Abstract
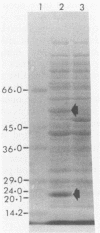
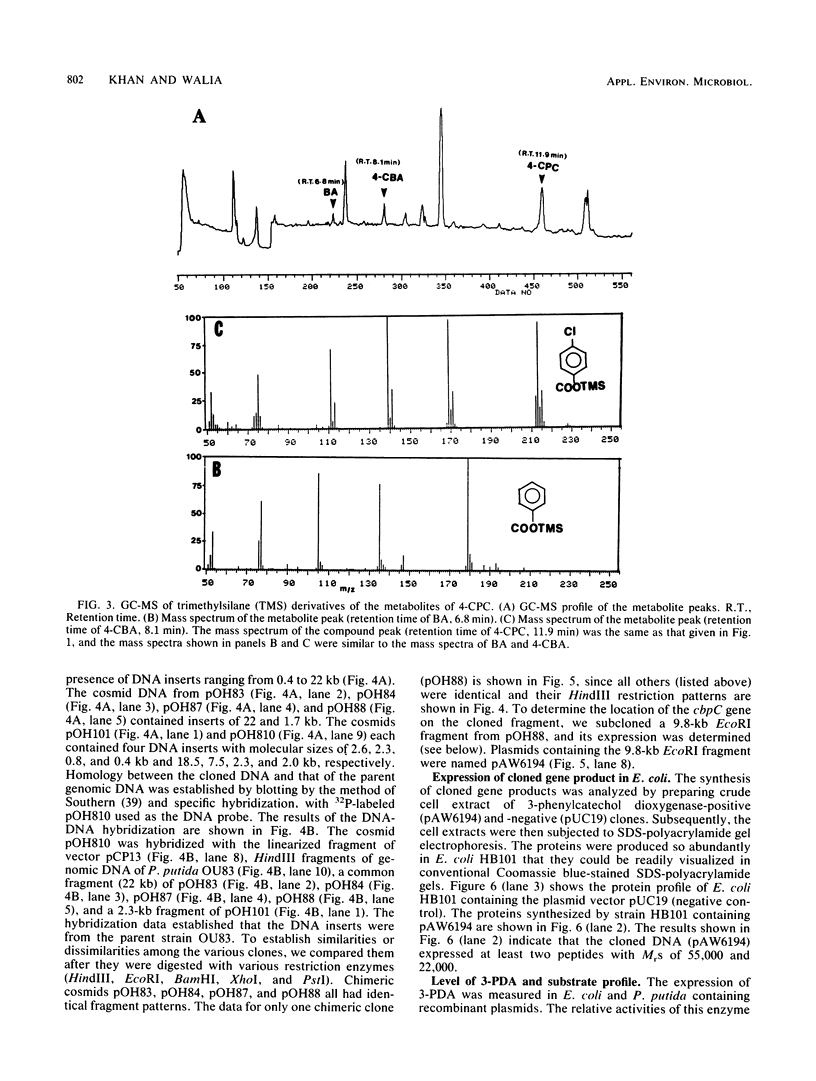
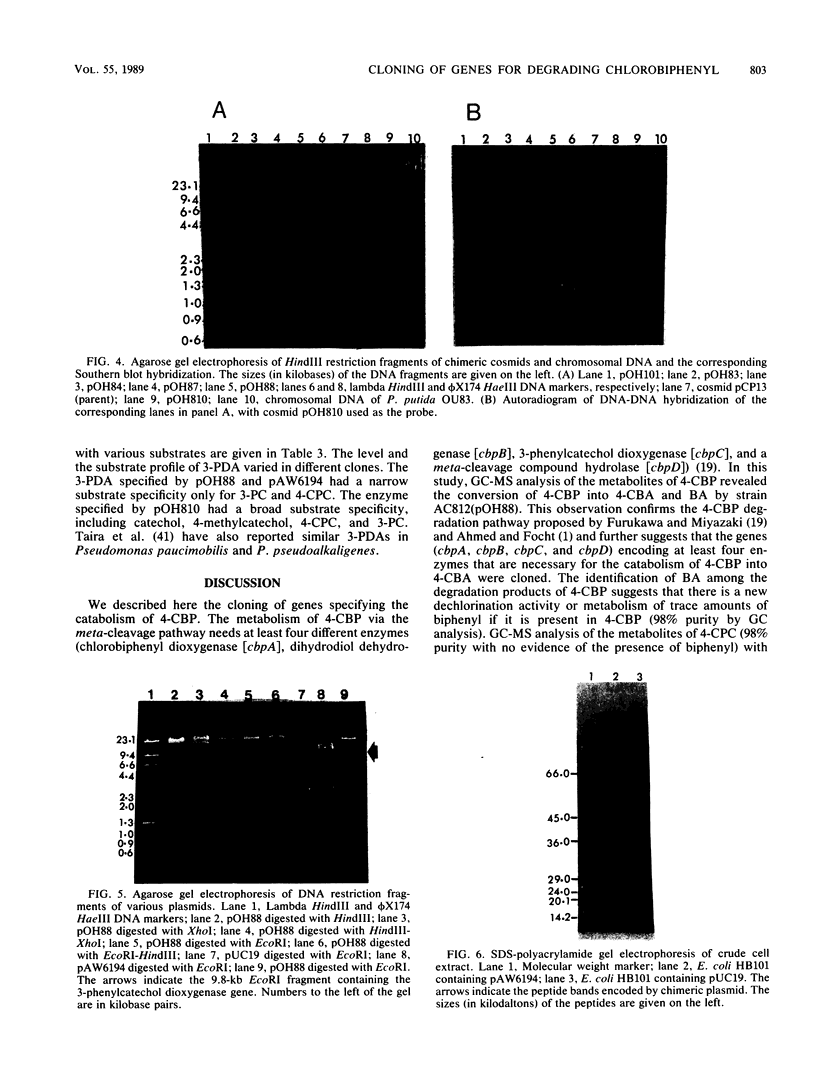
Genes capable of 4-chlorobiphenyl (4-CBP) degradation were cloned from 4-CBP-degrading Pseudomonas putida OU83 by using a genomic library which was constructed in the broad-host-range cosmid vector pCP13. P. putida AC812 containing chimeric cosmid-expressing enzymes involved in the 4-CBP degradation pathway were identified by detecting 3-phenylcatechol dioxygenase activity (3-PDA). Chimeric cosmid clones pOH83, pOH84, pOH85, pOH87, and pOH88 positive for 3-PDA grew in synthetic basal medium containing 4-CBP (5 mM) as a carbon source. Restriction digestion analysis of recombinant cosmids showed DNA inserts ranging from 6 to 30 kilobase pairs. Southern hybridization data revealed that the cloned DNA inserts originated from strain OU83. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of the metabolites of P. putida AC812(pOH88) incubated with 4-CBP and 4'-chloro-3-phenylcatechol showed the formation of 4-chlorobenzoic acid and benzoic acid. These results demonstrate that the cloned DNA fragments contain genes encoding for chlorobiphenyl dioxygenase (cbpA), dihydrodiol dehydrogenase (cbpB), 4'-chloro-3-phenylcatechol dioxygenase (cbpC), a meta-cleavage compound (a chloro derivative of 2-hydroxy-6-oxo-6-phenylhexa-2,4-dienoate) hydrolase (cbpD), and a new dechlorinating activity (dcpE). The location of the cbpC gene specifying 3-PDA was determined by subcloning an EcoRI DNA fragment (9.8 kilobase pairs) of pOH88 in plasmid vector pUC19. The cloned gene encoding 3-PDA was expressed in Escherichia coli HB101 and had substrate specificity only for 3-phenylcatechol and 4'-chloro-3-phenylcatechol.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed M., Focht D. D. Degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls by two species of Achromobacter. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Jan;19(1):47–52. doi: 10.1139/m73-007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander M. Biodegradation of chemicals of environmental concern. Science. 1981 Jan 9;211(4478):132–138. doi: 10.1126/science.7444456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amy P. S., Schulke J. W., Frazier L. M., Seidler R. J. Characterization of aquatic bacteria and cloning of genes specifying partial degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1237–1245. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1237-1245.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton M. R., Crawford R. L. Novel biotransformations of 4-chlorobiphenyl by a Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):594–595. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.594-595.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayly R. C., Dagley S., Gibson D. T. The metabolism of cresols by species of Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):293–301. doi: 10.1042/bj1010293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedard D. L., Haberl M. L., May R. J., Brennan M. J. Evidence for novel mechanisms of polychlorinated biphenyl metabolism in Alcaligenes eutrophus H850. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1103–1112. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1103-1112.