Abstract
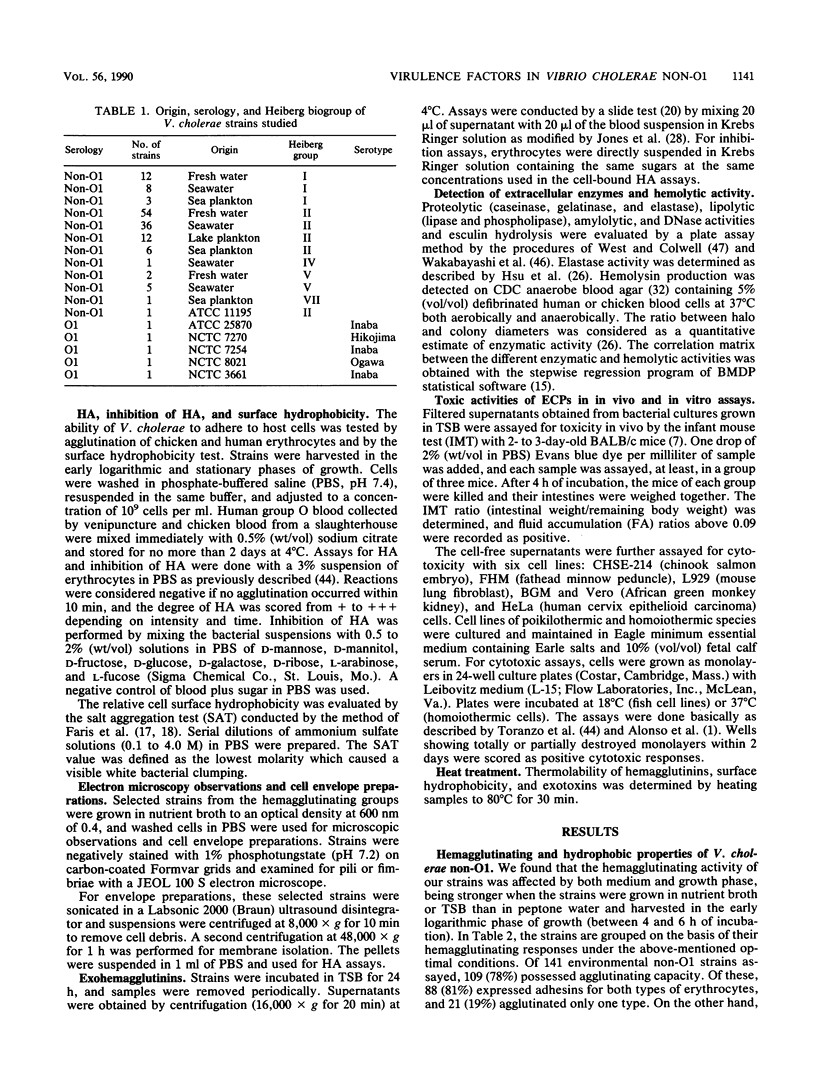
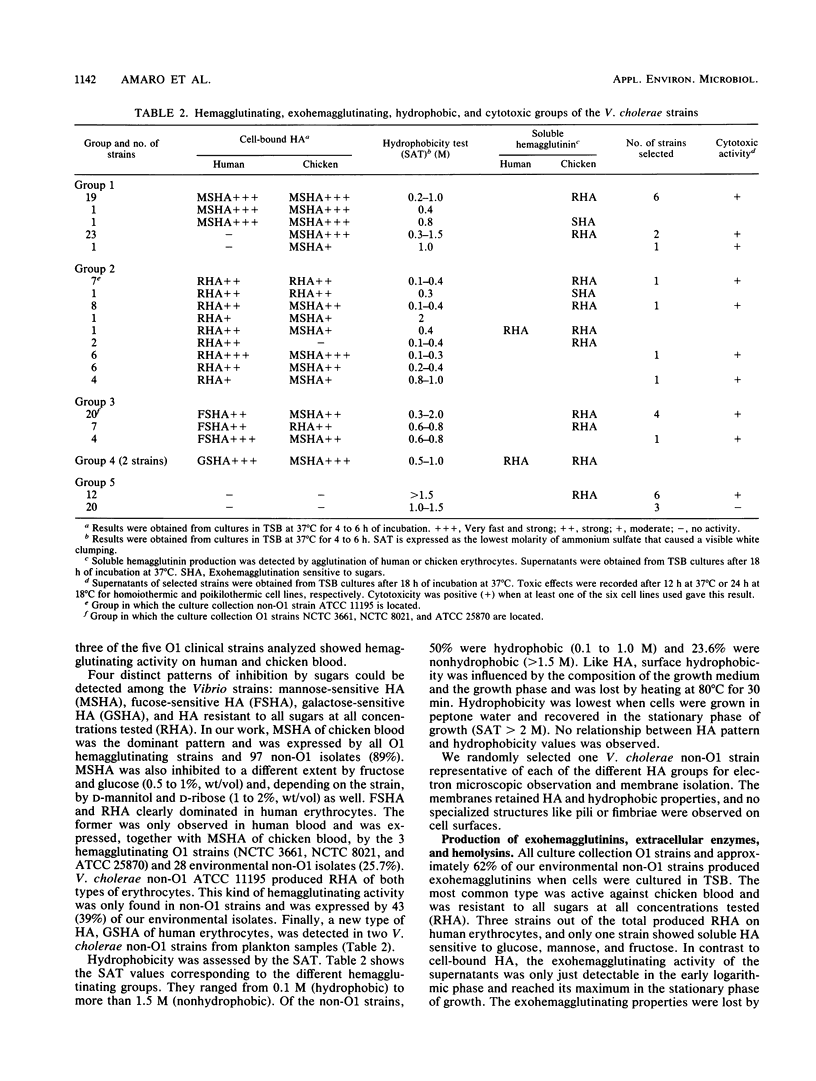
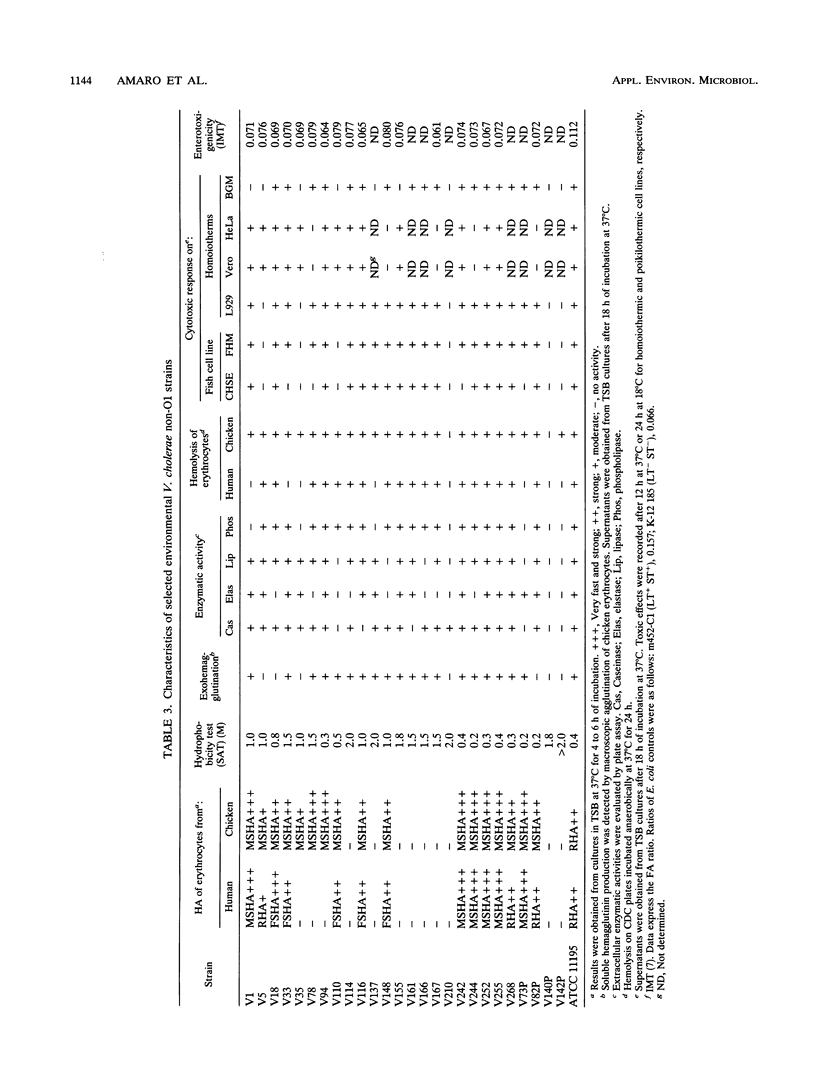
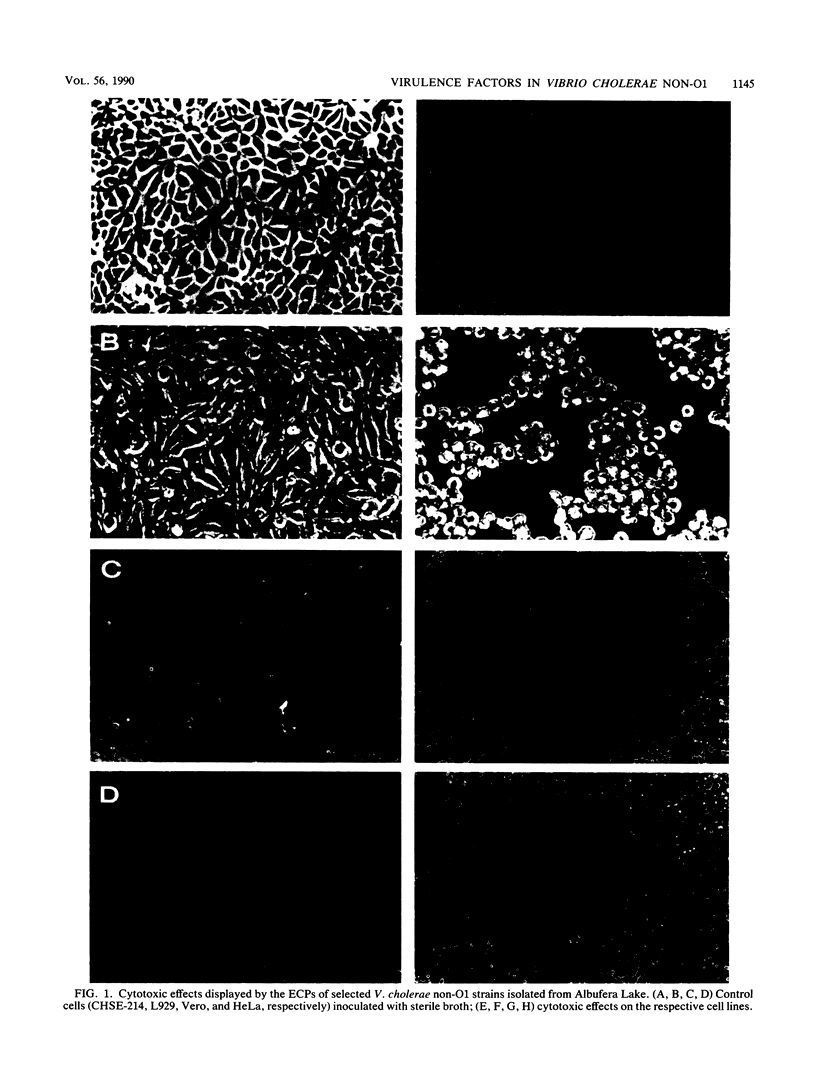
A total of 140 environmental Vibrio cholerae non-O1 isolates, together with several culture collection strains from both environmental and clinical sources, were studied in relation to hemagglutination, surface hydrophobicity, and the enzymatic, hemolytic, cytotoxic, and enterotoxic activities of their extracellular products. A total of 78 and 62% of the strains produced hemagglutinins and exohemagglutinins, respectively. Four different hemagglutinating and two exohemagglutinating activities were found by using eight sugars in the inhibition assays. Cell-bound mannose-sensitive hemagglutination was detected mainly in chicken blood, whereas fucose-sensitive hemagglutination was recorded only in human blood. Cell-bound hemagglutinin resistant to all sugars tested was the only one related to surface hydrophobicity. The surface properties varied along the growth curves. The non-O1 strains displayed strong enzymatic and hemolytic activities, except for esculin hydrolysis. Of 26 non-O1 isolates selected for cytotoxin and enterotoxin production, 23 showed a wide spectrum of cytotoxic effects on cell lines of poikilothermic and homoiothermic species, but they were weakly enterotoxigenic in the infant mouse test. All extracellular products of cytotoxic strains were proteolytic, lipolytic, and hemolytic, and a high percentage produced hemagglutination of chicken blood. The cytotoxic factors in the non-O1 strains analyzed were not R plasmid mediated.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amaro C., Aznar R., Garay E., Alcaide E. R plasmids in environmental Vibrio cholerae non-O1 strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Nov;54(11):2771–2776. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.11.2771-2776.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson H. M., Trust T. J. Hemagglutination properties and adherence ability of Aeromonas hydrophila. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):938–946. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.938-946.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerre-Jepsen K., Faris I., Henriksen O., Lassen N. A. Subcutaneous blood flow over 24-hour periods in patients with severe leg ischaemia. Clin Physiol. 