Abstract
A fusion of DNA sequences encoding the SPO2 promoter, the alpha-amylase signal sequence from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, and the mature part of the alpha-galactosidase from Cyamopsis tetragonoloba (guar) was constructed on a Bacillus subtilis multicopy vector. Bacillus cells of the protease-deficient strain DB104 harboring this vector produced and secreted the plant enzyme alpha-galactosidase up to levels of 1,700 U/liter. A growth medium suppressing the residual proteolytic activity of strain DB104 was used to reach these levels in a fermentor. Purification of the secreted product followed by NH2-terminal amino acid sequencing showed that the alpha-amylase signal sequence had been processed correctly. The molecular mass of the product estimated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis was slightly lower than that of the plant purified enzyme, which is most likely due to glycosylation of the latter. The alpha-galactosidase product was active both on the artificial substrate para-nitrophenyl-alpha-D-galactopyranoside and on the galactomannan substrate, guar gum. The activity of this Bacillus sp.-produced enzyme was similar to that of the glycosylated enzyme purified from guar seeds, indicating that glycosylation has no essential function for enzyme activity.
Full text
PDF

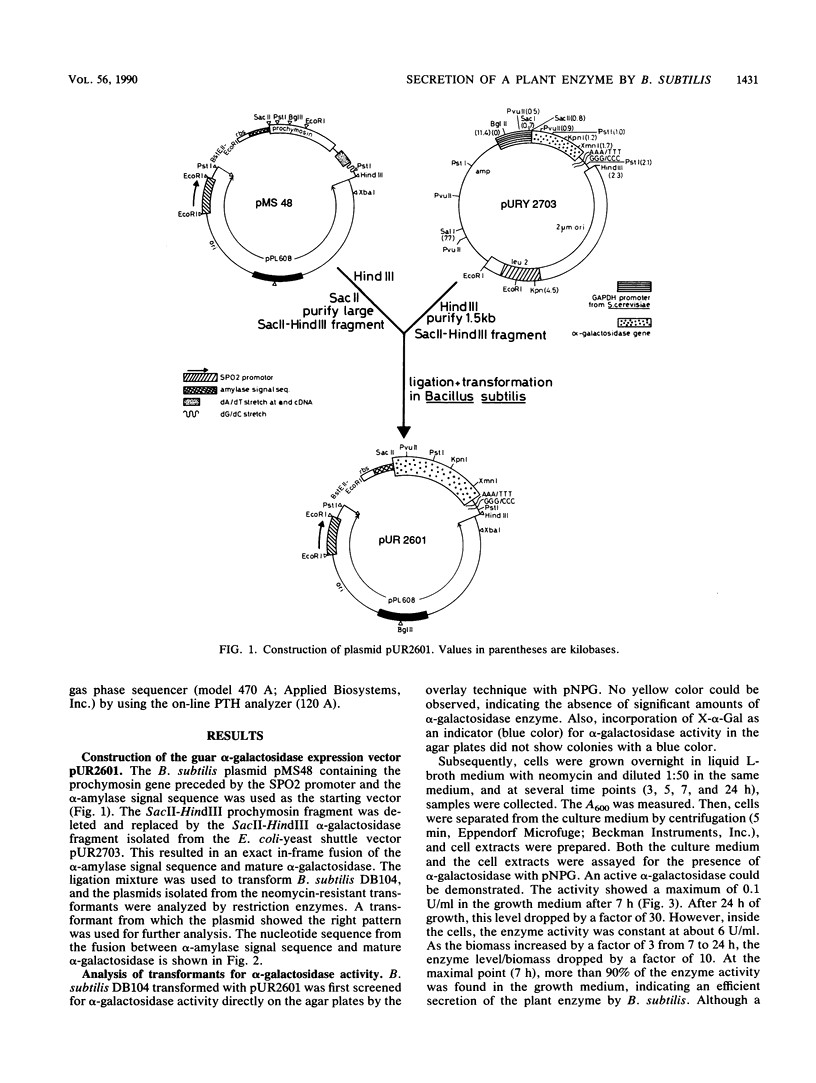
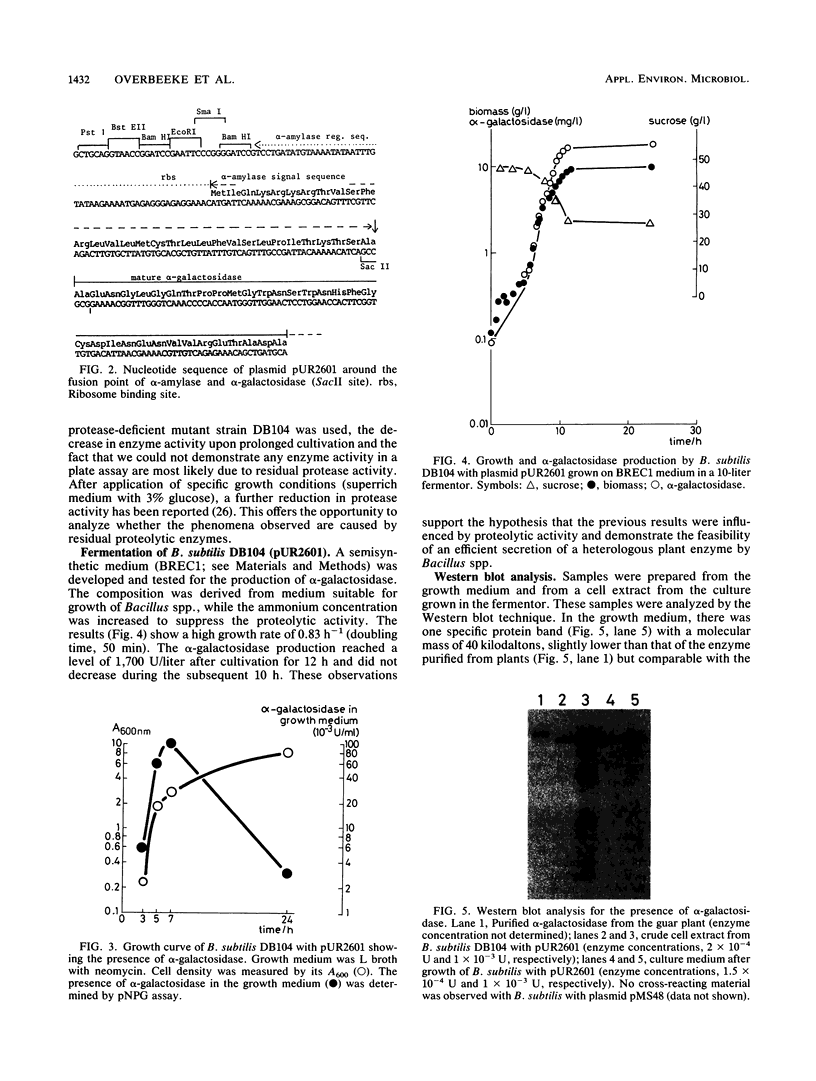


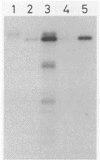
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckholz R. G., Adams B. G. Induction and genetics of two alpha-galactosidase activities in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(1):77–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00422770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S., Cohen S. N. High frequency transformation of Bacillus subtilis protoplasts by plasmid DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 5;168(1):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00267940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edens L., Heslinga L., Klok R., Ledeboer A. M., Maat J., Toonen M. Y., Visser C., Verrips C. T. Cloning of cDNA encoding the sweet-tasting plant protein thaumatin and its expression in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1982 Apr;18(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandi G., Del Bue M., Palla E., Mele A., Colletti E., Toma S. New plasmid expression vectors for Bacillus subtilis. Plasmid. 1986 Jul;16(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(86)90074-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura F., Doi R. H. Construction of a Bacillus subtilis double mutant deficient in extracellular alkaline and neutral proteases. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):442–444. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.442-444.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljeström P. L., Liljeström P. Nucleotide sequence of the melA gene, coding for alpha-galactosidase in Escherichia coli K-12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2213–2220. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljeström P. L. The nucleotide sequence of the yeast MEL1 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7257–7268. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmura K., Shiroza T., Nakamura K., Nakayama A., Yamane K., Yoda K., Yamasaki M., Tamura G. A Bacillus subtilis secretion vector system derived from the B. subtilis alpha-amylase promoter and signal sequence region, and secretion of Escherichia coli beta-lactamase by the vector system. J Biochem. 1984 Jan;95(1):87–93. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbeeke N., Fellinger A. J., Toonen M. Y., van Wassenaar D., Verrips C. T. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the alpha-galactosidase cDNA from Cyamopsis tetragonoloba (guar). Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Nov;13(5):541–550. doi: 10.1007/BF00027314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva I., Pettersson R. F., Kalkkinen N., Lehtovaara P., Sarvas M., Söderlund H., Takkinen K., Käriäinen L. Nucleotide sequence of the promoter and NH2-terminal signal peptide region of the alpha-amylase gene from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Gene. 1981 Oct;15(1):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarvas M. Protein secretion in bacilli. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;125:103–125. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71251-7_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders C. W., Schmidt B. J., Mallonee R. L., Guyer M. S. Secretion of human serum albumin from Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):2917–2925. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.2917-2925.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Duvall E. J., Lovett P. S. Cloning restriction fragments that promote expression of a gene in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):1162–1165. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.1162-1165.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. L., Kawamura F., Doi R. H. Use of the Bacillus subtilis subtilisin signal peptide for efficient secretion of TEM beta-lactamase during growth. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):1005–1009. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.1005-1009.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff M., Rodbard D., Chrambach A. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate-containing buffers using multiphasic buffer systems: properties of the stack, valid Rf- measurement, and optimized procedure. Anal Biochem. 1977 Apr;78(2):459–482. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura K., Toibana A., Kikuchi K., Kobayashi M., Hayakawa T., Nakahama K., Kikuchi M., Ikehara M. Differences between Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Bacillus subtilis in secretion of human lysozyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jun 15;145(2):712–718. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]