Abstract
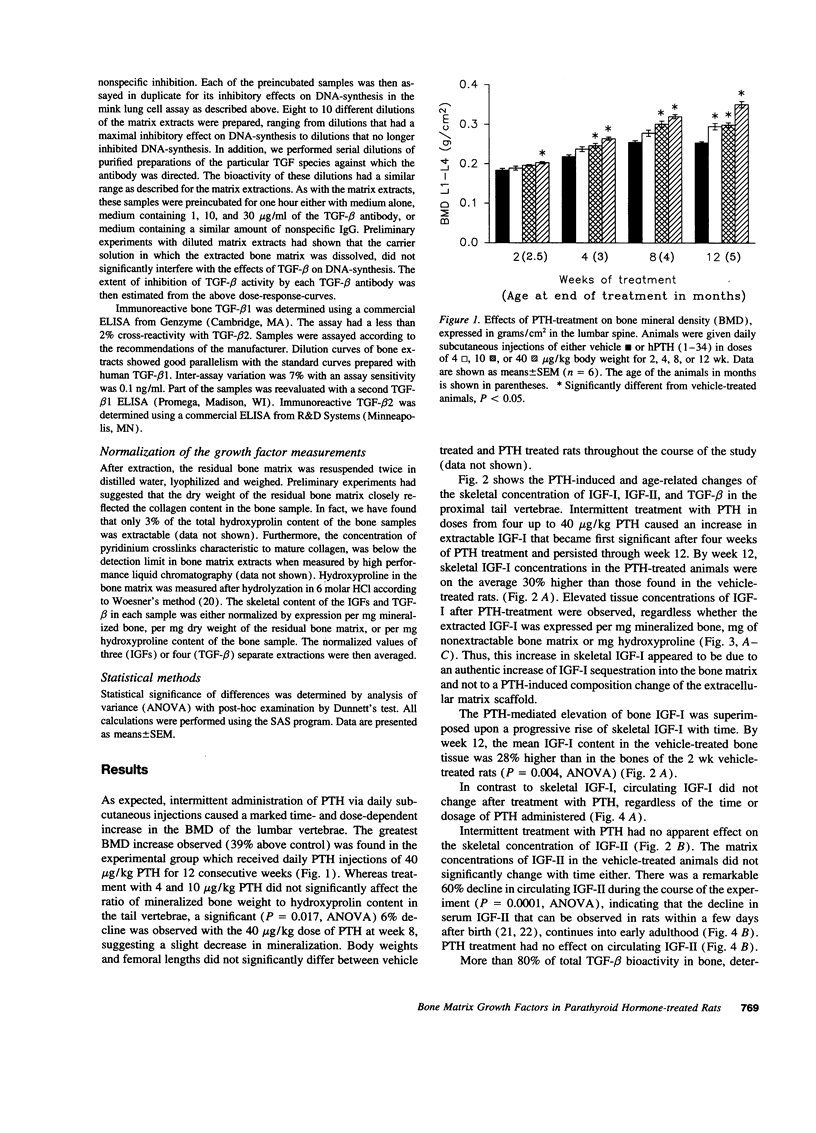
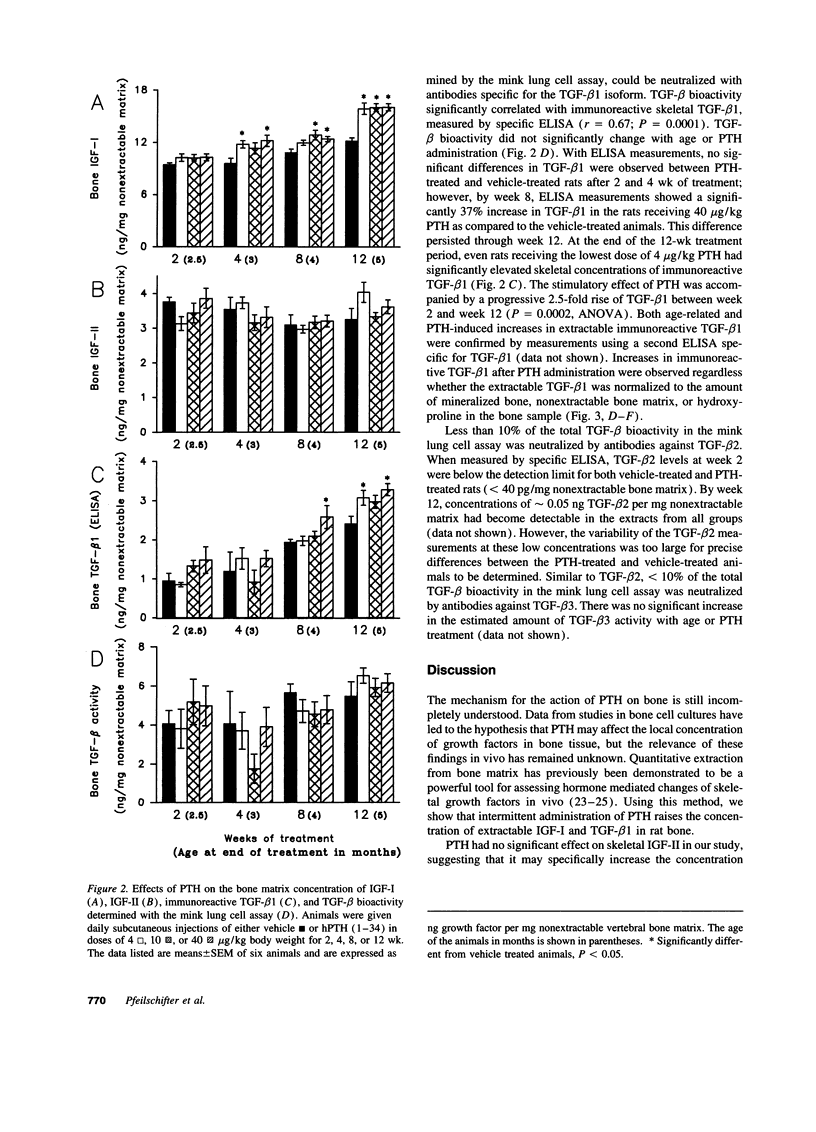
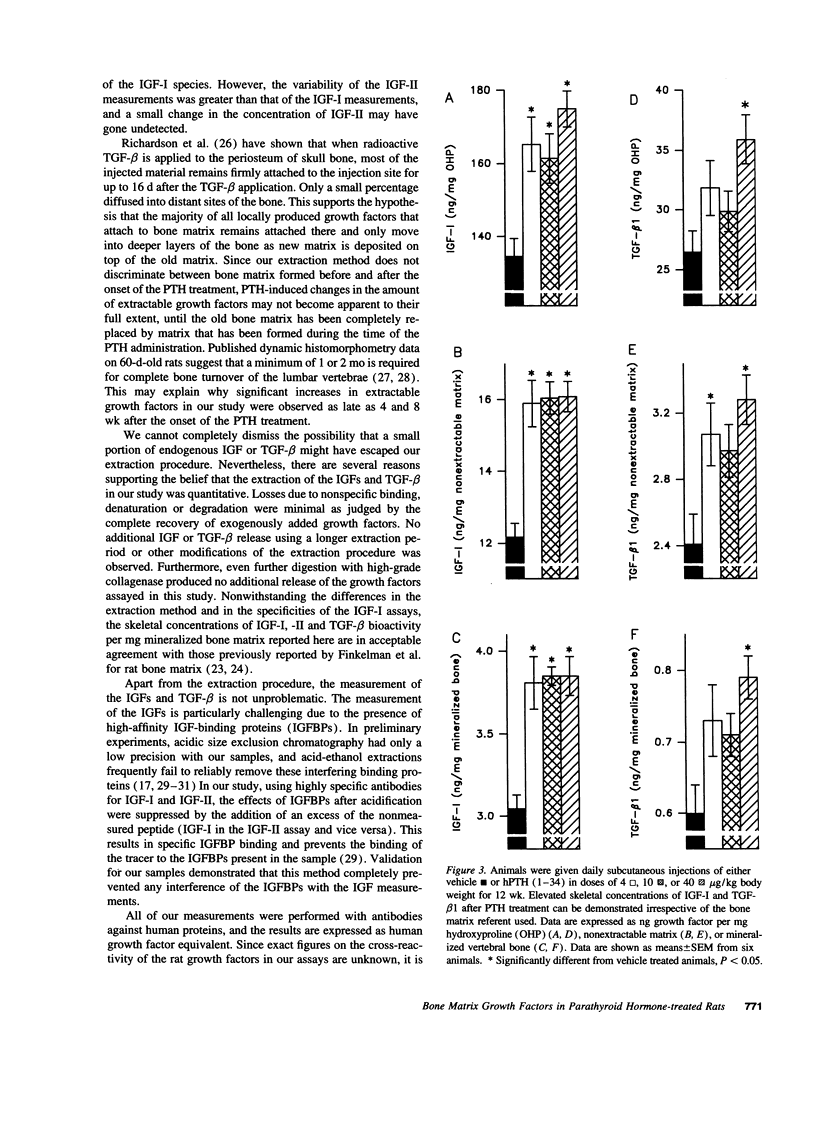
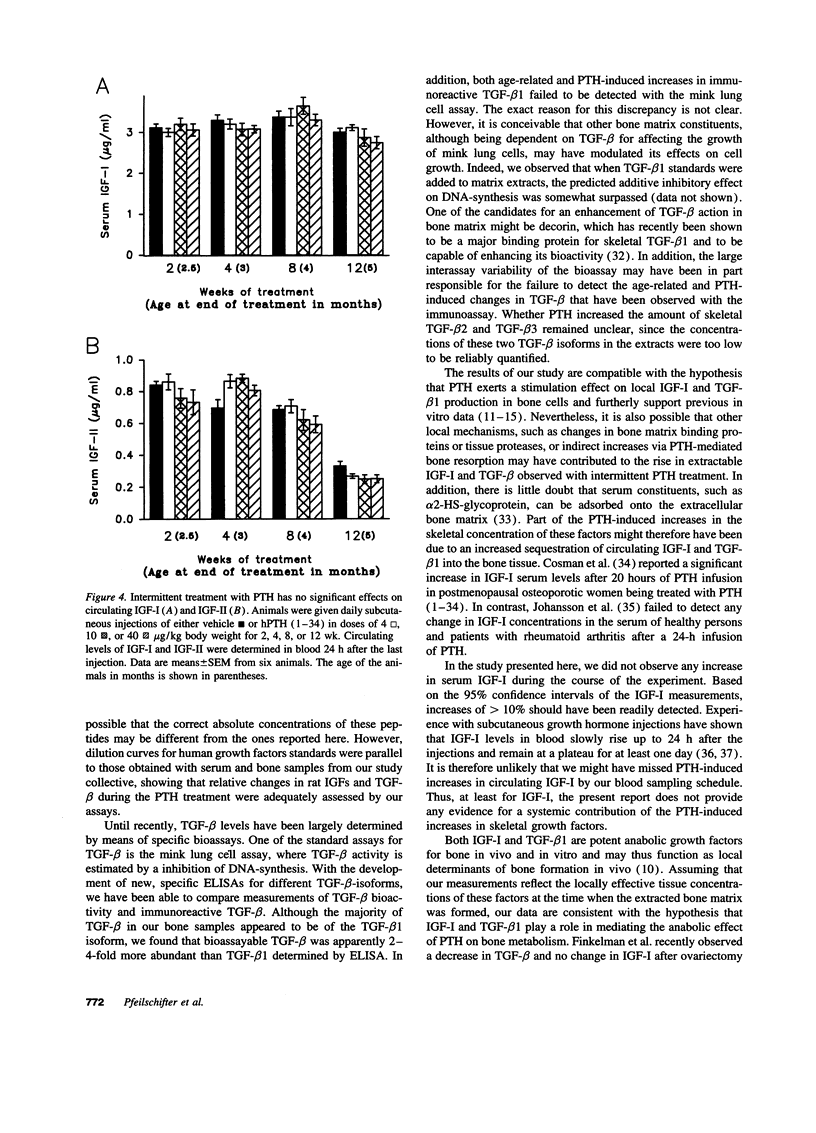
Intermittent treatment with parathyroid hormone (PTH) increases bone mass in experimental animals and humans. In vitro studies have suggested that the anabolic effect of PTH may be mediated by local growth factors. However, the relevance of these findings to in vivo situations remains unclear. In this study, we examined a time course of daily s.c. injections of hPTH (1-34) on the skeletal concentration of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF-II, and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) in the proximal tail vertebrae of male rats. PTH caused a time and dose-dependent increase in the bone mineral density of the lumbar spine. This anabolic effect on bone mass was accompanied by progressive increases in bone matrix-associated IGF-I and TGF-beta 1. Increases in IGF-I and TGF-beta 1 became apparent after four and eight weeks of PTH treatment respectively and persisted through week 12. PTH had no effect on circulating IGF-I, suggesting that the increase of bone matrix IGF-I was due to the local effect of PTH on bone tissue directly rather than to an increase of circulating IGF-I. These data are consistent with the hypothesis that IGF-I and TGF-beta 1 may play a role as local mediators of the anabolic effects of PTH on bone metabolism.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aerssens J., Van Audekercke R., Geusens P., Schot L. P., Osman A. A., Dequeker J. Mechanical properties, bone mineral content, and bone composition (collagen, osteocalcin, IGF-I) of the rat femur: influence of ovariectomy and nandrolone decanoate (anabolic steroid) treatment. Calcif Tissue Int. 1993 Oct;53(4):269–277. doi: 10.1007/BF01320913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum W. F., Breier B. H. Radioimmunoassays for IGFs and IGFBPs. Growth Regul. 