1982 Oct;2(5):357–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-097x.1982.tb00041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. A., Allegra D. T., Snyder J. D., Barrett T. J., McFarland L., Caraway C. T., Feeley J. C., Craig J. P., Lee J. V., Puhr N. D. Cholera--a possible endemic focus in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1980 Feb 7;302(6):305–309. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198002073020601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. A., Weaver R. E., Hollis D. G. Diseases of humans (other than cholera) caused by vibrios. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:341–367. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth B. A., Boesman-Finkelstein M., Finkelstein R. A. Vibrio cholerae hemagglutinin/protease nicks cholera enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):558–560. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.558-560.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth B. A., Finkelstein R. A. Presence of hemagglutinin/protease and other potential virulence factors in O1 and non-O1 Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):183–186. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colwell R. R., Kaper J., Joseph S. W. Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and other vibrios: occurrence and distribution in Chesapeake Bay. Science. 1977 Oct 28;198(4315):394–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H. A plasmid associated with virulence in the marine fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum specifies an iron-sequestering system. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):566–568. doi: 10.1038/284566a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumberbatch N., Gurwith M. J., Langston C., Sack R. B., Brunton J. L. Cytotoxic enterotoxin produced by Aeromonas hydrophila: relationship of toxigenic isolates to diarrheal disease. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):829–837. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.829-837.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Hermansson M., Kjelleberg S., Norkrans B. The hydrophobicity of bacteria - an important factor in their initial adhesion at the air-water interface. Arch Microbiol. 