Abstract
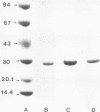
A simple method for the purification of staphylococcal enterotoxins A (SEA), B (SEB), and C2 (SEC2) from fermentor-grown cultures was developed. The toxins were purified by pseudo-affinity chromatography by using the triazine textile dye "Red A" and gave overall yields of 49% (SEA), 44% (SEB), and 53% (SEC2). The purified toxins were homogeneous when analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, but isoelectric focusing of the preparations revealed the microheterogeneity associated with these toxins. The SEA and SEB preparations each consisted of two isoelectric forms with pI values of 7.3 and 6.8 (SEA) and 8.9 and 8.55 (SEB); in contrast, SEC2 contained five different isoelectric forms, with pI values ranging between 7.6 and 6.85. The pattern of elution of the isoelectric forms from the column indicated a cationic-exchange process involved in the binding of toxin to Red A. Such a method forms the basis of a high-yielding, rapid means of purifying the staphylococcal enterotoxins that can easily be adapted to large-scale production.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avena R. M., Bergdoll M. S. Purification and some physicochemical properties of enterotoxin C, Staphylococcus aureus strain 361. Biochemistry. 1967 May;6(5):1474–1480. doi: 10.1021/bi00857a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGDOLL M. S., SUGIYAMA H., DACK G. M. Staphylococcal enterotoxin. I. Purification. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Nov;85:62–69. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90447-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergdoll M. S., Borja C. R., Avena R. M. Identification of a new enterotoxin as enterotoxin C. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1481–1485. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1481-1485.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergdoll M. S., Borja C. R., Robbins R. N., Weiss K. F. Identification of enterotoxin E. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):593–595. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.593-595.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergdoll M. S., Huang I. Y., Schantz E. J. Chemistry of the staphylococcal enterotoxins. J Agric Food Chem. 1974 Jan-Feb;22(1):9–13. doi: 10.1021/jf60191a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhme H. J., Kopperschläger G., Schulz J., Hofmann E. Affinity chromatography of phosphofructokinase using Cibacron blue F3G-A. J Chromatogr. 1972 Jun 28;69(1):209–214. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)83103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASMAN E. P., BERGDOLL M. S., ROBINSON J. DESIGNATION OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL EXTEROTOXINS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Mar;85:715–716. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.3.715-716.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casman E. P., Bennett R. W., Dorsey A. E., Issa J. A. Identification of a fourth staphylococcal enterotoxin, enterotoxin D. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1875–1882. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1875-1882.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casman E. P., Bennett R. W., Dorsey A. E., Stone J. E. The micro-slide gel double diffusion test for the detection and assay of staphylococcal enterotoxins. Health Lab Sci. 1969 Oct;6(4):185–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang P. C., Dickie N. Fractionation of staphylococcal enterotoxin B by isoelectric focusing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 May 25;236(2):367–375. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu F. S., Thadhani K., Schantz E. J., Bergdoll M. S. Purification and characterization of staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Biochemistry. 1966 Oct;5(10):3281–3289. doi: 10.1021/bi00874a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottreau D., Levin M. J., Kahn A. Purification and partial characterization of different forms of phosphofructokinase in man. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 10;568(1):183–194. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90285-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickie N., Yano Y., Robern H., Stavric S. On the heterogeneity of staphylococcal enterotoxin C 2 . Can J Microbiol. 1972 Jun;18(6):801–804. doi: 10.1139/m72-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. A., Woody R. W. Spectroscopic studies of Cibacron Blue and Congo Red bound to dehydrogenases and kinases. Evaluation of dyes as probes of the dinucleotide fold. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 13;18(23):5197–5204. doi: 10.1021/bi00590a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ende I. A., Terplan G., Kickhöfen B., Hammer D. K. Chromatofocusing: a new method for purification of staphylococcal enterotoxins B and C1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Dec;46(6):1323–1330. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.6.1323-1330.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey H., Pfister H., Rüegg O. Comparative evaluation of different enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay systems for the detection of staphylococcal enterotoxins A, B, C, and D. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):34–38. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.34-38.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung D. Y., Steinberg D. H., Miller R. D., Kurantnick M. J., Murphy T. F. Thermal inactivation of staphylococcal enterotoxins B and C. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Dec;26(6):938–942. doi: 10.1128/am.26.6.938-942.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamlang E. M., Bartlett M. L., Snyder H. E. Effect of pH, protein concentration, and ionic strength on heat inactivation of staphylococcal enterotoxin B 1 . Appl Microbiol. 1971 Dec;22(6):1034–1040. doi: 10.1128/am.22.6.1034-1040.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopperschläger G., Diezel W., Freyer R., Liebe S., Hofmann E. Wechselwirkungen der Hefe-Phosphofructokinase mit Dextranblau 2000. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Sep 13;22(1):40–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. L., Lin C. C. [Detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin by latex agglutination inhibition test]. Zhonghua Min Guo Wei Sheng Wu Ji Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 1984 May;17(2):77–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger J. F., Johnson A. D., Collins W. S., 2nd Fractionation and purification of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B by electrofocusing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 26;257(1):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90269-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger J. F., Johnson A. D., Spero L. Intrinsic and chemically produced microheterogeneity of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin type C. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):93–97. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.93-97.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. F., Palmieri M. J. Single radial immunodiffusion method for screening Staphylococcal isolates for enterotoxin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Dec;40(6):1080–1085. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.6.1080-1085.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser R. F., Robbins R. N., Noleto A. L., Khoe G. P., Bergdoll M. S. Identification, purification, and some physicochemical properties of staphylococcal enterotoxin C3. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):625–630. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.625-630.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds D., Tranter H. S., Sage R., Hambleton P. Novel method for purification of staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jul;54(7):1761–1765. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.7.1761-1765.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins R., Gould S., Bergdoll M. Detecting the enterotoxigenicity of Staphylococcus aureus strains. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Dec;28(6):946–950. doi: 10.1128/am.28.6.946-950.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robern H., Stavric S., Dickie N. Fractionation of staphylococcal enterotoxin A by isoelectric focusing. Experientia. 1974 Sep 15;30(9):1087–1089. doi: 10.1007/BF01939026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robern H., Stavric S., Dickie N. The application of QAE-Sephadex for the purification of two staphylococcal enterotoxins. I. Purification of enterotoxin C2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 30;393(1):148–158. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90225-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schantz E. J., Roessler W. G., Wagman J., Spero L., Dunnery D. A., Bergdoll M. S. Purification of staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Biochemistry. 1965 Jun;4(6):1011–1016. doi: 10.1021/bi00882a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schantz E. J., Roessler W. G., Woodburn M. J., Lynch J. M., Jacoby H. M., Silverman S. J., Gorman J. C., Spero L. Purification and some chemical and physical properties of staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 1;11(3):360–366. doi: 10.1021/bi00753a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spero L., Metzger J. F. Staphylococcal enterotoxin A (SEA). Methods Enzymol. 1981;78(Pt A):331–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windemann H., Baumgartner E. Bestimmung von Staphylokokken-Enterotoxinen A, B, C und D in Lebensmitteln mittels Sandwich-ELISA mit markiertem Antikörper. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1985 Dec;181(3-5):345–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]