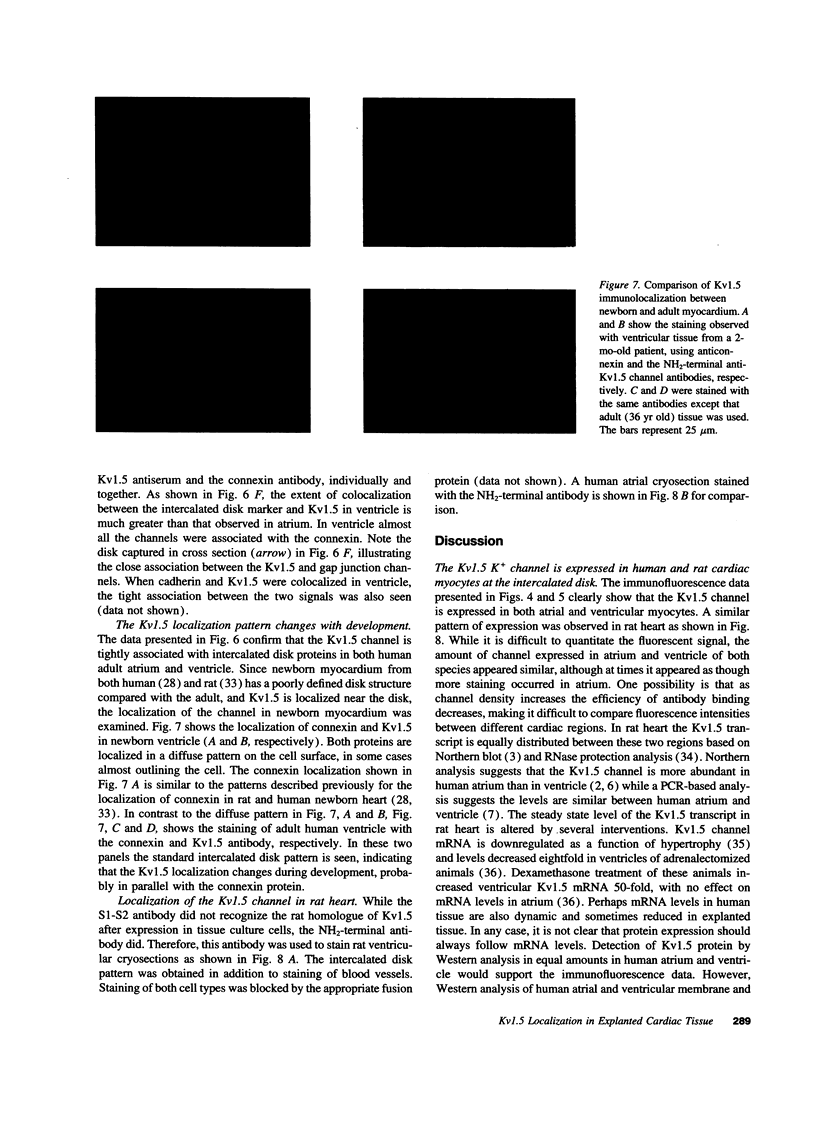
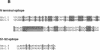Abstract
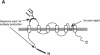
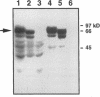
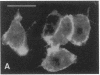
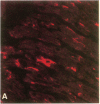
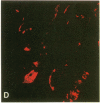
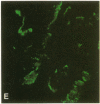
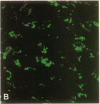
The cloned Kv1.5 K+ channel displays similar kinetics and pharmacology to a delayed rectifier channel found in atrial myocytes. To determine whether the Kv1.5 isoform plays a role in the cardiac action potential, it is necessary to confirm the expression of this channel in cardiac myocytes. Using antibodies directed against two distinct channel epitopes, the Kv1.5 isoform was localized in human atrium and ventricle. Kv1.5 was highly localized at intercalated disk regions as determined by colocalization with connexin and N-cadherin specific antibodies. While both antichannel antibodies localized the Kv1.5 protein in cardiac myocytes, only the NH2-terminal antibodies stained vascular smooth muscle. The selective staining of vasculature by this antiserum suggests that epitope accessibility, and perhaps channel structure, varies between cardiac and vascular myocytes. Kv1.5 expression was localized less in newborn tissue, with punctate antibody staining dispersed on the myocyte surface. This increasing organization with age was similar to that observed for connexin. Future work will address whether altered K+ channel localization is associated with cardiac disease in addition to changing with development.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attali B., Lesage F., Ziliani P., Guillemare E., Honoré E., Waldmann R., Hugnot J. P., Mattéi M. G., Lazdunski M., Barhanin J. Multiple mRNA isoforms encoding the mouse cardiac Kv1-5 delayed rectifier K+ channel. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):24283–24289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beech D. J., Bolton T. B. Two components of potassium current activated by depolarization of single smooth muscle cells from the rabbit portal vein. J Physiol. 1989 Nov;418:293–309. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. A., Nerbonne J. M. A novel type of depolarization-activated K+ current in isolated adult rat atrial myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1991 Apr;260(4 Pt 2):H1236–H1247. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.260.4.H1236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie M. J., North R. A., Osborne P. B., Douglass J., Adelman J. P. Heteropolymeric potassium channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes from cloned subunits. Neuron. 1990 Mar;4(3):405–411. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90052-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. A., Barchi R. L. Localization of epitopes for antibodies that differentially label sodium sodium channels in skeletal muscle surface and T-tubular membranes. J Membr Biol. 1992 Jun;128(3):219–226. doi: 10.1007/BF00231814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comer M. B., Campbell D. L., Rasmusson R. L., Lamson D. R., Morales M. J., Zhang Y., Strauss H. C. Cloning and characterization of an Ito-like potassium channel from ferret ventricle. Am J Physiol. 1994 Oct;267(4 Pt 2):H1383–H1395. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1994.267.4.H1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covarrubias M., Wei A. A., Salkoff L. Shaker, Shal, Shab, and Shaw express independent K+ current systems. Neuron. 1991 Nov;7(5):763–773. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90279-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deal K. K., Lovinger D. M., Tamkun M. M. The brain Kv1.1 potassium channel: in vitro and in vivo studies on subunit assembly and posttranslational processing. J Neurosci. 1994 Mar;14(3 Pt 2):1666–1676. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-03-01666.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. E., McKinnon D. Quantitative analysis of potassium channel mRNA expression in atrial and ventricular muscle of rats. Circ Res. 1994 Aug;75(2):252–260. doi: 10.1161/01.res.75.2.252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedida D., Wible B., Wang Z., Fermini B., Faust F., Nattel S., Brown A. M. Identity of a novel delayed rectifier current from human heart with a cloned K+ channel current. Circ Res. 1993 Jul;73(1):210–216. doi: 10.1161/01.res.73.1.