1981 Jan;128(3):267–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00422527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta-Roy K., Banerjee K., De S. P., Ghose A. C. Comparative study of expression of hemagglutinins, hemolysins, and enterotoxins by clinical and environmental isolates of non-O1 Vibrio cholerae in relation to their enteropathogenicity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):875–879. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.875-879.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garay E., Arnau A., Amaro C. Incidence of Vibrio cholerae and related vibrios in a coastal lagoon and seawater influenced by lake discharges along an annual cycle. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):426–430. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.426-430.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez E. A., Blanco J., Baloda S. B., Wadström T. Relative cell surface hydrophobicity of Escherichia coli strains with various recognized fimbrial antigens and without recognized fimbriae. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Aug;269(2):218–236. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80100-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyobu Y., Kodama H., Uetake H., Katsuda S. Studies on the enteropathogenic mechanism of non-O 1 Vibrio cholerae isolated from the environment and fish in Toyama Prefecture. Microbiol Immunol. 1984;28(7):735–745. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1984.tb00729.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanne L. F., Finkelstein R. A. Characterization and distribution of the hemagglutinins produced by Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):209–214. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.209-214.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Booth B. A., Boesman-Finkelstein M., Finkelstein R. A. Comparative study of Vibrio cholerae non-O1 protease and soluble hemagglutinin with those of Vibrio cholerae O1. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):451–454. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.451-454.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Abrams G. D., Freter R. Adhesive properties of Vibrio cholerae: adhesion to isolated rabbit brush border membranes and hemagglutinating activity. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):232–239. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.232-239.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabir S., Ali S. Characterization of surface properties of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1048–1058. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1048-1058.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J., Lockman H., Colwell R. R., Joseph S. W. Ecology, serology, and enterotoxin production of Vibrio cholerae in Chesapeake Bay. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jan;37(1):91–103. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.1.91-103.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaysner C. A., Abeyta C., Jr, Wekell M. M., DePaola A., Jr, Stott R. F., Leitch J. M. Incidence of Vibrio cholerae from estuaries of the United States West Coast. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jun;53(6):1344–1348. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.6.1344-1348.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCINTYRE O. R., FEELEY J. C., GREENOUGH W. B., 3rd, BENENSON A. S., HASSAN S. I., SAAD A. DIARRHEA CAUSED BY NON-CHOLERA VIBRIOS. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1965 May;14:412–418. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1965.14.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCardell B. A., Madden J. M., Shah D. B. Isolation and characterization of a cytolysin produced by Vibrio cholerae serogroup non-O1. Can J Microbiol. 1985 Aug;31(8):711–720. doi: 10.1139/m85-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Seidler R. J., Rollins D. M., Joseph S. W. Vibrio factors cause rapid fluid accumulation in suckling mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1083–1091. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1083-1091.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oishi K., Yokoshima S., Tomiyama T., Aida K. Exohemagglutinins: new products of vibrios. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jul;38(1):169–172. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.1.169-172.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathak S. P., Bhattacherjee J. W., Kalra N., Chandra S. Seasonal distribution of Aeromonas hydrophila in river water and isolation from river fish. J Appl Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;65(4):347–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1988.tb01901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos Y., Toranzo A. E., Barja J. L., Nieto T. P., Villa T. G. Virulence properties and enterotoxin production of Aeromonas strains isolated from fish. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3285–3293. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3285-3293.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva M. L., Scaletsky I. C., Reis M. H., Affonso M. H., Trabulsi L. R. Plasmid coding for drug resistance and production of heat-labile and heat-stable toxins harbored by an Escherichia coli strain of human origin. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):970–973. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.970-973.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tison D. L., Nishibuchi M., Seidler R. J., Siebeling R. J. Isolation of Non-O1 Vibrio cholerae Serovars from Oregon Coastal Environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Feb;51(2):444–445. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.2.444-445.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twedt R. M., Madden J. M., Hunt J. M., Francis D. W., Peeler J. T., Duran A. P., Hebert W. O., McCay S. G., Roderick C. N., Spite G. T. Characterization of Vibrio cholerae isolated from oysters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jun;41(6):1475–1478. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.6.1475-1478.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Ichinose Y., Nakasone N., Tanabe M., Nagahama M., Sakurai J., Iwanaga M. Identity of hemolysins produced by Vibrio cholerae non-O1 and V. cholerae O1, biotype El Tor. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):927–931. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.927-931.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Takeda Y., Miwatani T., Craig J. P. Evidence that a non-O1 Vibrio cholerae produces enterotoxin that is similar but not identical to cholera enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):896–901. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.896-901.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Kamano T., Uchimura M., Iwanaga M., Yokota T. Vibrio cholerae O1 adherence to villi and lymphoid follicle epithelium: in vitro model using formalin-treated human small intestine and correlation between adherence and cell-associated hemagglutinin levels. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3241–3250. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3241-3250.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