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedard D. L., Unterman R., Bopp L. H., Brennan M. J., Haberl M. L., Johnson C. Rapid assay for screening and characterizing microorganisms for the ability to degrade polychlorinated biphenyls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Apr;51(4):761–768. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.4.761-768.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey V. C., Walia S. K., Ingram L. O. Expression of a Lactose Transposon (Tn951) in Zymomonas mobilis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1163–1168. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1163-1168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee D. K., Chakrabarty A. M. Restriction mapping of a chlorobenzoate degradative plasmid and molecular cloning of the degradative genes. Gene. 1984 Feb;27(2):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90138-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzins A., Chakrabarty A. M. Cloning of genes controlling alginate biosynthesis from a mucoid cystic fibrosis isolate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):9–18. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.9-18.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finette B. A., Subramanian V., Gibson D. T. Isolation and characterization of Pseudomonas putida PpF1 mutants defective in the toluene dioxygenase enzyme system. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1003–1009. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1003-1009.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin F. C., Bagdasarian M., Bagdasarian M. M., Timmis K. N. Molecular and functional analysis of the TOL plasmid pWWO from Pseudomonas putida and cloning of genes for the entire regulated aromatic ring meta cleavage pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7458–7462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. M., Long S. R., Brown S. E., Buikema W. J., Ausubel F. M. Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Arimura N. Purification and properties of 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl dioxygenase from polychlorinated biphenyl-degrading Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes and Pseudomonas aeruginosa carrying the cloned bphC gene. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):924–927. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.924-927.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Chakrabarty A. M. Involvement of plasmids in total degradation of chlorinated biphenyls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Sep;44(3):619–626. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.3.619-626.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Miyazaki T. Cloning of a gene cluster encoding biphenyl and chlorobiphenyl degradation in Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):392–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.392-398.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosal D., You I. S., Chatterjee D. K., Chakrabarty A. M. Microbial degradation of halogenated compounds. Science. 1985 Apr 12;228(4696):135–142. doi: 10.1126/science.228.4696.