Abstract
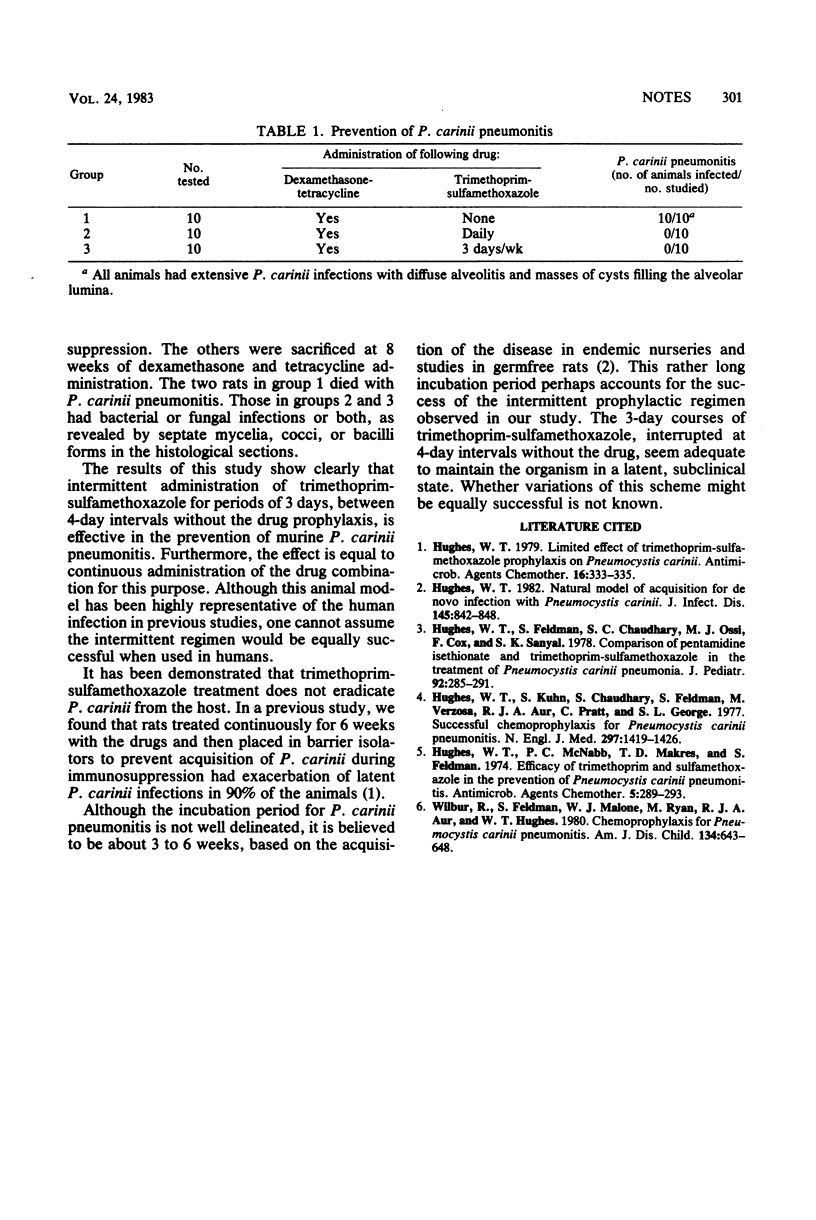
An intermittent regimen of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole was tested in the corticosteroid-treated rat model to learn whether or not administration for 3 consecutive days a week would provide prophylaxis equal to continuous daily doses. Although all of the untreated control animals acquired Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, none of the animals given either continuous or intermittent trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole became infected.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hughes W. T., Feldman S., Chaudhary S. C., Ossi M. J., Cox F., Sanyal S. K. Comparison of pentamidine isethionate and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in the treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. J Pediatr. 1978 Feb;92(2):285–291. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Kuhn S., Chaudhary S., Feldman S., Verzosa M., Aur R. J., Pratt C., George S. L. Successful chemoprophylaxis for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 29;297(26):1419–1426. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712292972602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T. Limited effect of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole prophylaxis on Pneumocystis carinii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Sep;16(3):333–335. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.3.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., McNabb P. C., Makres T. D., Feldman S. Efficacy of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole in the prevention and treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):289–293. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T. Natural mode of acquisition for de novo infection with Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jun;145(6):842–848. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.6.842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilber R. B., Feldman S., Malone W. J., Ryan M., Aur R. J., Hughes W. T. Chemoprophylaxis for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis: outcome of unstructured delivery. Am J Dis Child. 1980 Jul;134(7):643–648. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1980.02130190011004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


