Abstract
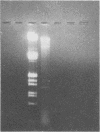
Presumptive bacteriophage P1 transductants of Escherichia coli, isolated from soil inoculated with lysates of transducing phage P1 and E. coli, were confirmed to be lysogenic for phage P1 by hybridization with a biotinylated DNA probe prepared from the 1.2-kilobase-pair HindIII 3 fragment of bacteriophage P1. No P1 lysogens of indigenous soil bacteria were detected with the DNA probe. The sensitivity and specificity of the DNA probe were assessed with purified and dot blot DNA, respectively. In addition, two techniques for the lysis and deproteinization of bacteria and bacteriophages on nitrocellulose filters were compared. These studies indicated that biotinylated DNA probes may be an effective alternative to conventional radiolabeled DNA probes for detecting specific gene sequences in bacteria indigenous to or introduced into soil.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Briaux S., Gerbaud G., Jaffé-Brachet A. Studies of a plasmid coding for tetracycline resistance and hydrogen sulfide production incompatible with the prophage P1. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Mar 5;170(3):319–325. doi: 10.1007/BF00267065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bächi B., Arber W. Physical mapping of BglII, BamHI, EcoRI, HindIII and PstI restriction fragments of bacteriophage P1 DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jun 24;153(3):311–324. doi: 10.1007/BF00431596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germida J. J., Khachatourians G. G. Transduction of Escherichia coli in soil. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Feb;34(2):190–193. doi: 10.1139/m88-035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg R. B., Bender R. A., Streicher S. L. Direct selection for P1-sensitive mutants of enteric bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):810–814. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.810-814.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M. J., Fleming D. J. Use of biotinylated DNA probes in colony hybridization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 12;14(9):3976–3976. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.9.3976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holben William E., Jansson Janet K., Chelm Barry K., Tiedje James M. DNA Probe Method for the Detection of Specific Microorganisms in the Soil Bacterial Community. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Mar;54(3):703–711. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.3.703-711.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda H., Inuzuka M., Tomizawa J. I. P1-like plasmid in Escherichia coli 15. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 14;50(2):457–470. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90204-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. V., Ku C. M. Characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants deficient in the establishment of lysogeny. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):875–883. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.875-883.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison W. D., Miller R. V., Sayler G. S. Frequency of F116-mediated transduction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a freshwater environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Nov;36(5):724–730. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.5.724-730.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mural R. J., Chesney R. H., Vapnek D., Kropf M. M., Scott J. R. Isolation and characterization of cloned fragments of bacteriophage P1 DNA. Virology. 1979 Mar;93(2):387–397. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90243-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafii F., Crawford D. L. Transfer of conjugative plasmids and mobilization of a nonconjugative plasmid between Streptomyces strains on agar and in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1334–1340. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1334-1340.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner J. L. Formation, induction, and curing of bacteriophage P1 lysogens. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):679–689. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saye D. J., Ogunseitan O., Sayler G. S., Miller R. V. Potential for transduction of plasmids in a natural freshwater environment: effect of plasmid donor concentration and a natural microbial community on transduction in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):987–995. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.987-995.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stotzky G., Babich H. Survival of, and genetic transfer by, genetically engineered bacteria in natural environments. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1986;31:93–138. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70440-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeph L. R., Onaga M. A., Stotzky G. Transduction of Escherichia coli by bacteriophage P1 in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jul;54(7):1731–1737. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.7.1731-1737.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]