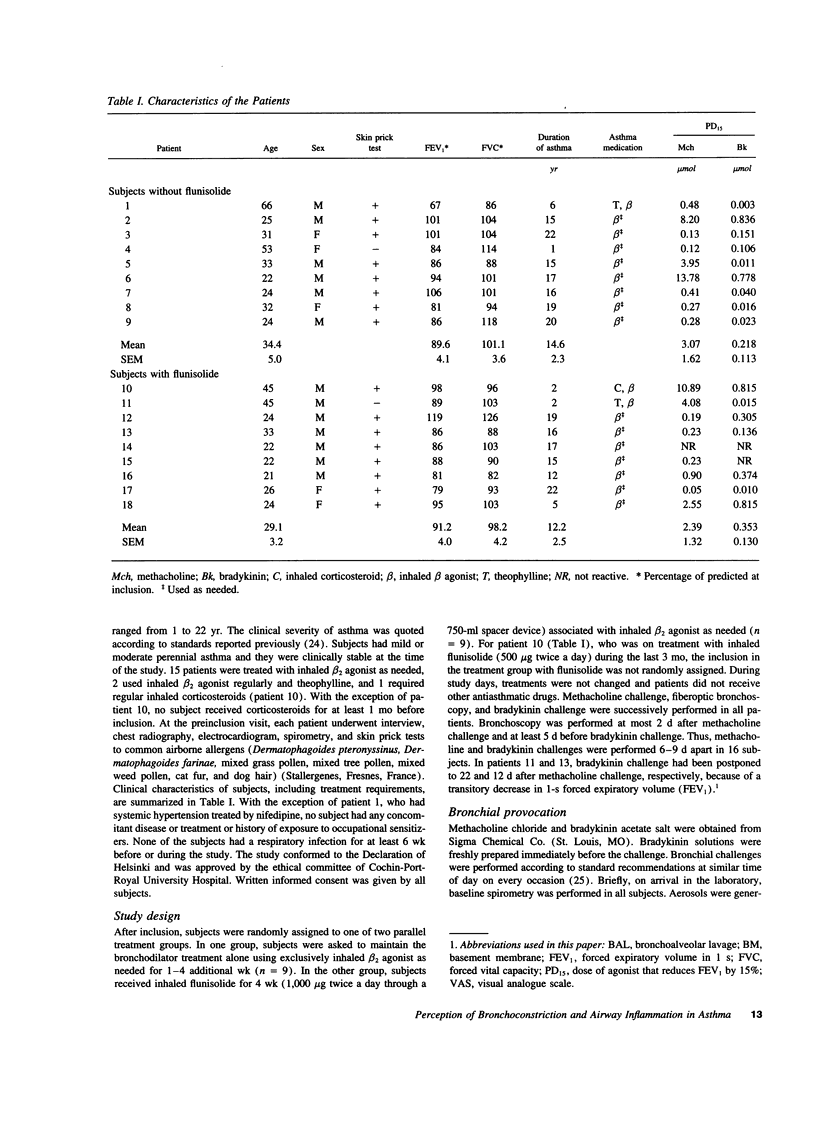
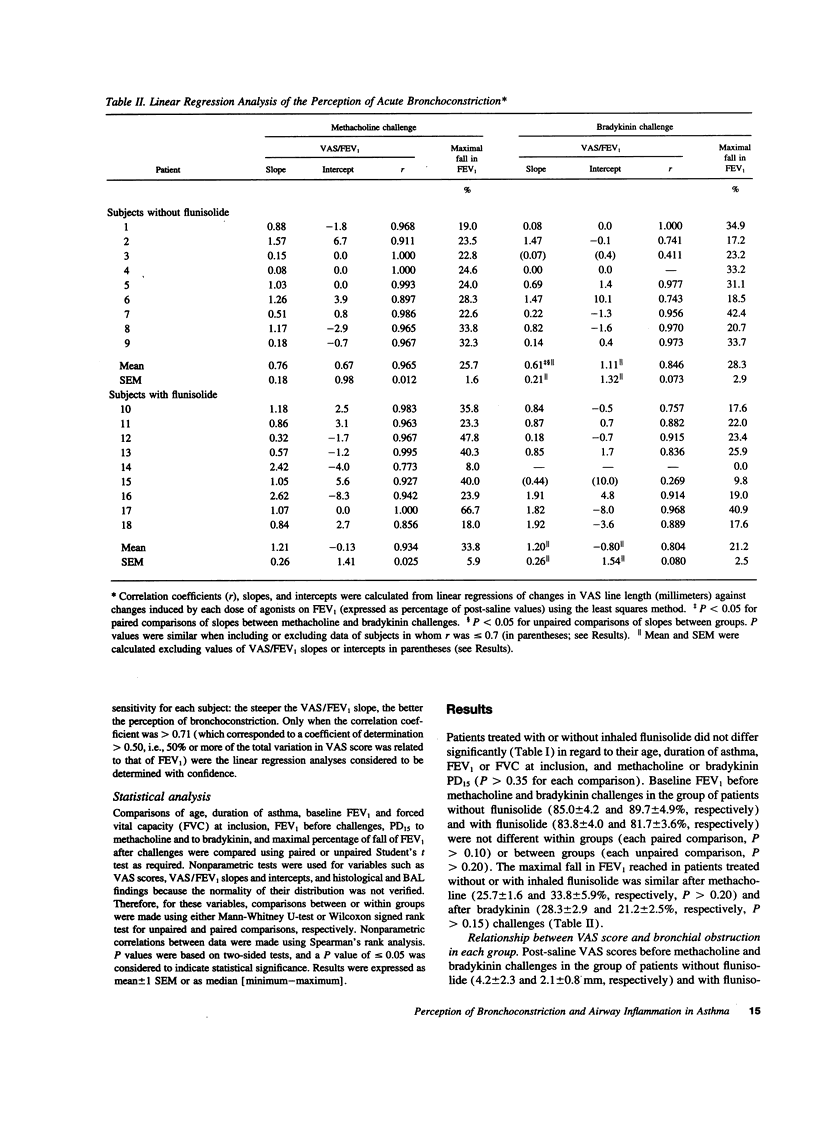
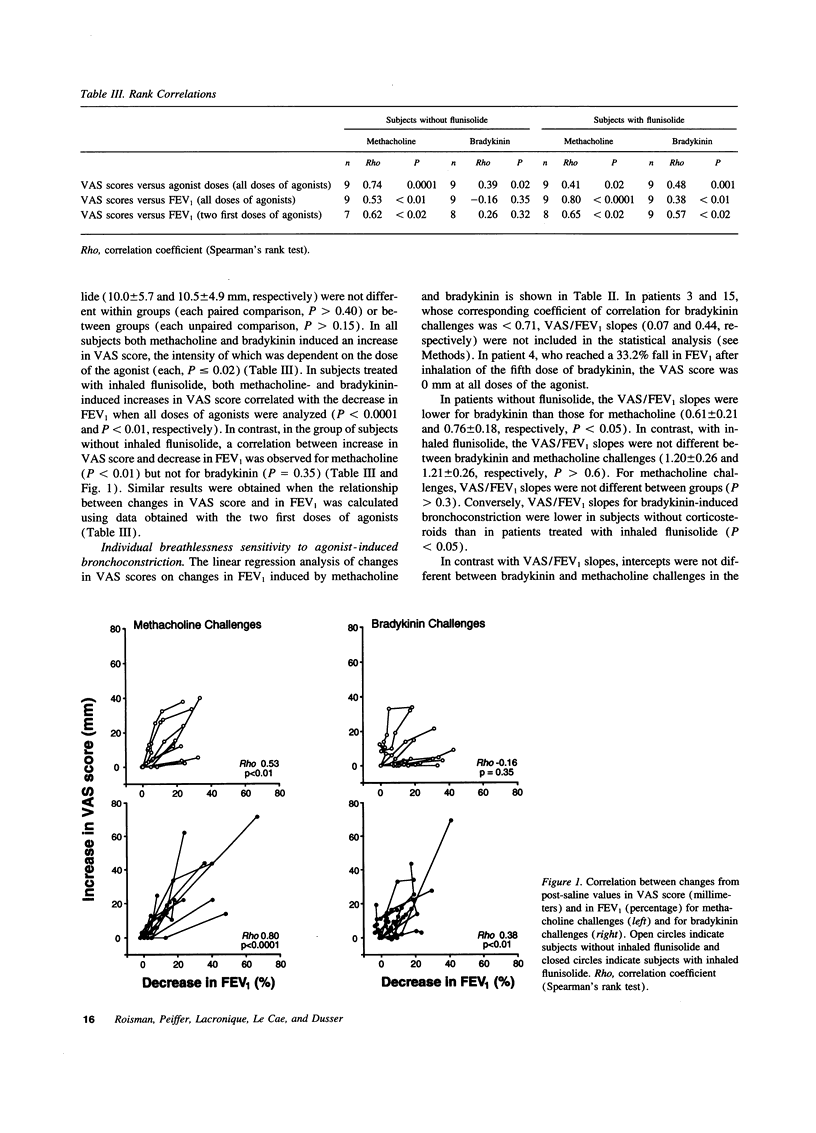
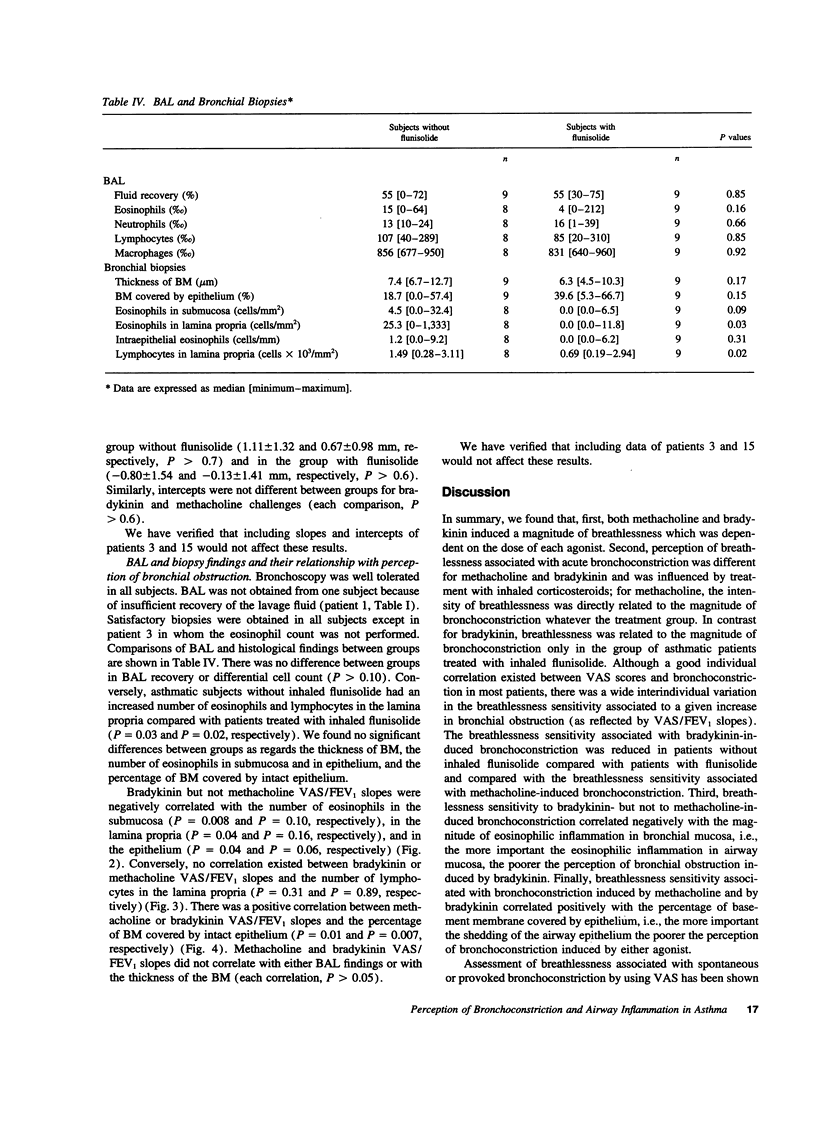
Abstract
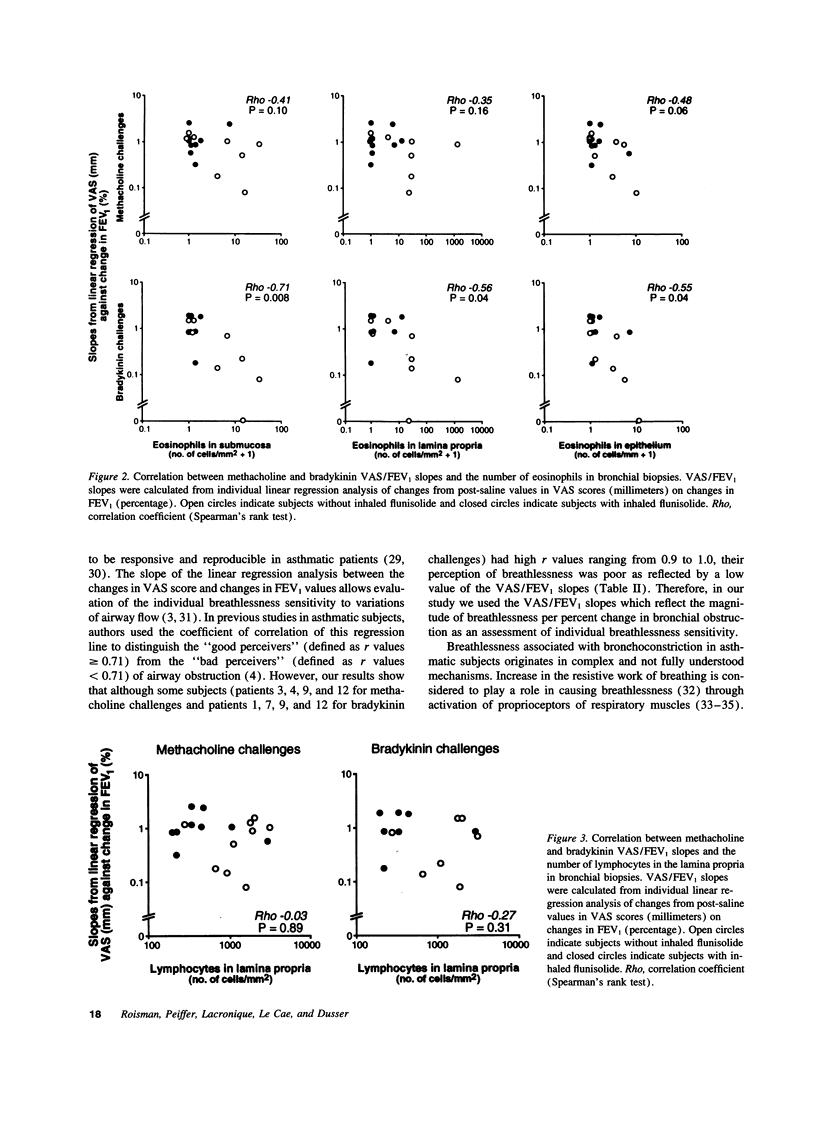
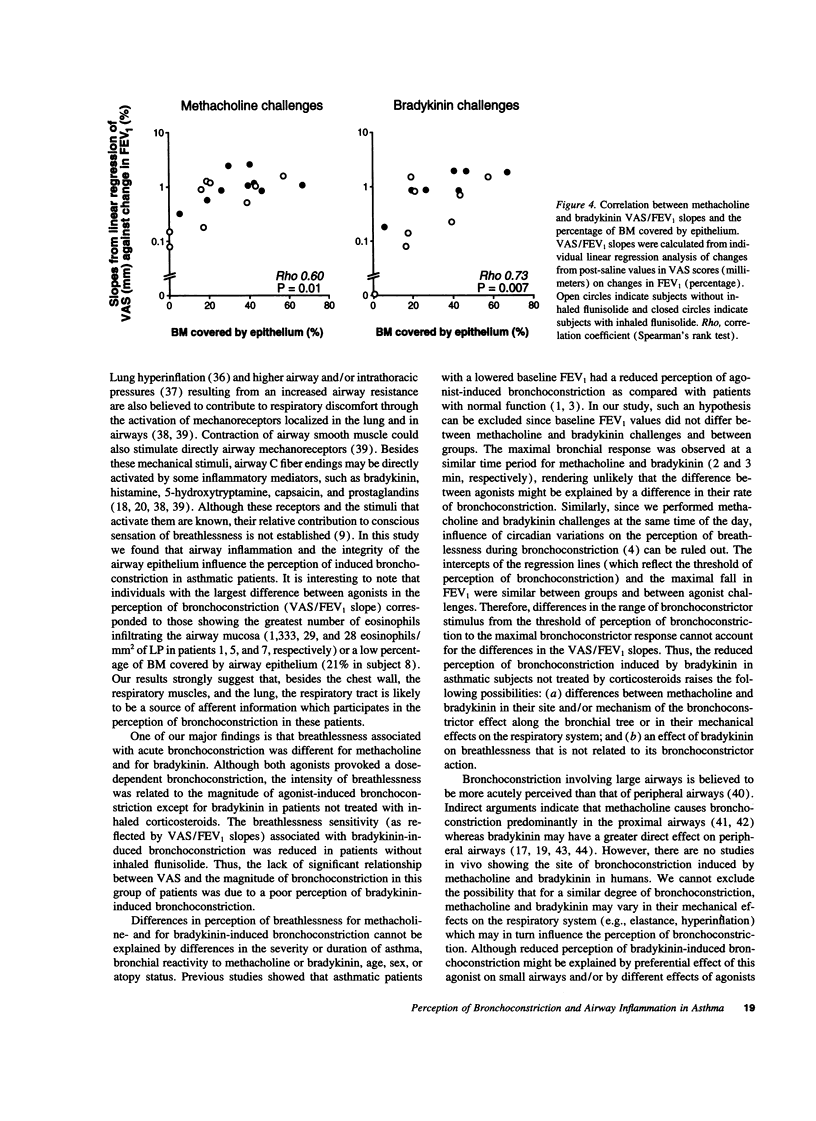
We studied the perception of bronchoconstriction in asthmatic subjects who were randomly treated with inhaled beta 2 agonist given either alone (n = 9) or associated with inhaled corticosteroids (n = 9). Methacholine and bradykinin challenges, bronchoalveolar lavage, and bronchial biopsies were performed in all subjects. After each dose of agonist, breathlessness was assessed using a visual analog scale (VAS) and the forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1) was measured. The relationship between VAS scores and FEV1 and the slope of the regression line of VAS scores on the corresponding FEV1 (VAS/FEV1 slope) were analyzed for each agonist. Subjects without corticosteroids had good perception of methacholine but poor perception of bradykinin-induced bronchoconstriction. In subjects with corticosteroids, bronchoconstriction was well perceived whatever the agonist. VAS/FEV1 slopes for bradykinin but not for methacholine correlated negatively with the magnitude of eosinophilic inflammation in airway mucosa. VAS/FEV1 slopes for each agonist correlated positively with the percentage of basement membrane covered by airway epithelium. We conclude that in asthmatic patients perception of bronchoconstriction is related to eosinophilic inflammation and to epithelial damage in airways and that corticosteroid treatment is associated with improved perception of bronchoconstriction induced by bradykinin, a mediator endogenously produced in asthma.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baraniuk J. N., Lundgren J. D., Mizoguchi H., Peden D., Gawin A., Merida M., Shelhamer J. H., Kaliner M. A. Bradykinin and respiratory mucous membranes. Analysis of bradykinin binding site distribution and secretory responses in vitro and in vivo. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Mar;141(3):706–714. