Abstract
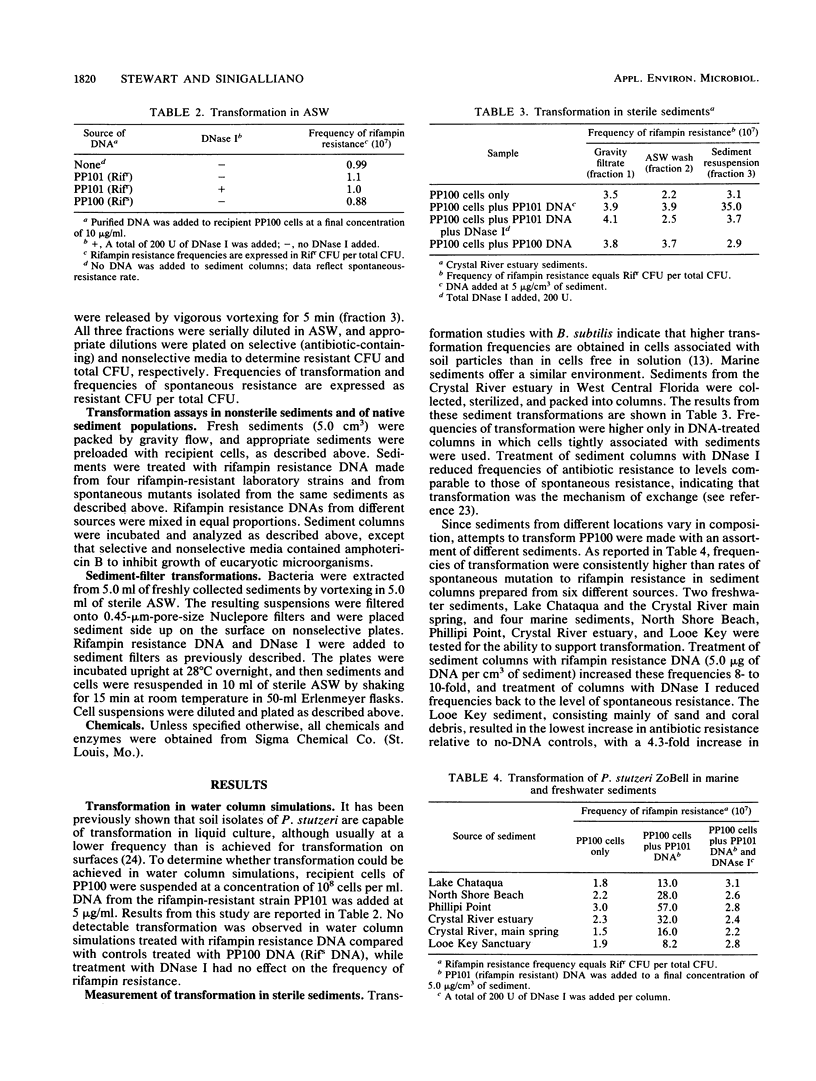
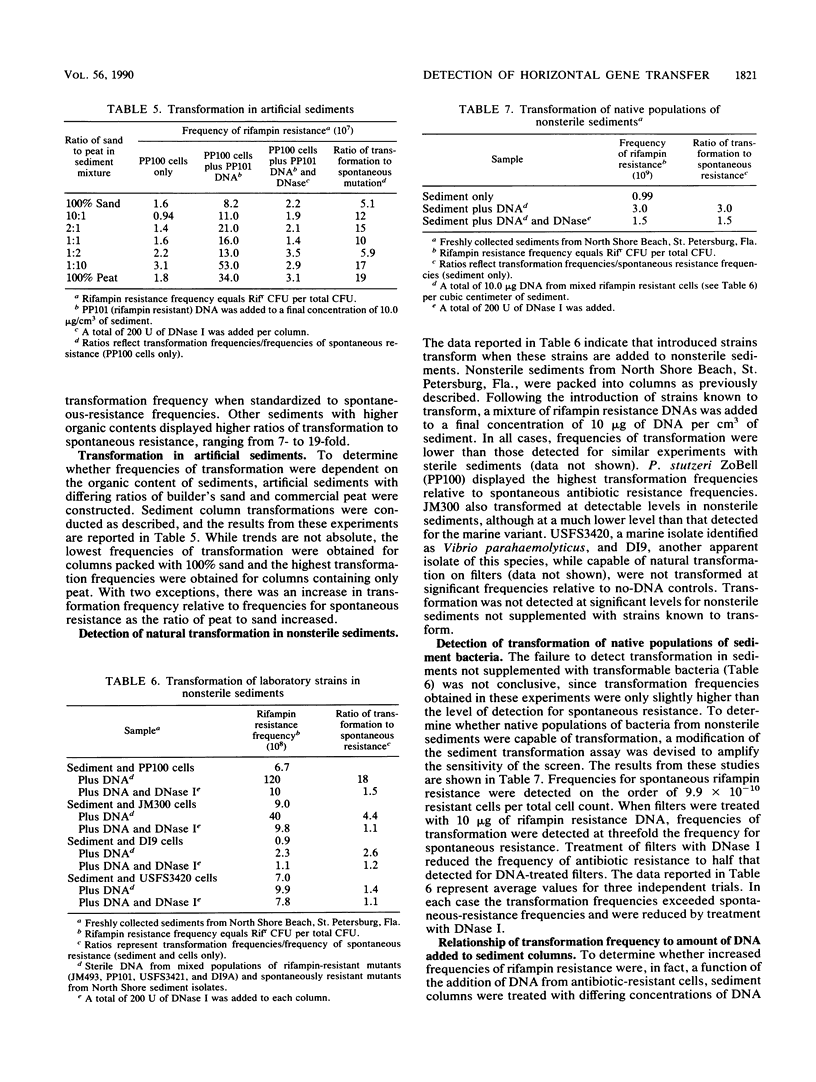
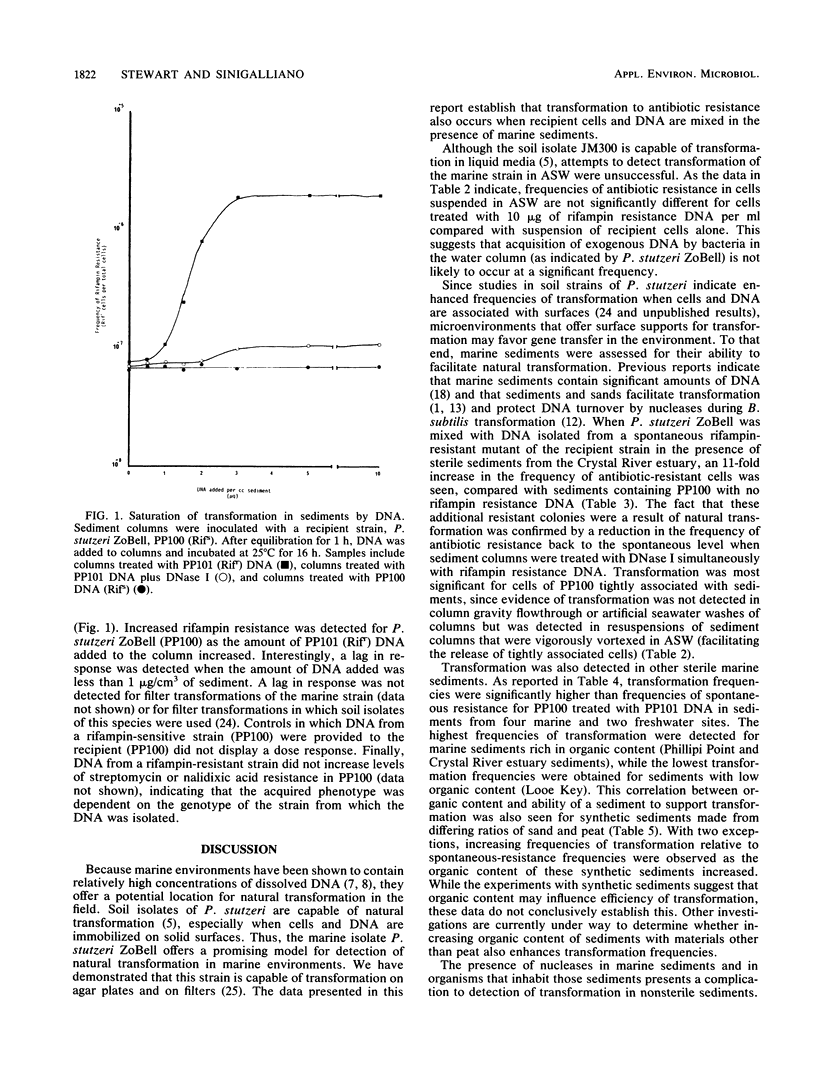
Both naturally occurring marine sediments and artificial sediments were used as supports for natural transformation of marine bacteria. While transformation of Pseudomonas stutzeri ZoBell suspended in artificial seawater was not detected when recipient cells and rifampin resistance DNA were loaded onto sterile sediment columns, transformation could be detected at frequencies 4 to 20 times that of spontaneous resistance when recipient cells and rifampin resistance DNA were loaded onto sterile sediment columns. Treatment of these columns with DNase I reduced transformation frequencies to levels comparable to those of spontaneous-resistance frequencies. Sediments with higher organic contents supported higher frequencies of transformation than did those with lower amounts of organic matter. Transformation was also detected when recipient cells and DNA were loaded on columns prepared from nonsterile sediments, although the frequencies of transformation were lower than when sterile sediments were used. Finally, nonsterilized sediments that were not supplemented with laboratory strains did not support detectable levels of transformation in sediment columns, but when these same sediments were transferred to filters and placed on complex media, transformation was detected at a frequency three times that for spontaneous resistance. This transformation frequency was partially reduced to levels near that for spontaneous resistance by the addition of DNase I to sediment filters. These results indicate that marine sediments facilitate the uptake and expression of exogenous DNA by transformable marine bacteria and that sediments are a more likely niche for natural transformation than the water column in the marine environment.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aardema B. W., Lorenz M. G., Krumbein W. E. Protection of sediment-adsorbed transforming DNA against enzymatic inactivation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Aug;46(2):417–420. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.2.417-420.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bale M. J., Fry J. C., Day M. J. Plasmid transfer between strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on membrane filters attached to river stones. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Nov;133(11):3099–3107. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-11-3099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bale M. J., Fry J. C., Day M. J. Transfer and occurrence of large mercury resistance plasmids in river epilithon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Apr;54(4):972–978. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.4.972-978.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson C. A., Pierson L. S., Rosen J. J., Ingraham J. L. Pseudomonas stutzeri and related species undergo natural transformation. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):93–99. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.93-99.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughter J. P., Stewart G. J. Genetic exchange in the environment. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1989;55(1):15–22. doi: 10.1007/BF02309615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deflaun M. F., Paul J. H., Davis D. Simplified method for dissolved DNA determination in aquatic environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):654–659. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.654-659.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gealt M. A., Chai M. D., Alpert K. B., Boyer J. C. Transfer of plasmids pBR322 and pBR325 in wastewater from laboratory strains of Escherichia coli to bacteria indigenous to the waste disposal system. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Apr;49(4):836–841. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.4.836-841.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz M. G., Wackernagel W. Adsorption of DNA to sand and variable degradation rates of adsorbed DNA. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Dec;53(12):2948–2952. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.12.2948-2952.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini P., Fertels S., Nave D., Gealt M. A. Mobilization of plasmid pHSV106 from Escherichia coli HB101 in a laboratory-scale waste treatment facility. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Apr;53(4):665–671. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.4.665-671.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara T., Frunzke K., Zumft W. G. Modulation by copper of the products of nitrite respiration in Pseudomonas perfectomarinus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):816–823. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.816-823.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson P., Gealt M. A. Isolation of indigenous wastewater bacterial strains capable of mobilizing plasmid pBR325. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):904–909. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.904-909.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Morchoe S. B., Ogunseitan O., Sayler G. S., Miller R. V. Conjugal transfer of R68.45 and FP5 between Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains in a freshwater environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Aug;54(8):1923–1929. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.8.1923-1929.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J. H., Myers B. Fluorometric determination of DNA in aquatic microorganisms by use of hoechst 33258. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1393–1399. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1393-1399.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saye D. J., Ogunseitan O., Sayler G. S., Miller R. V. Potential for transduction of plasmids in a natural freshwater environment: effect of plasmid donor concentration and a natural microbial community on transduction in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):987–995. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.987-995.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Danner D. B., Deich R. A. Genetic transformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:41–68. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.000353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. J., Carlson C. A., Ingraham J. L. Evidence for an active role of donor cells in natural transformation of Pseudomonas stutzeri. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):30–35. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.30-35.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. J., Carlson C. A. The biology of natural transformation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:211–235. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.001235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeph L. R., Onaga M. A., Stotzky G. Transduction of Escherichia coli by bacteriophage P1 in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jul;54(7):1731–1737. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.7.1731-1737.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zobell C. E. The Effect of Solid Surfaces upon Bacterial Activity. J Bacteriol. 1943 Jul;46(1):39–56. doi: 10.1128/jb.46.1.39-56.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


