Abstract
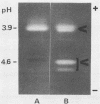
Pectinase production by Aspergillus flavus was determined by measuring clear zones formed around colonies stained with ruthenium red. Several isolates produced red zones instead of clear zones. Red zones were reproduced with pectinesterase and correlated with absence of specific polygalacturonases. Of 87 isolates tested, 15 produced red zones.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amonkar S. V., Nair K. K. Pathogenicity of Aspergillus flavus Link to Musca domestica nebulo Fabricius. J Invertebr Pathol. 1965 Dec;7(4):513–514. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(65)90130-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggon K. K., Viswanathan L., Venkitasubramanian T. A., Mukerji K. G. Aflatoxin production by some Indian strains of Aspergillus flavus Link ex Fries. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Nov;59(1):119–124. doi: 10.1099/00221287-59-1-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtomo T., Murakoshi S., Sugiyama J., Kurata H. Detection of aflatoxin B1 in silkworm larvae attacked by an Aspergillus flavus isolate from a sericultural farm. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Dec;30(6):1034–1035. doi: 10.1128/am.30.6.1034-1035.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]