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.3.706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J. Bradykinin and asthma. Thorax. 1992 Nov;47(11):979–983. doi: 10.1136/thx.47.11.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J. Neural control of human airways in health and disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Dec;134(6):1289–1314. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.5.1289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet J., Chanez P., Lacoste J. Y., Barnéon G., Ghavanian N., Enander I., Venge P., Ahlstedt S., Simony-Lafontaine J., Godard P. Eosinophilic inflammation in asthma. N Engl J Med. 1990 Oct 11;323(15):1033–1039. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199010113231505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdon J. G., Juniper E. F., Killian K. J., Hargreave F. E., Campbell E. J. The perception of breathlessness in asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Nov;126(5):825–828. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.5.825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL E. J., HOWELL J. B. The sensation of breathlessness. Br Med Bull. 1963 Jan;19:36–40. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen S. C., Proud D., Cochrane C. G. Detection of tissue kallikrein in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of asthmatic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):188–197. doi: 10.1172/JCI112782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen S. C., Proud D., Sarnoff R. B., Juergens U., Cochrane C. G., Zuraw B. L. Elevation of tissue kallikrein and kinin in the airways of asthmatic subjects after endobronchial allergen challenge. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Apr;145(4 Pt 1):900–905. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/145.4_Pt_1.900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft A., Guz A. Breathlessness. Postgrad Med J. 1987 Aug;63(742):637–641. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.63.742.