Abstract
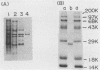
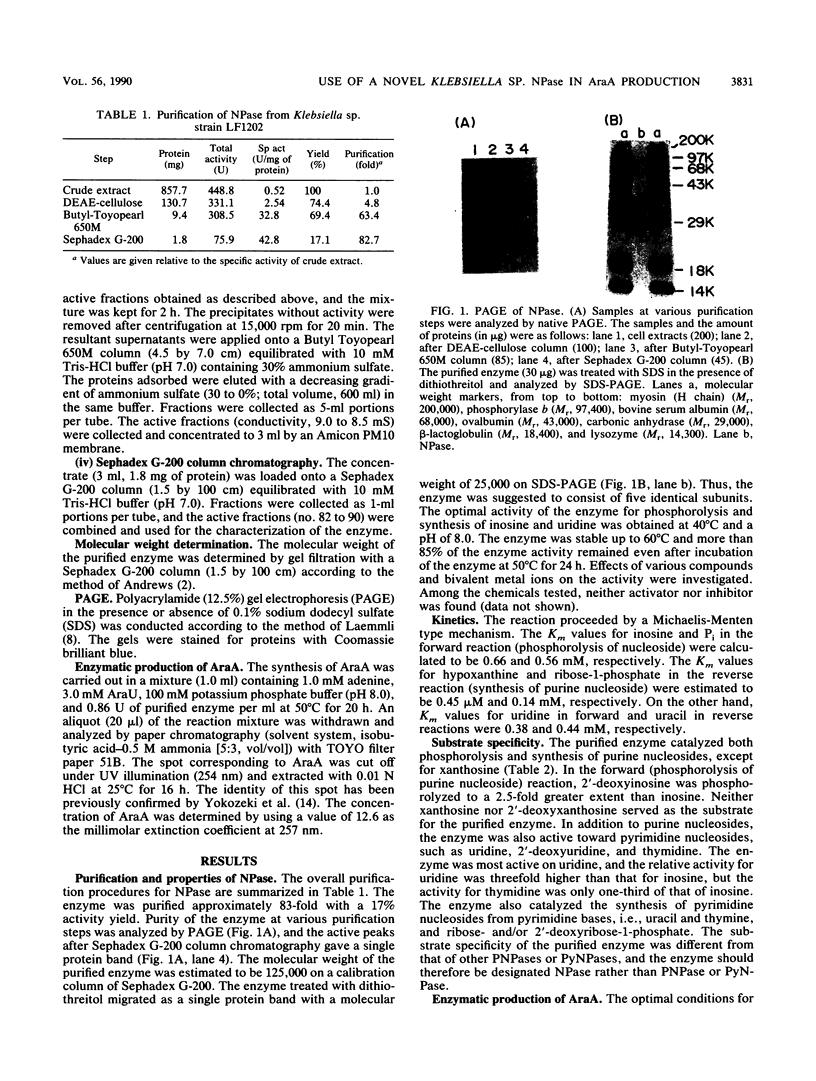
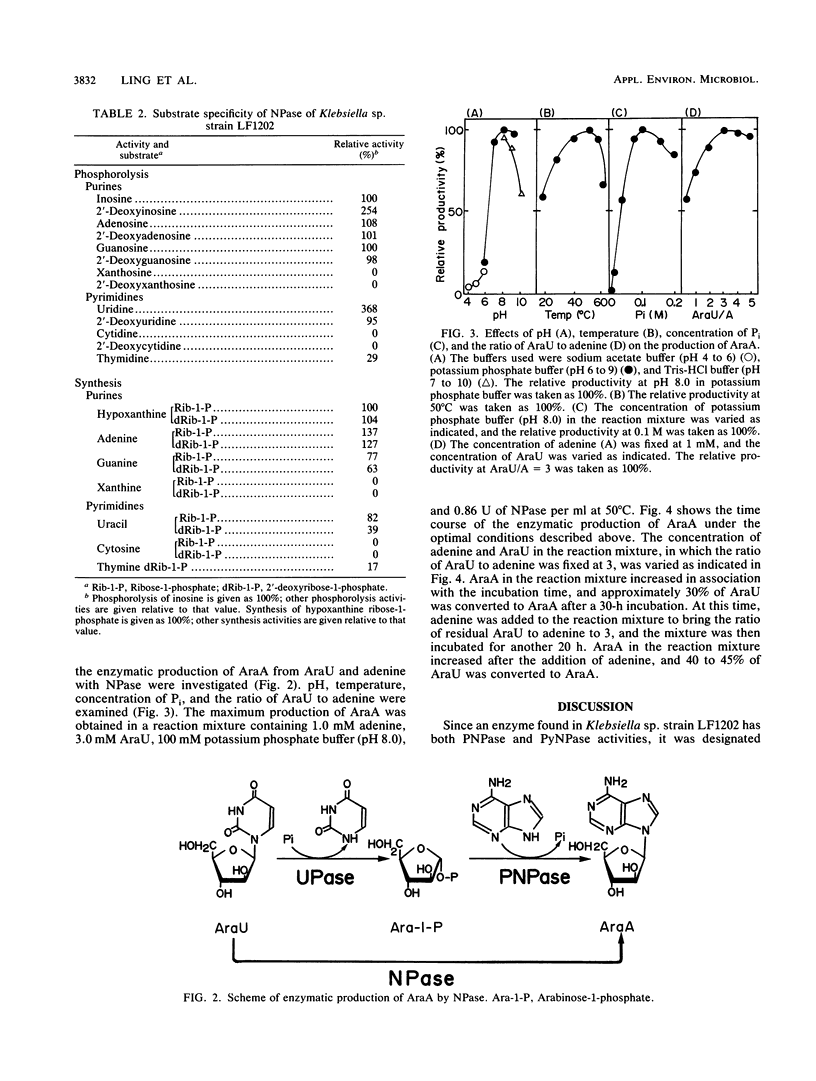
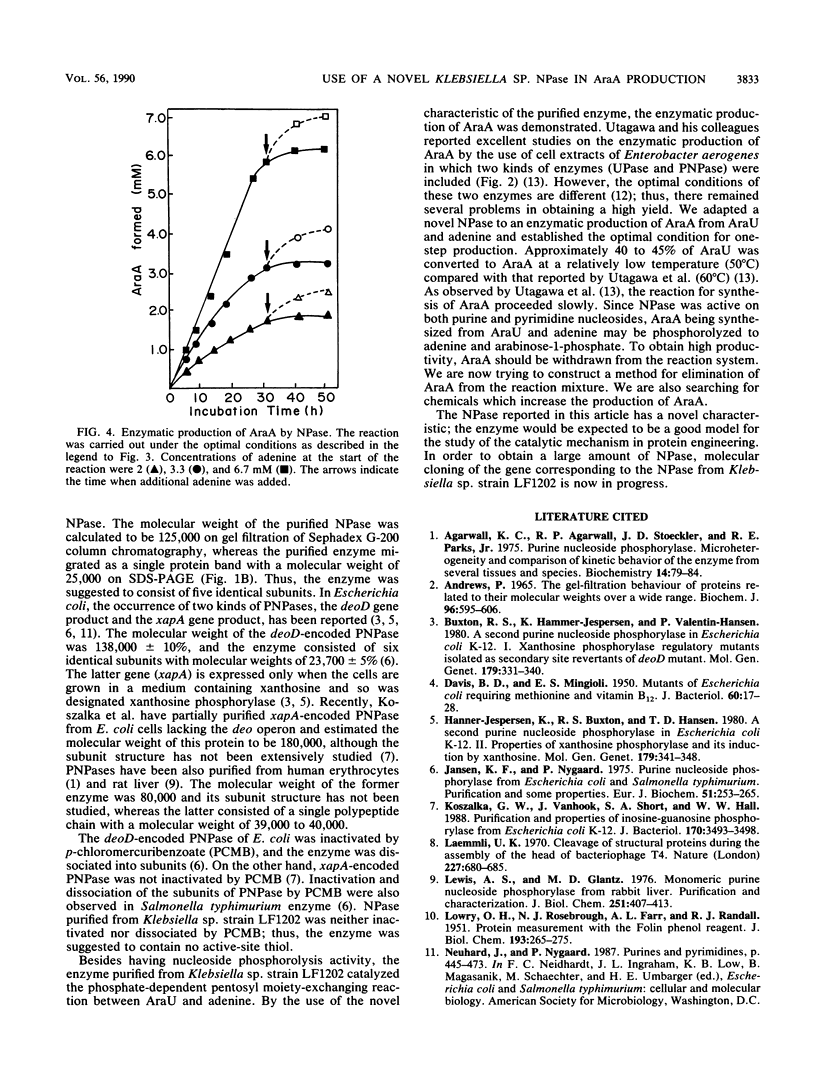
An adenosine-assimilating bacterium, Klebsiella sp. strain LF1202, inducibly formed a novel nucleoside phosphorylase which acted on both purine and pyrimidine nucleosides when the cells were cultured in medium containing adenosine as a sole source of carbon and nitrogen. The enzyme was purified (approximately 83-fold, with a 17% activity yield) to the homogeneous state by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The molecular weight of the purified enzyme was calculated to be 125,000 by gel filtration of Sephadex G-200 column chromatography, although the enzyme migrated as a single protein band with a molecular weight of 25,000 on sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; thus, it was thought to consist of five identical subunits. Besides purine nucleosides (adenosine, inosine, and guanosine), the purified enzyme also acted on pyrimidine nucleosides such as uridine, 2'-deoxyuridine, and thymidine. The purified enzyme catalyzed the synthesis of adenine arabinoside, a selective antiviral pharmaceutic agent, from uridine arabinoside and adenine.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal K. C., Agarwal R. P., Stoeckler J. D., Parks R. E., Jr Purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Microheterogeneity and comparison of kinetic behavior of the enzyme from several tissues and species. Biochemistry. 1975 Jan 14;14(1):79–84. doi: 10.1021/bi00672a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton R. S., Hammer-Jespersen K., Valentin-Hansen P. A second purine nucleoside phosphorylase in Escherichia coli K-12. I. Xanthosine phosphorylase regulatory mutants isolated as secondary-site revertants of a deoD mutant. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;179(2):331–340. doi: 10.1007/BF00425461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer-Jespersen K., Buxton R. S., Hansen T. D. A second purine nucleoside phosphorylase in Escherichia coli K-12. II. Properties of xanthosine phosphorylase and its induction by xanthosine. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;179(2):341–348. doi: 10.1007/BF00425462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen K. F., Nygaard P. Purine nucleoside phosphorylase from Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Purification and some properties. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Feb 3;51(1):253–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03925.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koszalka G. W., Vanhooke J., Short S. A., Hall W. W. Purification and properties of inosine-guanosine phosphorylase from Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3493–3498. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3493-3498.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. S., Glantz M. D. Monomeric purine nucleoside phosphorylase from rabbit liver. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):407–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]