Abstract
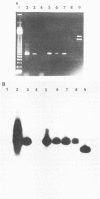
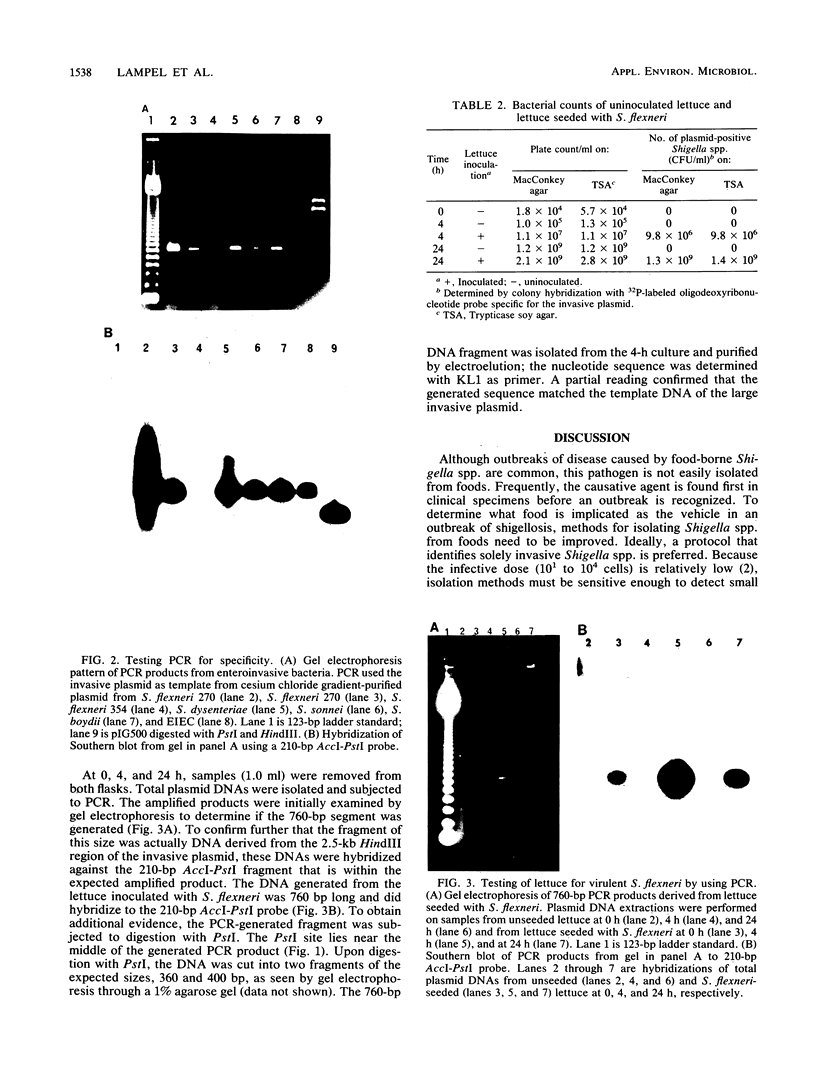
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was used to amplify a 760-base-pair (bp) fragment with the 220-kbp invasive plasmids of enteroinvasive Escherichia coli, Shigella flexneri, Shigella dysenteriae, Shigella boydii, and Shigella sonnei as templates. This PCR product was easily detected by agarose gel electrophoresis. A 210-bp AccI-PstI fragment lying within the amplified region was used as a probe in Southern hybridization blots and showed that the PCR-generated product was derived from the invasive plasmid. The application of PCR as a rapid method to detect enteroinvasive bacteria in foods was tested by inoculating lettuce with 10(4) S. flexneri cells per g in shigella broth base. Plasmid DNA was isolated from cultures of inoculated and uninoculated lettuce in broth after 0, 4, and 24 h of incubation. With the PCR, the 760-bp fragment was generated only from lettuce inoculated with S. flexneri, as shown by gel electrophoresis and confirmed both by Southern blotting and by nucleotide sequencing of the amplified region. Because the isolation of plasmid DNA, the performance of PCR, and gel electrophoresis all can be completed in 6 to 7 h, invasive enteric bacteria can be detected in less than 1 day.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chosa H., Makino S., Sasakawa C., Okada N., Yamada M., Komatsu K., Suk J. S., Yoshikawa M. Loss of virulence in Shigella strains preserved in culture collections due to molecular alteration of the invasion plasmid. Microb Pathog. 1989 May;6(5):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90075-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. Carolyne Davis: achieving in a new frontier. Interview by Michele Ward-Schaefer. Health Matrix. 1986 Spring;4(1):62–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis H., Taylor J. P., Perdue J. N., Stelma G. N., Jr, Humphreys J. M., Jr, Rowntree R., 3rd, Greene K. D. A shigellosis outbreak traced to commercially distributed shredded lettuce. Am J Epidemiol. 1988 Dec;128(6):1312–1321. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Jr, Takeuchi A., Washington O., Formal S. B. Shigellosis due to Shigella dysenteriae. 1. Relative importance of mucosal invasion versus toxin production in pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1972 Nov;126(5):523–530. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.5.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Sansonetti P. J., Schad P. A., Austin S., Formal S. B. Characterization of virulence plasmids and plasmid-associated outer membrane proteins in Shigella flexneri, Shigella sonnei, and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):340–350. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.340-350.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. E., Ferreira J. L., Payne W. L., Jones V. M. Probability of recovering pathogenic Escherichia coli from foods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1374–1378. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1374-1378.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. E., Payne W. L., Crouch R. J., Davis V. M., English L. L., Ferreira J. L., Gemski P., Jagow J. A., Moseley S. L., Noah C. W. Genetic methods for the detection of microbial pathogens. Identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by DNA colony hybridization: collaborative study. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1984 Jul-Aug;67(4):801–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. E., Wentz B. A., Payne W. L., Jagow J. A., Zon G. DNA colony hybridization method using synthetic oligonucleotides to detect enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: collaborative study. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1986 May-Jun;69(3):531–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maas R. An improved colony hybridization method with significantly increased sensitivity for detection of single genes. Plasmid. 1983 Nov;10(3):296–298. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive D. M., Atta A. I., Setti S. K. Detection of toxigenic Escherichia coli using biotin-labelled DNA probes following enzymatic amplification of the heat labile toxin gene. Mol Cell Probes. 1988 Mar;2(1):47–57. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(88)90043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive D. M. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli after polymerase chain reaction amplification with a thermostable DNA polymerase. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):261–265. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.261-265.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERENY B. Experimental shigella keratoconjunctivitis; a preliminary report. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1955;2(3):293–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Involvement of a plasmid in the invasive ability of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):852–860. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.852-860.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Shigella sonnei plasmids: evidence that a large plasmid is necessary for virulence. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):75–83. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.75-83.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollison S. B., Johnson M. G. Sensitivity to bile salts of Shigella flexneri sublethally heat stressed in buffer or broth. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):337–341. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.337-341.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan M., Buysse J. M., Vandendries E., Kopecko D. J. Development and testing of invasion-associated DNA probes for detection of Shigella spp. and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Feb;26(2):261–266. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.2.261-266.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Nakamura A. Identification of Shigella sonnei form I plasmid genes necessary for cell invasion and their conservation among Shigella species and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):352–358. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.352-358.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. K., Morris J. G., Jr, Small P. L., Sethabutr O., Toledo M. R., Trabulsi L., Kaper J. B. Comparison of DNA probes and the Sereny test for identification of invasive Shigella and Escherichia coli strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Sep;24(3):498–500. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.3.498-500.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]