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corfield D. R., Webber S. E., Hanafi Z., Widdicombe J. G. The actions of bradykinin and lys-bradykinin on tracheal blood flow and smooth muscle in anaesthetized sheep. Pulm Pharmacol. 1991;4(2):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0952-0600(91)90057-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Monchy J. G., Kauffman H. F., Venge P., Koëter G. H., Jansen H. M., Sluiter H. J., De Vries K. Bronchoalveolar eosinophilia during allergen-induced late asthmatic reactions. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Mar;131(3):373–376. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.3.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon C. M., Barnes P. J. Bradykinin-induced bronchoconstriction: inhibition by nedocromil sodium and sodium cromoglycate. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989 Jun;27(6):831–836. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1989.tb03446.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djukanović R., Roche W. R., Wilson J. W., Beasley C. R., Twentyman O. P., Howarth R. H., Holgate S. T. Mucosal inflammation in asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Aug;142(2):434–457. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.2.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T., Ackerman S. J., Loegering D. A., Gleich G. J. Purification of human eosinophil-derived neurotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5165–5169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredens K., Dahl R., Venge P. The Gordon phenomenon induced by the eosinophil cationic protein and eosinophil protein X. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1982 Nov;70(5):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(82)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredens K., Tøttrup A., Kristensen I. B., Dahl R., Jacobsen N. O., Funch-Jensen P., Thommesen P. Severe destruction of esophageal nerves in a patient with achalasia secondary to gastric cancer. A possible role of eosinophil neurotoxic proteins. Dig Dis Sci. 1989 Feb;34(2):297–303. doi: 10.1007/BF01536066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. W., Dixon C. M., Cuss F. M., Barnes P. J. Bradykinin-induced bronchoconstriction in humans. Mode of action. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jan;135(1):176–180. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.1.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gift A. G., Plaut S. M., Jacox A. Psychologic and physiologic factors related to dyspnea in subjects with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Heart Lung. 1986 Nov;15(6):595–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J. The eosinophil and bronchial asthma: current understanding. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1990 Feb;85(2):422–436. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(90)90151-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidelines for standardization of bronchial challenges with (nonspecific) bronchoconstricting agents. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1983 Sep-Oct;19(5):495–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose M., Barnes P. J. Bradykinin-induced airway microvascular leakage and bronchoconstriction are mediated via a bradykinin B2 receptor. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Nov;142(5):1104–1107. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.5.1104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose M., Nakajima N., Takahashi T., Yamauchi H., Inoue H., Takishima T. Protection against bradykinin-induced bronchoconstriction in asthmatic patients by neurokinin receptor antagonist. Lancet. 1992 Nov 21;340(8830):1248–1251. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92948-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson J. A., Sant'Ambrogio G., Widdicombe J. Afferent neural pathways in cough and reflex bronchoconstriction. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Sep;65(3):1007–1023. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.3.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman M. P., Coleridge H. M., Coleridge J. C., Baker D. G. Bradykinin stimulates afferent vagal C-fibers in intrapulmonary airways of dogs. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Mar;48(3):511–517. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.48.3.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Okabe S., Tamura G., Hida W., Homma M., Shirato K., Takishima T. Chemosensitivity and perception of dyspnea in patients with a history of near-fatal asthma. N Engl J Med. 1994 May 12;330(19):1329–1334. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199405123301901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laitinen L. A., Laitinen A., Haahtela T. A comparative study of the effects of an inhaled corticosteroid, budesonide, and a beta 2-agonist, terbutaline, on airway inflammation in newly diagnosed asthma: a randomized, double-blind, parallel-group controlled trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992 Jul;90(1):32–42. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(06)80008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lougheed M. D., Lam M., Forkert L., Webb K. A., O'Donnell D. E. Breathlessness during acute bronchoconstriction in asthma. Pathophysiologic mechanisms. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Dec;148(6 Pt 1):1452–1459. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/148.6_Pt_1.1452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak J. C., Barnes P. J. Autoradiographic visualization of bradykinin receptors in human and guinea pig lung. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Feb 26;194(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden E. R., Jr, Kiser R., DeGroot W. J. Acute bronchial asthma. Relations between clinical and physiologic manifestations. N Engl J Med. 1973 Feb 1;288(5):221–225. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197302012880501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura M., Belvisi M. G., Barnes P. J. Effect of bradykinin on airway neural responses in vitro. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1992 Oct;73(4):1537–1541. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1992.73.4.1537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molimard M., Martin C. A., Naline E., Hirsch A., Advenier C. Contractile effects of bradykinin on the isolated human small bronchus. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Jan;149(1):123–127. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.149.1.7509245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noseda A., Schmerber J., Prigogine T., Yernault J. C. How do patients with either asthma or COPD perceive acute bronchodilation? Eur Respir J. 1993 May;6(5):636–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orehek J., Beaupré A., Badier M., Nicoli M. M., Delpierre S. Perception of airway tone by asthmatic patients. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1982 Jul-Aug;18(4):601–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peiffer C., Marsac J., Lockhart A. Chronobiological study of the relationship between dyspnoea and airway obstruction in symptomatic asthmatic subjects. Clin Sci (Lond) 1989 Sep;77(3):237–244. doi: 10.1042/cs0770237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polosa R., Holgate S. T. Comparative airway response to inhaled bradykinin, kallidin, and [des-Arg9]bradykinin in normal and asthmatic subjects. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Dec;142(6 Pt 1):1367–1371. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.6_Pt_1.1367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puddy A., Giesbrecht G., Sanii R., Younes M. Mechanism of detection of resistive loads in conscious humans. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1992 Jun;72(6):2267–2270. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1992.72.6.2267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinfeld A. R., Pain M. C. Perception of asthma. Lancet. 1976 Apr 24;1(7965):882–884. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffin R. E., Latimer K. M., Schembri D. A. Longitudinal study of near fatal asthma. Chest. 1991 Jan;99(1):77–83. doi: 10.1378/chest.99.