Abstract
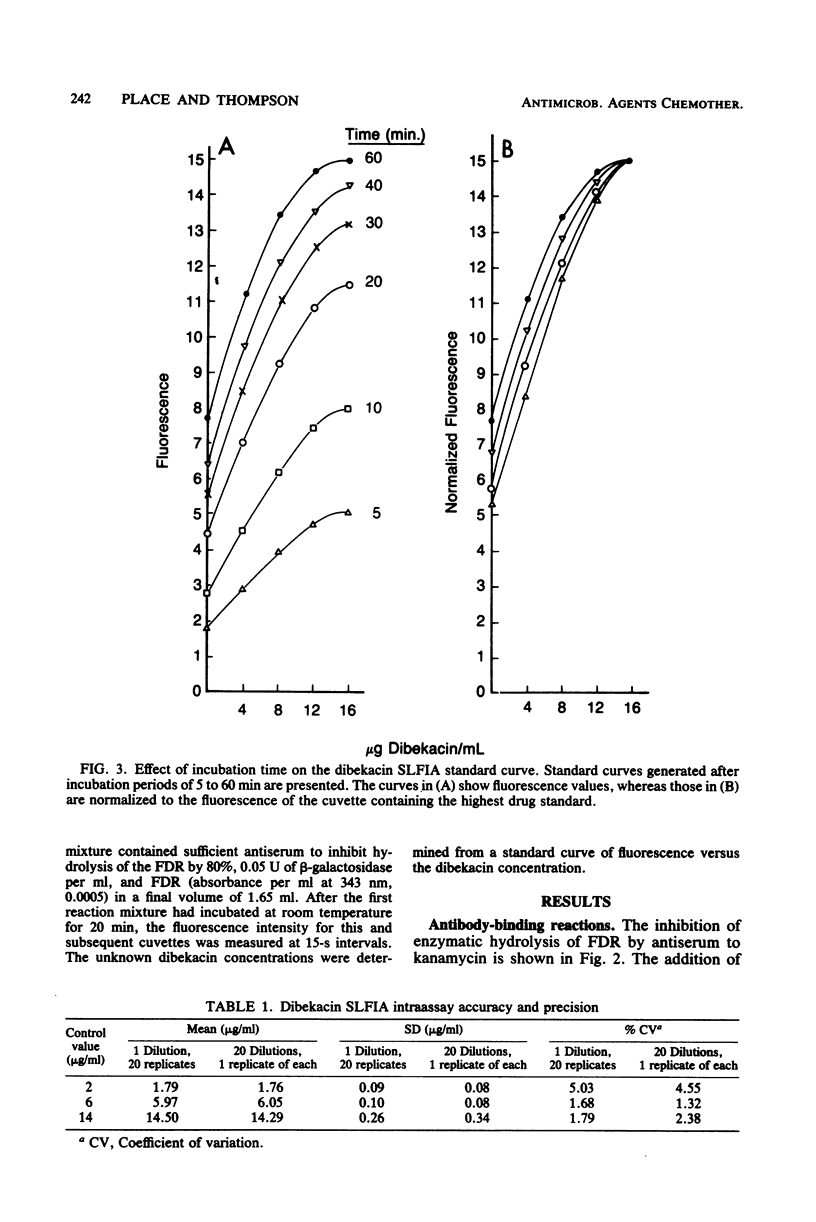
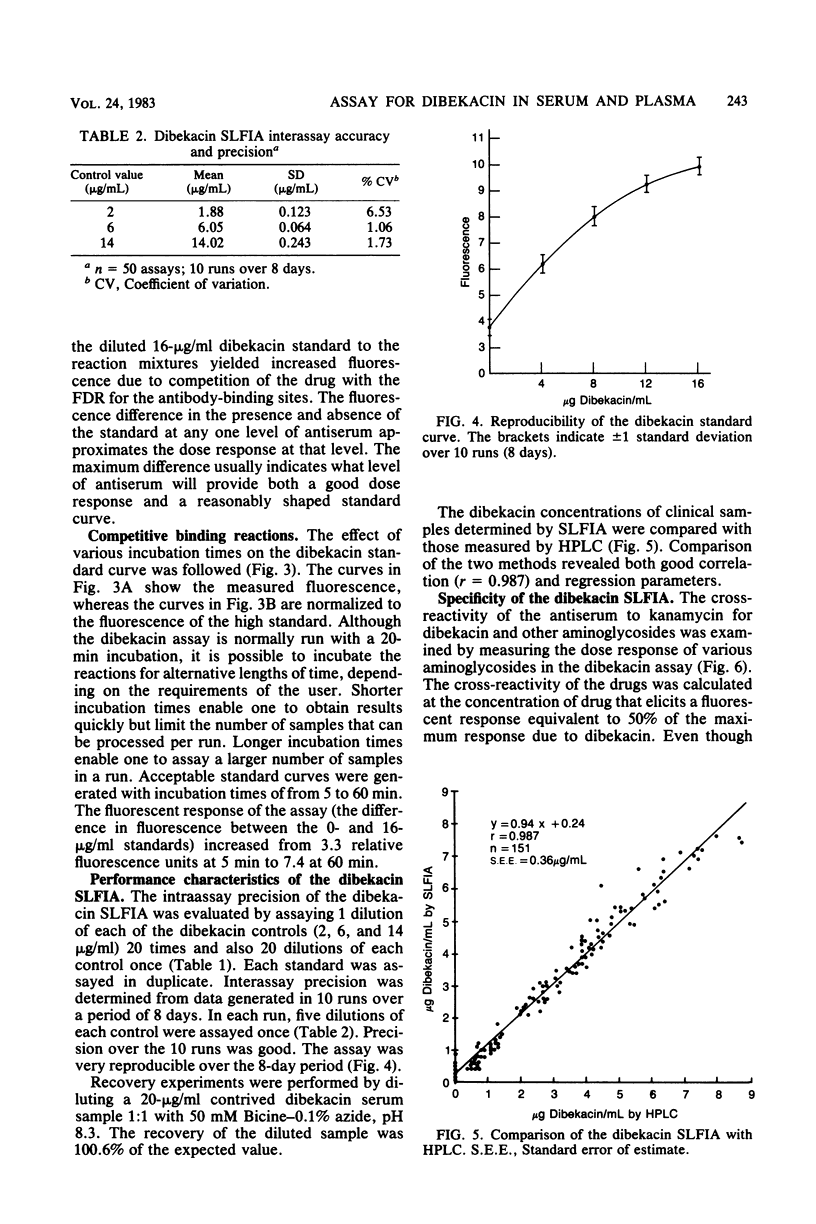
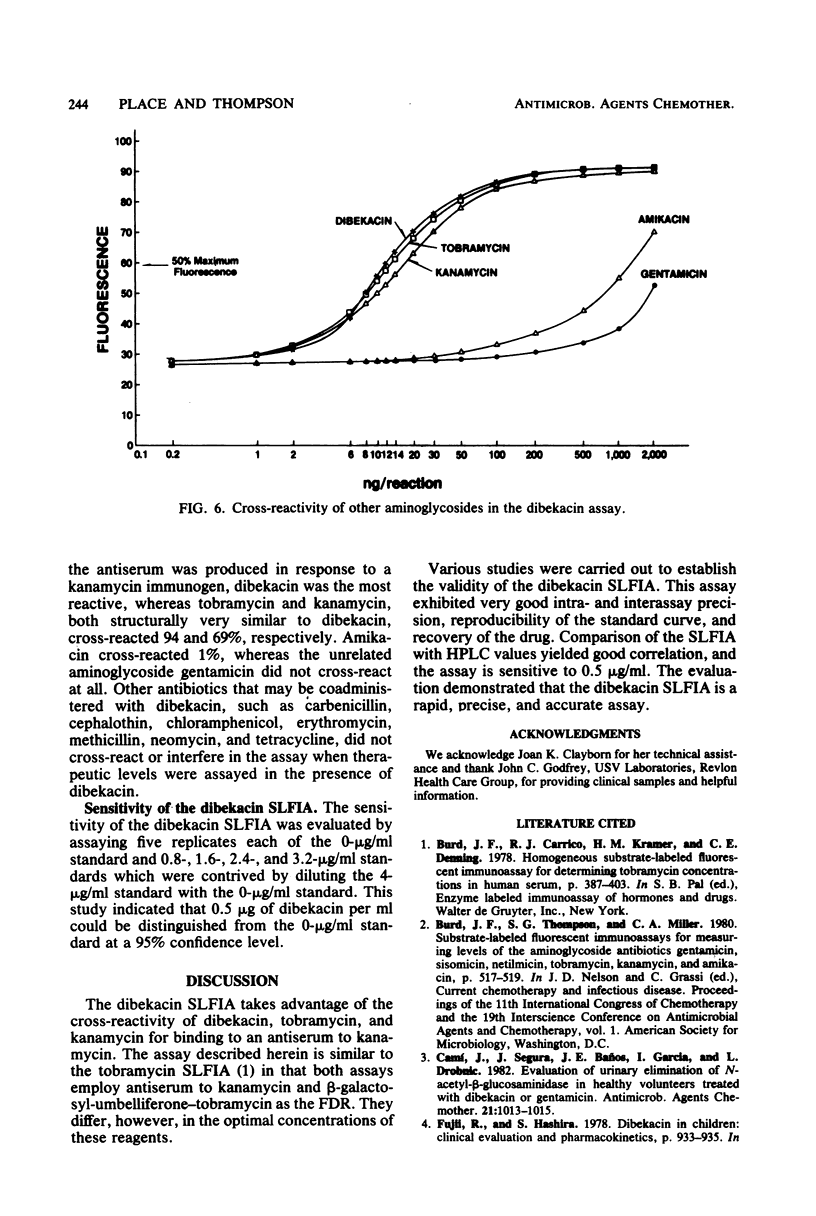
We have developed a homogeneous substrate-labeled fluorescent immunoassay for the measurement of dibekacin concentrations in serum and plasma. The fluorogenic enzyme substrate beta-galactosyl-umbelliferone was covalently attached to tobramycin, an aminoglycoside structurally similar to dibekacin, to prepare a fluorogenic drug reagent (FDR). The FDR is nonfluorescent under assay conditions, but fluoresces upon hydrolysis by beta-galactosidase. However, binding of the FDR by antiserum to the cross-reactive drug kanamycin prevents enzyme hydrolysis. The fixed level of FDR competes with dibekacin within the sample for the limiting number of antibody-binding sites in the reaction mixture. Unbound FDR is hydrolyzed by beta-galactosidase to release a fluorescent product that is proportional to the dibekacin concentration in the sample. The assay exhibits good precision, standard curve reproducibility, recovery, sensitivity, and correlation with a comparative method. Additionally, the substrate-labeled fluorescent immunoassay is rapid and easy to perform.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Camí J., Segura J., Baños J. E., Garcia I., Drobnic L. Evaluation of urinary elimination of N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase in healthy volunteers treated with dibekacin or gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jun;21(6):1013–1015. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.6.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. E., Nelson J. C., Elder H. A. Radioimmunoassay of an antibiotic: gentamicin. Nat New Biol. 1972 Oct 18;239(94):214–216. doi: 10.1038/newbio239214a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulliam L., Hadley W. K., Mills J. In vitro comparison of third-generation cephalosporins, piperacillin, dibekacin, and other aminoglycosides against aerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Mar;19(3):490–492. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.3.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


