Abstract
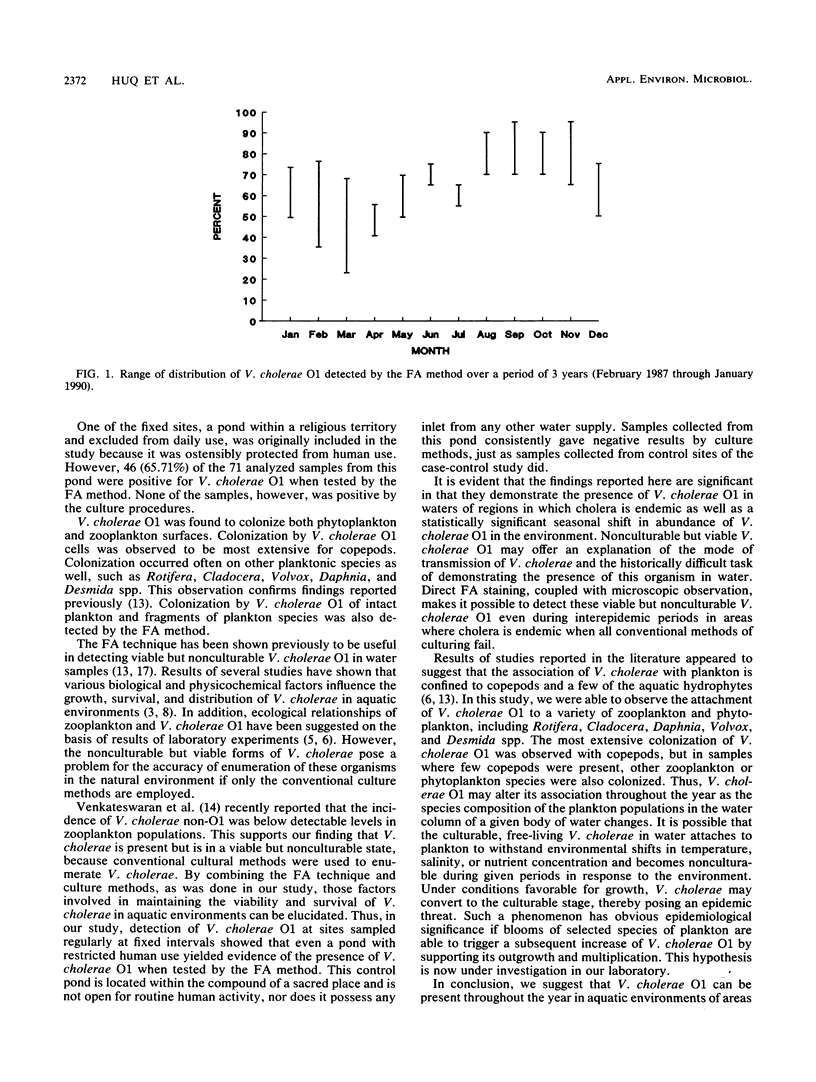
Vibrio cholerae O1 in plankton samples collected from ponds and rivers between February 1987 and January 1990 in Matlab, Bangladesh, was detected by the fluorescent-monoclonal antibody (FA) technique. Samples were collected at sites which were monitored fortnightly (fixed sites) as well as at sites that were part of a case-control study. FA results were compared with those obtained by conventional culture methods (CM). A total of 876 samples were collected; V. cholerae O1 was detected in 563 samples (64.27%) by the FA method and in 3 samples (0.34%) by CM. Of the fixed-site plankton samples, 439 (63.62%) were positive by FA and none were positive by CM. Of the 93 case sites sampled on the day after the occurrence of a case of cholera, 73 (78.49%) were positive for V. cholerae O1 by FA and 3 (3.2%) were positive by CM. In comparison, of the 93 first-day sample collections at control sites at the time a case of cholera occurred, only 51 (54.83%) were positive by FA and none were positive by CM. From the data, it is concluded that V. cholerae O1 is present throughout the year in the ponds and rivers of Bangladesh that were examined in this study and that V. cholerae can be detected by FA but not always by CM. The FA procedure was found to be very useful in detecting V. cholerae in plankton, with which it was associated and often occurred in large numbers in the nonculturable stage. Thus, studies investigating the significance of the role of environmental factors in the epidemiology of cholera can be performed effectively by using FA. Such studies are in progress.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brayton P. R., Tamplin M. L., Huq A., Colwell R. R. Enumeration of Vibrio cholerae O1 in Bangladesh waters by fluorescent-antibody direct viable count. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Dec;53(12):2862–2865. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.12.2862-2865.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colwell R. R., Seidler R. J., Kaper J., Joseph S. W., Garges S., Lockman H., Maneval D., Bradford H., Roberts N., Remmers E. Occurrence of Vibrio cholerae serotype O1 in Maryland and Louisiana estuaries. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):555–558. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.555-558.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feachem R., Miller C., Drasar B. Environmental aspects of cholera epidemiology. II. Occurrence and survival of Vibrio cholerae in the environment. Trop Dis Bull. 1981 Oct;78(10):865–880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass R. I., Becker S., Huq M. I., Stoll B. J., Khan M. U., Merson M. H., Lee J. V., Black R. E. Endemic cholera in rural Bangladesh, 1966-1980. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 Dec;116(6):959–970. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huq A., Small E. B., West P. A., Huq M. I., Rahman R., Colwell R. R. Ecological relationships between Vibrio cholerae and planktonic crustacean copepods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):275–283. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.275-283.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. J., Drasar B. S., Feachem R. G. Response of toxigenic Vibrio cholerae 01 to physico-chemical stresses in aquatic environments. J Hyg (Lond) 1984 Dec;93(3):475–495. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400065074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roszak D. B., Colwell R. R. Survival strategies of bacteria in the natural environment. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Sep;51(3):365–379. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.3.365-379.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton F. L., Attwell R. W., Jangi M. S., Colwell R. R. Influence of salinity and organic nutrient concentration on survival and growth of Vibrio cholerae in aquatic microcosms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1080–1085. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1080-1085.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamplin M. L., Gauzens A. L., Huq A., Sack D. A., Colwell R. R. Attachment of Vibrio cholerae serogroup O1 to zooplankton and phytoplankton of Bangladesh waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1977–1980. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1977-1980.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkateswaran K., Takai T., Navarro I. M., Nakano H., Hashimoto H., Siebeling R. J. Ecology of Vibrio cholerae non-O1 and Salmonella spp. and role of zooplankton in their seasonal distribution in Fukuyama coastal waters, Japan. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1591–1598. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1591-1598.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