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelband C. H., Hume J. R. Ionic currents in single smooth muscle cells of the canine renal artery. Circ Res. 1992 Oct;71(4):745–758. doi: 10.1161/01.res.71.4.745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourdie R. G., Green C. R., Severs N. J., Thompson R. P. Immunolabelling patterns of gap junction connexins in the developing and mature rat heart. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1992;185(4):363–378. doi: 10.1007/BF00188548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyt R. H., Cohen M. L., Corr P. B., Saffitz J. E. Alterations of intercellular junctions induced by hypoxia in canine myocardium. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 2):H1439–H1448. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.5.H1439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huynh T. V., Chen F., Wetzel G. T., Friedman W. F., Klitzner T. S. Developmental changes in membrane Ca2+ and K+ currents in fetal, neonatal, and adult rabbit ventricular myocytes. Circ Res. 1992 Mar;70(3):508–515. doi: 10.1161/01.res.70.3.508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isacoff E. Y., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Putative receptor for the cytoplasmic inactivation gate in the Shaker K+ channel. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):86–90. doi: 10.1038/353086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeck C. D., Boyden P. A. Age-related appearance of outward currents may contribute to developmental differences in ventricular repolarization. Circ Res. 1992 Dec;71(6):1390–1403. doi: 10.1161/01.res.71.6.1390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kijima Y., Saito A., Jetton T. L., Magnuson M. A., Fleischer S. Different intracellular localization of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and ryanodine receptors in cardiomyocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3499–3506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis Carl S. A., Gillete-Ferguson I., Ferguson D. G. An indirect immunofluorescence procedure for staining the same cryosection with two mouse monoclonal primary antibodies. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993 Aug;41(8):1273–1278. doi: 10.1177/41.8.7687266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lue W. M., Boyden P. A. Abnormal electrical properties of myocytes from chronically infarcted canine heart. Alterations in Vmax and the transient outward current. Circulation. 1992 Mar;85(3):1175–1188. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.85.3.1175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara H., Liman E. R., Hess P., Koren G. Pretranslational mechanisms determine the type of potassium channels expressed in the rat skeletal and cardiac muscles. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13324–13328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara H., Suzuki J., Inada M. Shaker-related potassium channel, Kv1.4, mRNA regulation in cultured rat heart myocytes and differential expression of Kv1.4 and Kv1.5 genes in myocardial development and hypertrophy. J Clin Invest. 1993 Oct;92(4):1659–1666. doi: 10.1172/JCI116751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overturf K. E., Russell S. N., Carl A., Vogalis F., Hart P. J., Hume J. R., Sanders K. M., Horowitz B. Cloning and characterization of a Kv1.5 delayed rectifier K+ channel from vascular and visceral smooth muscles. Am J Physiol. 1994 Nov;267(5 Pt 1):C1231–C1238. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.267.5.C1231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters N. S., Green C. R., Poole-Wilson P. A., Severs N. J. Reduced content of connexin43 gap junctions in ventricular myocardium from hypertrophied and ischemic human hearts. Circulation. 1993 Sep;88(3):864–875. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.88.3.864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters N. S., Severs N. J., Rothery S. M., Lincoln C., Yacoub M. H., Green C. R. Spatiotemporal relation between gap junctions and fascia adherens junctions during postnatal development of human ventricular myocardium. Circulation. 1994 Aug;90(2):713–725. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.90.2.713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson L. H., Malayev A., Kuznetsov A., Chang C., Nelson D. J. Functional and biochemical characterization of the human potassium channel Kv1.5 with a transplanted carboxyl-terminal epitope in stable mammalian cell lines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Nov 21;1153(1):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90282-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Po S., Roberds S., Snyders D. J., Tamkun M. M., Bennett P. B. Heteromultimeric assembly of human potassium channels. Molecular basis of a transient outward current? Circ Res. 1993 Jun;72(6):1326–1336. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.6.1326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettig J., Heinemann S. H., Wunder F., Lorra C., Parcej D. N., Dolly J. O., Pongs O. Inactivation properties of voltage-gated K+ channels altered by presence of beta-subunit. Nature. 1994 May 26;369(6478):289–294. doi: 10.1038/369289a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberds S. L., Tamkun M. M. Cloning and tissue-specific expression of five voltage-gated potassium channel cDNAs expressed in rat heart. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1798–1802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberds S. L., Tamkun M. M. Developmental expression of cloned cardiac potassium channels. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jun 24;284(2):152–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80673-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., Liao Y. J., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Presynaptic A-current based on heteromultimeric K+ channels detected in vivo. Nature. 1993 Sep 2;365(6441):72–75. doi: 10.1038/365072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Gigengack S., James D. E., Lienhard G. E. Translocation of the glucose transporter GLUT4 in cardiac myocytes of the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7815–7819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. H., Green C. R., Peters N. S., Rothery S., Severs N. J. Altered patterns of gap junction distribution in ischemic heart disease. An immunohistochemical study of human myocardium using laser scanning confocal microscopy. Am J Pathol. 1991 Oct;139(4):801–821. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyders D. J., Tamkun M. M., Bennett P. B. A rapidly activating and slowly inactivating potassium channel cloned from human heart. Functional analysis after stable mammalian cell culture expression. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Apr;101(4):513–543. doi: 10.1085/jgp.101.4.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson R., Marshall J., Smith J. S., Williams J. B., Boyle M. B., Folander K., Luneau C. J., Antanavage J., Oliva C., Buhrow S. A. Cloning and expression of cDNA and genomic clones encoding three delayed rectifier potassium channels in rat brain. Neuron. 1990 Jun;4(6):929–939. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90146-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takimoto K., Levitan E. S. Glucocorticoid induction of Kv1.5 K+ channel gene expression in ventricle of rat heart. Circ Res. 1994 Dec;75(6):1006–1013. doi: 10.1161/01.res.75.6.1006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun M. M., Knoth K. M., Walbridge J. A., Kroemer H., Roden D. M., Glover D. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of two voltage-gated K+ channel cDNAs from human ventricle. FASEB J. 1991 Mar 1;5(3):331–337. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.3.2001794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uebele V. N., Yeola S. W., Snyders D. J., Tamkun M. M. Deletion of highly conserved C-terminal sequences in the Kv1 K+ channel sub-family does not prevent expression of currents with wild-type characteristics. FEBS Lett. 1994 Feb 28;340(1-2):104–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80181-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Kunkel D. D., Martin T. M., Schwartzkroin P. A., Tempel B. L. Heteromultimeric K+ channels in terminal and juxtaparanodal regions of neurons. Nature. 1993 Sep 2;365(6441):75–79. doi: 10.1038/365075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z., Fermini B., Nattel S. Sustained depolarization-induced outward current in human atrial myocytes. Evidence for a novel delayed rectifier K+ current similar to Kv1.5 cloned channel currents. Circ Res. 1993 Dec;73(6):1061–1076. doi: 10.1161/01.res.73.6.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]