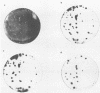
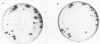Abstract
Specific sequences of 23S rRNA of Lactococcus lactis, Enterococcus faecalis, Enteroccus faecium, and Enterococcus malodoratus/Enterococcus avium were identified, and complementary oligonucleotide probes were synthesized. The specificity of the probes was evaluated by dot blot and colony hybridizations. The probes can be used for the specific detection and identification of colonies of the corresponding species in mixed cultures.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buluwela L., Forster A., Boehm T., Rabbitts T. H. A rapid procedure for colony screening using nylon filters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):452–452. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta A. R., Wentz B. A., Hill W. E. Detection of hemolytic Listeria monocytogenes by using DNA colony hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Sep;53(9):2256–2259. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.9.2256-2259.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Embley T. M., Smida J., Stackebrandt E. Reverse transcriptase sequencing of 16S ribosomal RNA from Faenia rectivirgula, Pseudonocardia thermophila and Saccharopolyspora hirsuta, three wall type IV actinomycetes which lack mycolic acids. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Apr;134(4):961–966. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-4-961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Festl H., Ludwig W., Schleifer K. H. DNA hybridization probe for the Pseudomonas fluorescens group. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Nov;52(5):1190–1194. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.5.1190-1194.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannoni S. J., DeLong E. F., Olsen G. J., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic group-specific oligodeoxynucleotide probes for identification of single microbial cells. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):720–726. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.720-726.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höpfl P., Ludwig W., Schleifer K. H., Larsen N. The 23S ribosomal RNA higher-order structure of Pseudomonas cepacia and other prokaryotes. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Nov 6;185(2):355–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15123.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews J. A., Kricka L. J. Analytical strategies for the use of DNA probes. Anal Biochem. 1988 Feb 15;169(1):1–25. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90251-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regensburger A., Ludwig W., Schleifer K. H. DNA probes with different specificities from a cloned 23S rRNA gene of Micrococcus luteus. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 May;134(5):1197–1204. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-5-1197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi B. E., Sandine W. E. Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.807-813.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]