram L. O. Promoter and nucleotide sequences of the Zymomonas mobilis pyruvate decarboxylase. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):949–954. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.949-954.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotta M. A., Hespell R. B. Proteolytic activity of the ruminal bacterium Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jul;52(1):51–58. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.1.51-58.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehority B. A. Pectin-fermenting bacteria isolated from the bovine rumen. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):189–196. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.189-196.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehority B. A. Rate of isolated hemicellulose degradation and utilization by pure cultures of rumen bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Sep;15(5):987–993. doi: 10.1128/am.15.5.987-993.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD B. H., JONES G., PURDOM M. R. The pentosanases of some rumen bacteria. Biochem J. 1960 Jan;74:173–180. doi: 10.1042/bj0740173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hespell R. B., Wolf R., Bothast R. J. Fermentation of xylans by Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens and other ruminal bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Dec;53(12):2849–2853. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.12.2849-2853.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobson P. N., Wallace R. J. Microbial ecology and activities in the rumen: Part II. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1982 May;9(4):253–320. doi: 10.3109/10408418209104492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. F., Forsberg C. W. Isolation and Some Properties of a beta-d-Xylosidase from Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Apr;53(4):651–654. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.4.651-654.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama H., Fukusaki E., Cabrera Crespo J., Shinmyo A., Okada H. Structure and expression of genes coding for xylan-degrading enzymes of Bacillus pumilus. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Aug 3;166(3):539–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13547.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panbangred W., Kawaguchi O., Tomita T., Shinmyo A., Okada H. Isolation of two beta-xylosidase genes of Bacillus pumilus and comparison of their gene products. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 16;138(2):267–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07911.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panbangred W., Kondo T., Negoro S., Shinmyo A., Okada H. Molecular cloning of the genes for xylan degradation of Bacillus pumilus and their expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;192(3):335–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00392172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewell G. W., Aldrich H. C., Williams D., Mannarelli B., Wilkie A., Hespell R. B., Smith P. H., Ingram L. O. Isolation and Characterization of Xylan-Degrading Strains of Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens from a Napier Grass-Fed Anaerobic Digester. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 May;54(5):1085–1090. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.5.1085-1090.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipat A., Taylor K. A., Lo R. Y., Forsberg C. W., Krell P. J. Molecular cloning of a xylanase gene from Bacteroides succinogenes and its expression in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Mar;53(3):477–481. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.3.477-481.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stack R. J. Neutral sugar composition of extracellular polysaccharides produced by strains of Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Apr;54(4):878–883. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.4.878-883.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stack R. J. Neutral sugar composition of extracellular polysaccharides produced by strains of Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Apr;54(4):878–883. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.4.878-883.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]