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosal D., You I. S., Gunsalus I. C. Nucleotide sequence and expression of gene nahH of plasmid NAH7 and homology with gene xylE of TOL pWWO. Gene. 1987;55(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90244-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A., Tewari R., Walia S. Molecular cloning of 3-phenylcatechol dioxygenase involved in the catabolic pathway of chlorinated biphenyl from Pseudomonas putida and its expression in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Nov;54(11):2664–2671. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.11.2664-2671.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massé R., Messier F., Péloquin L., Ayotte C., Sylvestre M. Microbial biodegradation of 4-chlorobiphenyl, a model compound of chlorinated biphenyls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 May;47(5):947–951. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.947-951.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risebrough R. W., Rieche P., Peakall D. B., Herman S. G., Kirven M. N. Polychlorinated biphenyls in the global ecosystem. Nature. 1968 Dec 14;220(5172):1098–1102. doi: 10.1038/2201098a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala-Trepat J. M., Evans W. C. The meta cleavage of catechol by Azotobacter species. 4-Oxalocrotonate pathway. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jun 11;20(3):400–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields M. S., Hooper S. W., Sayler G. S. Plasmid-mediated mineralization of 4-chlorobiphenyl. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):882–889. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.882-889.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiert J. G., Pignatello J. J., Crawford R. L. Degradation of chlorinated phenols by a pentachlorophenol-degrading bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):907–910. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.907-910.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira K., Hayase N., Arimura N., Yamashita S., Miyazaki T., Furukawa K. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl dioxygenase gene from the PCB-degrading strain of Pseudomonas paucimobilis Q1. Biochemistry. 1988 May 31;27(11):3990–3996. doi: 10.1021/bi00411a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walia S. K., Duckworth D. H. The relationship of the delta transfer factor and KColIb to the ColIb plasmid. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Dec;132(12):3261–3268. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-12-3261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walia S. K., Madhavan T., Chugh T. D., Sharma K. B. Characterization of self-transmissible plasmids determining lactose fermentation and multiple antibiotic resistance in clinical strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Plasmid. 1987 Jan;17(1):3–12. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(87)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walia S., Madhavan T., Williamson T., Kaiser A., Tewari R. Protein patterns, serotyping and plasmid DNA profiles in the epidemiologic fingerprinting of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;7(2):248–255. doi: 10.1007/BF01963096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisshaar M. P., Franklin F. C., Reineke W. Molecular cloning and expression of the 3-chlorobenzoate-degrading genes from Pseudomonas sp. strain B13. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):394–402. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.394-402.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]