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sant'Ambrogio G. Nervous receptors of the tracheobronchial tree. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:611–627. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.003143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears M. R., Rea H. H. Patients at risk for dying of asthma: New Zealand experience. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1987 Sep;80(3 Pt 2):477–481. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(87)90079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioya T., Solway J., Munoz N. M., Mack M., Leff A. R. Distribution of airway contractile responses within the major diameter bronchi during exogenous bronchoconstriction. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 May;135(5):1105–1111. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.5.1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark R. D., Gambles S. A., Chatterjee S. S. An exercise test to assess clinical dyspnoea: estimation of reproducibility and sensitivity. Br J Dis Chest. 1982 Jul;76(3):269–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turcotte H., Boulet L. P. Perception of breathlessness during early and late asthmatic responses. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Aug;148(2):514–518. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/148.2.514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turcotte H., Corbeil F., Boulet L. P. Perception of breathlessness during bronchoconstriction induced by antigen, exercise, and histamine challenges. Thorax. 1990 Dec;45(12):914–918. doi: 10.1136/thx.45.12.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardlaw A. J., Dunnette S., Gleich G. J., Collins J. V., Kay A. B. Eosinophils and mast cells in bronchoalveolar lavage in subjects with mild asthma. Relationship to bronchial hyperreactivity. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Jan;137(1):62–69. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.1.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


