Abstract
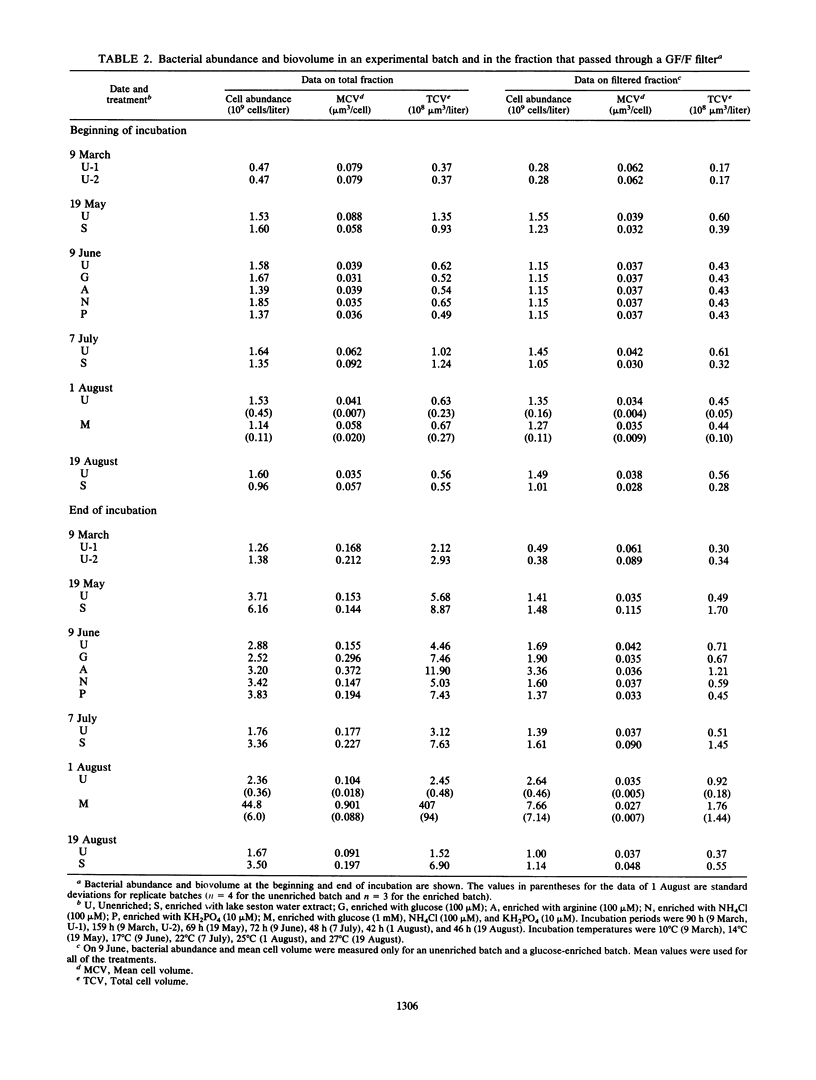
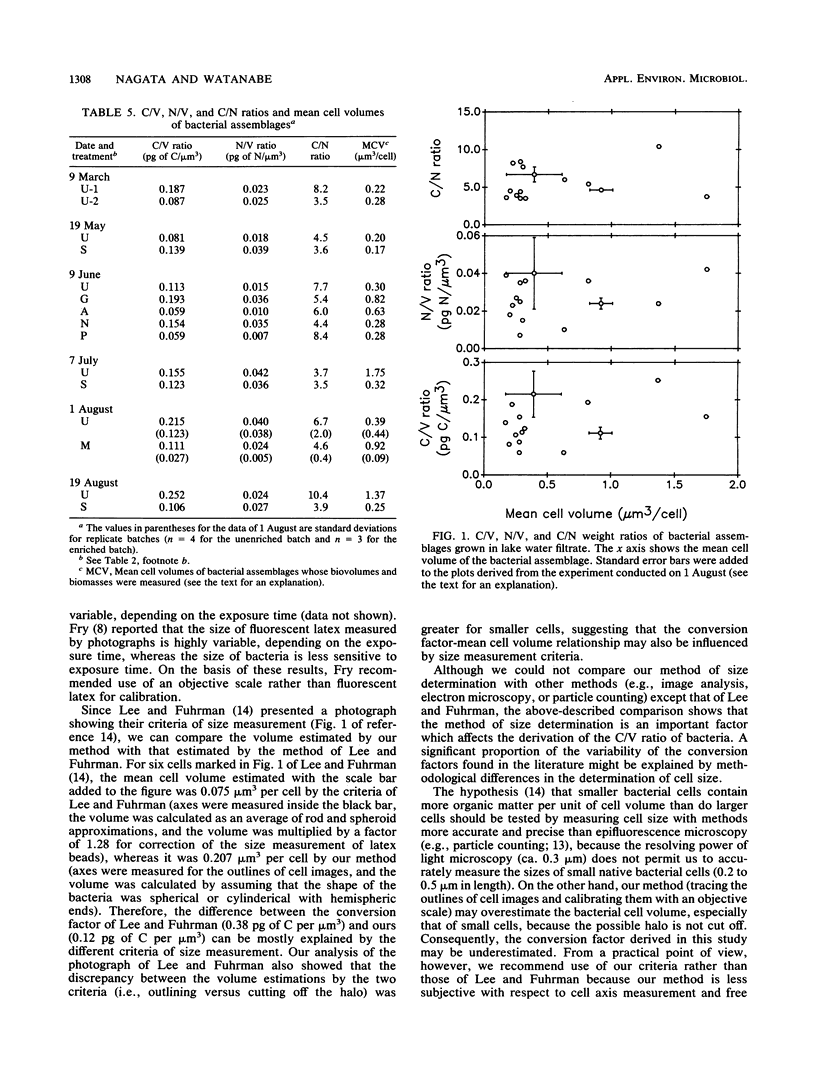
Carbon- and nitrogen-to-volume (C/V and N/V) ratios were determined for freshwater bacterial assemblages grown in lake water filtrate or in water enriched with nutrients (aqueous extract of lake seston, glucose, arginine, phosphate, or ammonium). Biovolume was measured by epifluorescence microphotography, and carbon and nitrogen biomasses were measured with a CHN analyzer. Despite large variations of nutritional conditions (i.e., the composition and concentration of the dissolved organic carbon) and different mean cell sizes of the bacterial assemblage (0.17 to 1.8 μm3 per cell), the C/V, N/V, and carbon-to-nitrogen weight ratios varied little (C/V ratio, 0.14 pg of C per μm3 [standard deviation, 0.057; n = 15]; N/V ratio, 0.027 pg of N per μm3 [standard deviation; 0.011, n = 15]; carbon-to-nitrogen weight ratio, 5.6 [standard deviation, 2.2, n = 15]). An average C/V ratio of 0.12 pg of C per μm3 that was derived from natural and cultured bacterial assemblages is proposed as an appropriate conversion factor for estimation of the biomass of freshwater bacteria.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjørnsen P. K. Automatic determination of bacterioplankton biomass by image analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jun;51(6):1199–1204. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.6.1199-1204.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratbak G. Bacterial biovolume and biomass estimations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1488–1493. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1488-1493.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratbak G., Dundas I. Bacterial dry matter content and biomass estimations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):755–757. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.755-757.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagström A., Larsson U., Hörstedt P., Normark S. Frequency of dividing cells, a new approach to the determination of bacterial growth rates in aquatic environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 May;37(5):805–812. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.5.805-812.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbie J. E., Daley R. J., Jasper S. Use of nuclepore filters for counting bacteria by fluorescence microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1225–1228. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1225-1228.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogure K., Koike I. Particle counter determination of bacterial biomass in seawater. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Feb;53(2):274–277. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.2.274-277.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S., Fuhrman J. A. Relationships between Biovolume and Biomass of Naturally Derived Marine Bacterioplankton. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jun;53(6):1298–1303. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.6.1298-1303.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata T. Carbon and nitrogen content of natural planktonic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jul;52(1):28–32. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.1.28-32.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata T. Production rate of planktonic bacteria in the north basin of lake biwa, Japan. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Dec;53(12):2872–2882. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.12.2872-2882.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tranvik L. J., Höfle M. G. Bacterial growth in mixed cultures on dissolved organic carbon from humic and clear waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Mar;53(3):482–488. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.3.482-488.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. W., Novitsky T. J., Quinby H. L., Valois F. W. Determination of bacterial number and biomass in the marine environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):940–946. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.940-946.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


