Abstract
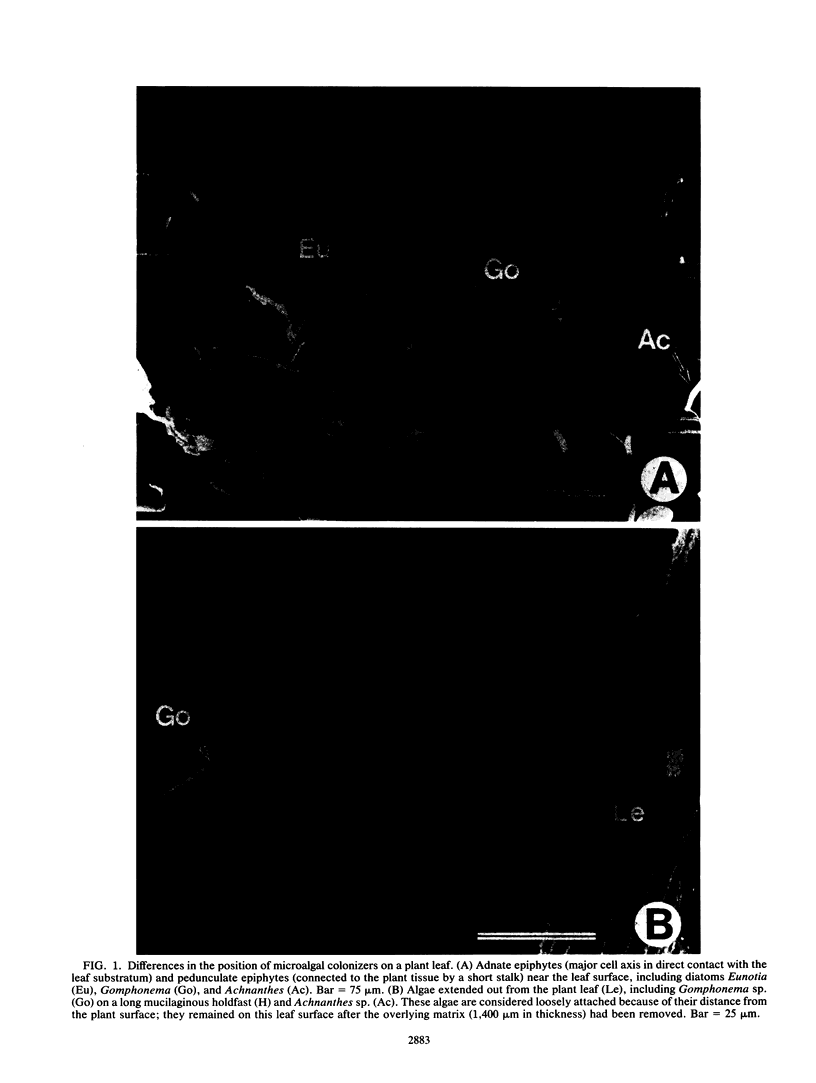
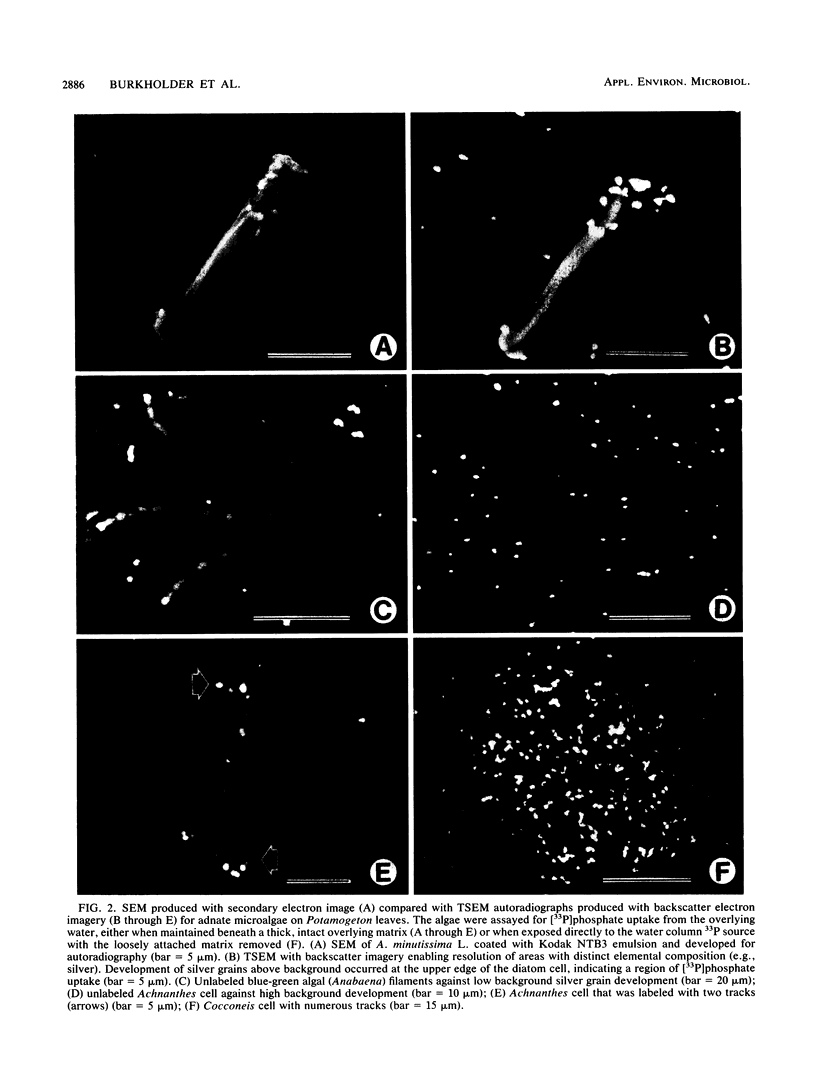
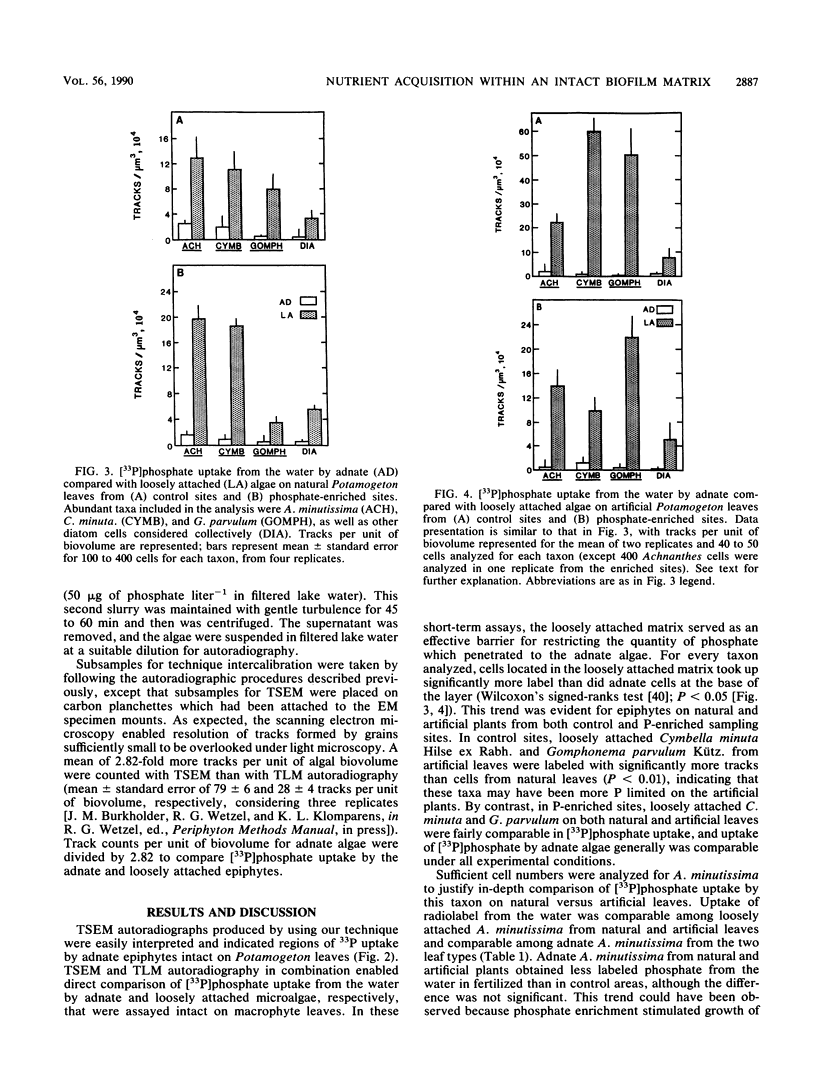
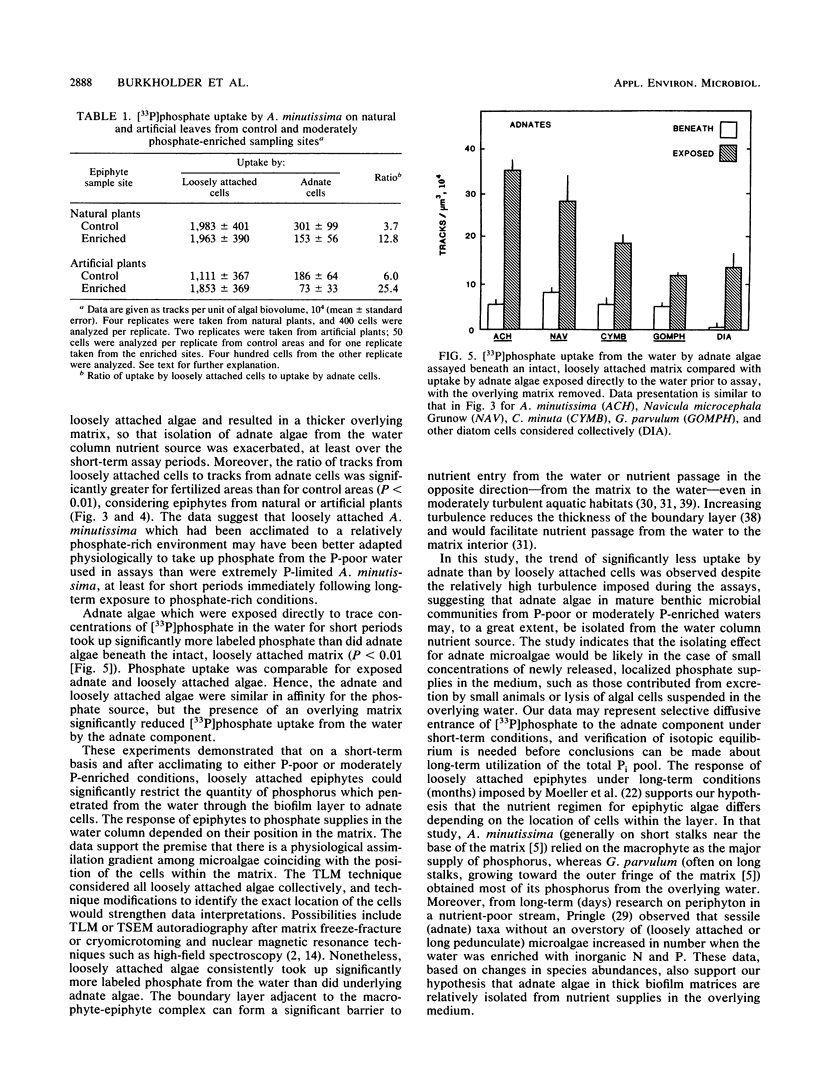
We report a direct comparison of phosphate uptake by adnate and loosely attached microalgae in an intact biofilm matrix, with resolution at the level of individual cells. Track scanning electron microscope autoradiography enabled assay of [33P]phosphate uptake from the overlying water by adnate algae left undisturbed on mature leaves of the macrophyte Potamogeton illinoensis or on artificial plant mimics. The epiphyte communities developed in either phosphate-poor or moderately phosphate-enriched water, and they were assayed on both natural and artificial plants. All adnate taxa examined from both natural and artificial plants in both habitats took up significantly less radiolabel when assayed beneath the overlying matrix than when they were exposed to the water upon removal of the overstory material. Track scanning electron microscope autoradiography and track light microscope autoradiography were intercalibrated to enable comparison of [33P]phosphate uptake by adnate and loosely attached components of the epiphyte matrix. Loosely attached cells on substrata from both habitats took up significantly more radiolabel than did underlying adnate cells, indicating that access to phosphate supplies from the water depended on the position of microbial cells in the matrix. In this short-term assay, the adnate microalgae were relatively isolated from the water column nutrient source.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Costerton J. W., Geesey G. G., Cheng K. J. How bacteria stick. Sci Am. 1978 Jan;238(1):86–95. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0178-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darley P. J., Macfarlane B. J. Scanning electron microscope autoradiography. A technique for the location and study of microscopic beta-active particles. Health Phys. 1977 Apr;32(4):259–270. doi: 10.1097/00004032-197704000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karl D. M. Cellular nucleotide measurements and applications in microbial ecology. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Dec;44(4):739–796. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.4.739-796.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul D., Gröbe A., Zimmer F. Autoradiography in the scanning electron microscope. Nature. 1970 Aug 1;227(5257):488–489. doi: 10.1038/227488a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]