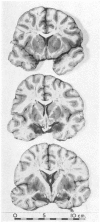
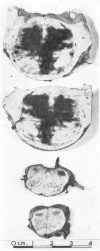
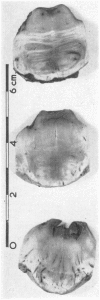
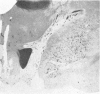
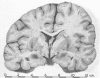
Full text
PDF
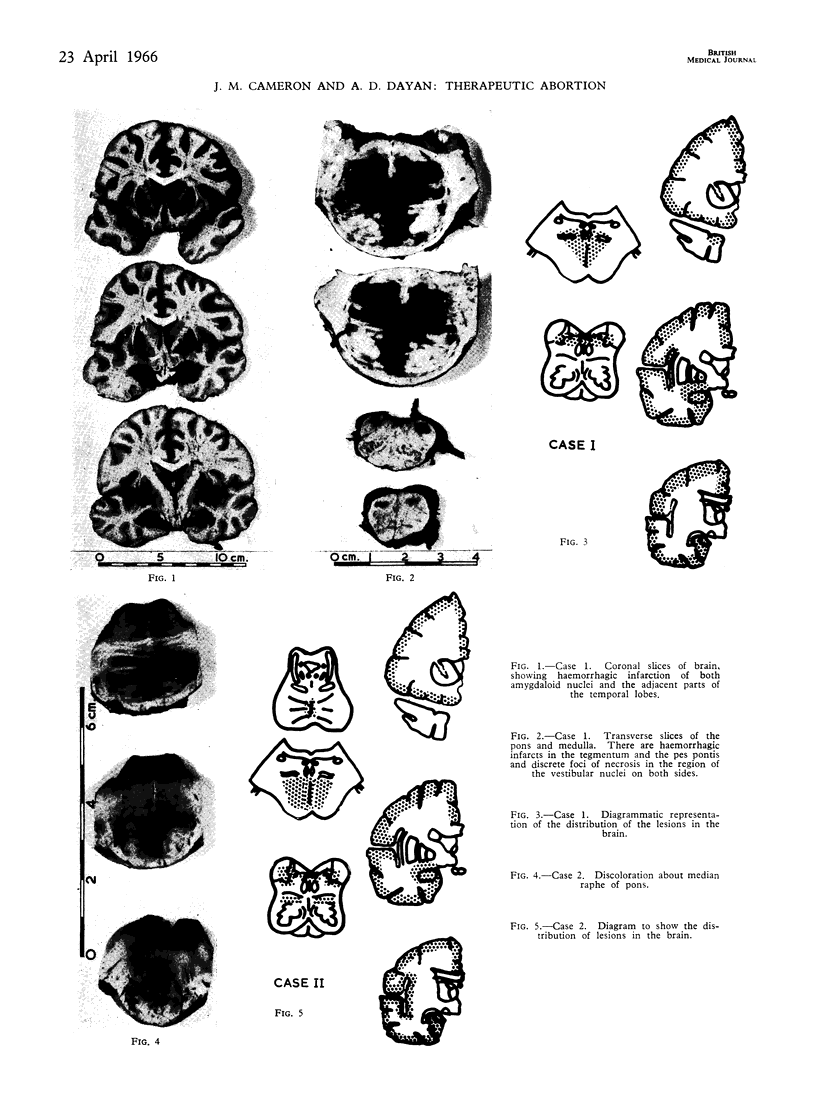
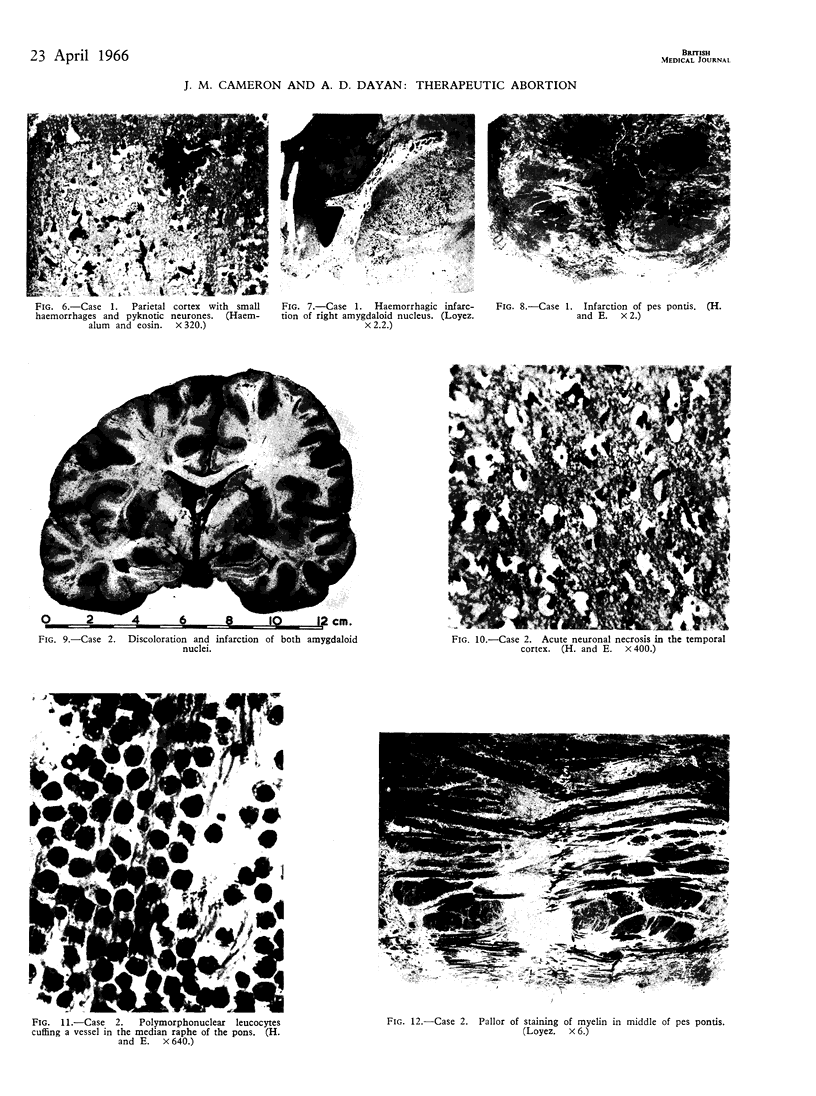



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CROME L. Encephalopathy following infantile gastro-enteritis. Arch Dis Child. 1952 Oct;27(135):468–472. doi: 10.1136/adc.27.135.468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINBERG L., KILEY J., LUTTRELL C. N. Mass accidental salt poisoning in infancy. A study of a hospital disaster. JAMA. 1963 Apr 20;184:187–190. doi: 10.1001/jama.1963.03700160063009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINBERG L. Pathogenesis of lesions in the nervous system in hypernatremic states. I. Clinical ovservations of infants. Pediatrics. 1959 Jan;23(1 Pt 1):40–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDENBERG R. Compression of brain arteries as pathogenetic factor for tissue necroses and their areas of predilection. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1955 Jul;14(3):223–243. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195507000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUDWIG J. [Hypernatremic hemorrhagic encephalopathy in adult]. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1963 May 11;93:705–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUTTRELL C. N., FINBERG L., DRAWDY L. P. Hemorrhagic encephalopathy induced by hypernatremia. II. Experimental observations on hyperosmolarity in cats. Arch Neurol. 1959 Aug;1:153–160. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1959.03840020027005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- METRAUX H. R., BINSWANGER U. DER HYPERNATRIAEMISCHE HYPERVOLAEMISCHE GEHIRNSCHADEN. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1963 Nov 2;93:1563–1565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLL F. C., SKINNER A. L. Hypernatremia accompanying infant diarrhea. AMA J Dis Child. 1956 Dec;92(6):562–575. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1956.02060030556004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSOMOFF H. L. Distribution of intracranial contents after hypertonic urea. J Neurosurg. 1962 Oct;19:859–864. doi: 10.3171/jns.1962.19.10.0859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSH B. F., Jr, FINBERG L., DAVIGLUS G. F., CHEUNG C. S. Pathologic lesions in experimental hypernatremia induced by extracorporeal dialysis. Surgery. 1961 Aug;50:359–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMALL J. M., WOOLF A. L. Fatal damage to the brain by epileptic convulsions after a trivial injury to the head. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1957 Nov;20(4):293–301. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.20.4.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUBBS J., PENNYBACKER J. Reduction of intracranial pressure with hypertonic urea. Lancet. 1960 May 21;1(7134):1094–1097. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)90983-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARD D. J. Fatal hypernatremia after a saline emetic. Br Med J. 1963 Aug 17;2(5354):432–432. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5354.432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD C., BOOTH R. T., PINKERTON J. H. Induction of labour by intra-amniotic injection of hypertonic glucose solution. Br Med J. 1962 Sep 15;2(5306):706–709. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5306.706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagatsuma T. Intra-amniotic injection of saline for therapeutic abortion. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1965 Nov 1;93(5):743–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]