Abstract
A glycoside hydrolase characterized by β-fucosidase (EC 3.2.1.38) and β-glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.21) activities was purified from the culture medium of the anaerobic ruminal phycomycete Neocallimastix frontalis grown on 0.5% Avicel. The enzyme had a molecular mass of 120 kilodaltons and a pI of 3.85. Optimal activity against p-nitrophenyl-β-d-fucoside and p-nitrophenyl-β-D-glucoside occurred at pH 6.0 and 50°C. The β-fucosidase and β-glucosidase activities were stable from pH 6.0 to pH 7.8 and up to 40°C. They were both inhibited by gluconolactone, sodium dodecyl sulfate, p-chloromercuribenzoate, and Hg2+ cation. The enzyme had Kms of 0.26 mg/ml for p-nitrophenyl-β-d-fucoside and 0.08 mg/ml for p-nitrophenyl-β-d-glucoside. The purified protein also had low β-galactosidase activity.
Full text
PDF
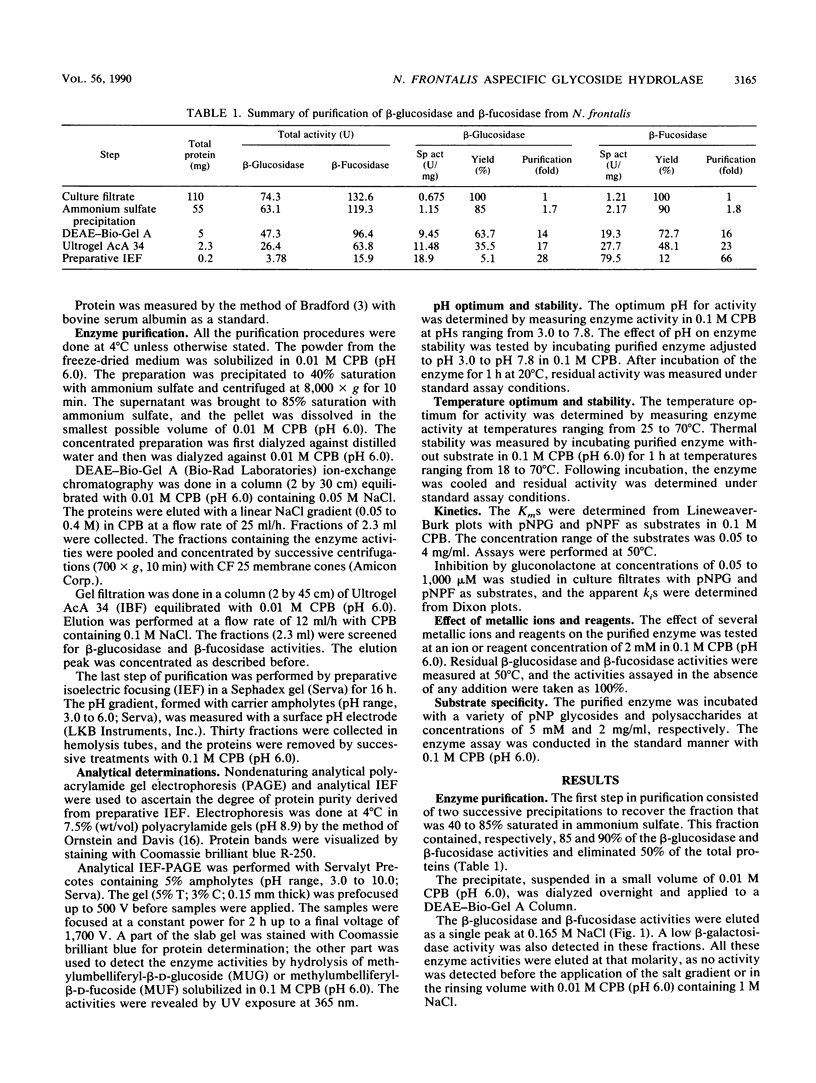
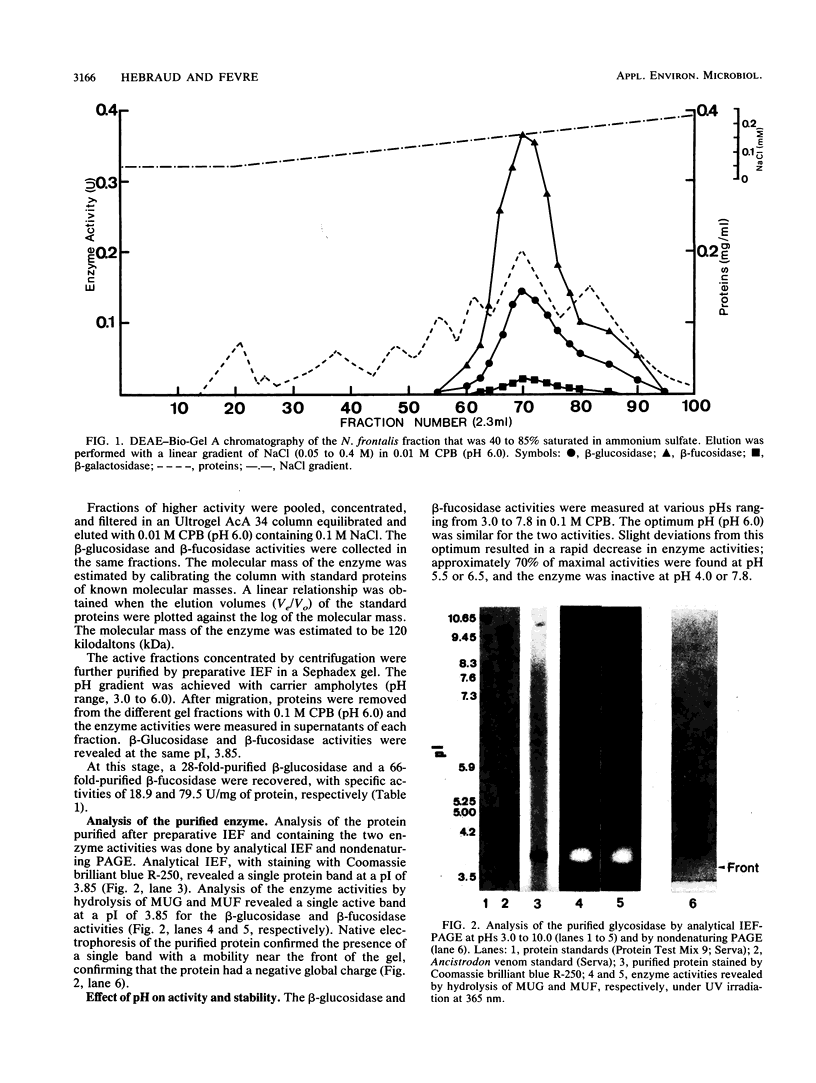



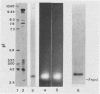
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akin D. E., Benner R. Degradation of polysaccharides and lignin by ruminal bacteria and fungi. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 May;54(5):1117–1125. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.5.1117-1125.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beldman G., Searle-Van Leeuwen M. F., Rombouts F. M., Voragen F. G. The cellulase of Trichoderma viride. Purification, characterization and comparison of all detectable endoglucanases, exoglucanases and beta-glucosidases. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jan 15;146(2):301–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08653.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirico W. J., Brown R. D., Jr Purification and characterization of a beta-glucosidase from Trichoderma reesei. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jun 1;165(2):333–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon G. L., Phillips M. W. Degradation and utilization of cellulose and straw by three different anaerobic fungi from the ovine rumen. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jul;55(7):1703–1710. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.7.1703-1710.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. E., Theodorou M. K., Trinci A. P. Cellulases and xylanase of an anaerobic rumen fungus grown on wheat straw, wheat straw holocellulose, cellulose, and xylan. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jun;53(6):1216–1223. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.6.1216-1223.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountfort D. O., Asher R. A. Production and regulation of cellulase by two strains of the rumen anaerobic fungus Neocallimastix frontalis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1314–1322. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1314-1322.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORNSTEIN L. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. I. BACKGROUND AND THEORY. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:321–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmiya K., Shirai M., Kurachi Y., Shimizu S. Isolation and properties of beta-glucosidase from Ruminococcus albus. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):432–434. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.432-434.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce P. D., Bauchop T. Glycosidases of the rumen anaerobic fungus Neocallimastix frontalis grown on cellulosic substrates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1265–1269. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1265-1269.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodionova N. A., Tavobilov I. M., Martinovich L. I., Buachidze T. S., Kvesitadze G. I., Bezborodov A. M. beta-Glucosidases from cellulolytic fungi Aspergillus terreus, Geotrichum candidum, and Trichoderma longibrachiatum as typical glycosidases. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 1987 Jun;9(3):239–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1470-8744.1987.tb00475.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. G., Orpin C. G. Glycoside hydrolase enzymes present in the zoospore and vegetative growth stages of the rumen fungi Neocallimastix patriciarum, Piromonas communis, and an unidentified isolate, grown on a range of carbohydrates. Can J Microbiol. 1987 May;33(5):427–434. doi: 10.1139/m87-072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. G., Orpin C. G. Polysaccharide-degrading enzymes formed by three species of anaerobic rumen fungi grown on a range of carbohydrate substrates. Can J Microbiol. 1987 May;33(5):418–426. doi: 10.1139/m87-071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]