1994 Feb;4 (Suppl 1):11–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum W. F., Ranke M. B., Bierich J. R. A specific radioimmunoassay for insulin-like growth factor II: the interference of IGF binding proteins can be blocked by excess IGF-I. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1988 Jul;118(3):374–380. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1180374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canalis E., Centrella M., Burch W., McCarthy T. L. Insulin-like growth factor I mediates selective anabolic effects of parathyroid hormone in bone cultures. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):60–65. doi: 10.1172/JCI113885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosman F., Shen V., Xie F., Seibel M., Ratcliffe A., Lindsay R. Estrogen protection against bone resorbing effects of parathyroid hormone infusion. Assessment by use of biochemical markers. Ann Intern Med. 1993 Mar 1;118(5):337–343. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-118-5-199303010-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Parker K. A., Borowsky S., Trivedi B., Kapadia M. Measurement of somatomedin-related peptides in fetal, neonatal, and maternal rat serum by insulin-like growth factor (IGF) I radioimmunoassay, IGF-II radioreceptor assay (RRA), and multiplication-stimulating activity RRA after acid-ethanol extraction. Endocrinology. 1982 Feb;110(2):575–581. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-2-575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dequeker J., Mohan S., Finkelman R. D., Aerssens J., Baylink D. J. Generalized osteoarthritis associated with increased insulin-like growth factor types I and II and transforming growth factor beta in cortical bone from the iliac crest. Possible mechanism of increased bone density and protection against osteoporosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Dec;36(12):1702–1708. doi: 10.1002/art.1780361209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelman R. D., Bell N. H., Strong D. D., Demers L. M., Baylink D. J. Ovariectomy selectively reduces the concentration of transforming growth factor beta in rat bone: implications for estrogen deficiency-associated bone loss. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12190–12193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelman R. D., Linkhart T. A., Mohan S., Lau K. H., Baylink D. J., Bell N. H. Vitamin D deficiency causes a selective reduction in deposition of transforming growth factor beta in rat bone: possible mechanism for impaired osteoinduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3657–3660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein J. S., Klibanski A., Schaefer E. H., Hornstein M. D., Schiff I., Neer R. M. Parathyroid hormone for the prevention of bone loss induced by estrogen deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1994 Dec 15;331(24):1618–1623. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199412153312404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunness-Hey M., Hock J. M. Increased trabecular bone mass in rats treated with human synthetic parathyroid hormone. Metab Bone Dis Relat Res. 1984;5(4):177–181. doi: 10.1016/0221-8747(84)90026-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hefti E., Trechsel U., Bonjour J. P., Fleisch H., Schenk R. Increase of whole-body calcium and skeletal mass in normal and osteoporotic adult rats treated with parathyroid hormone. Clin Sci (Lond) 1982 Apr;62(4):389–396. doi: 10.1042/cs0620389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hock J. M., Gera I., Fonseca J., Raisz L. G. Human parathyroid hormone-(1-34) increases bone mass in ovariectomized and orchidectomized rats. Endocrinology. 1988 Jun;122(6):2899–2904. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-6-2899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holly J. M., Hughes S. C. Measuring insulin-like growth factors: why, where and how? J Endocrinol. 1994 Feb;140(2):165–169. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1400165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings J. C., Mohan S., Linkhart T. A., Widstrom R., Baylink D. J. Comparison of the biological actions of TGF beta-1 and TGF beta-2: differential activity in endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Oct;137(1):167–172. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041370120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson A. G., Baylink D. J., af Ekenstam E., Lindh E., Mohan S., Ljunghall S. Circulating levels of insulin-like growth factor-I and -II, and IGF-binding protein-3 in inflammation and after parathyroid hormone infusion. Bone Miner. 1994 Jan;24(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/s0169-6009(08)80128-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laursen T., Jørgensen J. O., Orskov H., Møller J., Harris A. G., Christiansen J. S. Effects of octreotide on insulin-like growth factor I and metabolic indices in growth hormone-treated growth hormone-deficient patients. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1993 Nov;129(5):399–408. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1290399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linkhart T. A., Keffer M. J. Differential regulation of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF-II release from cultured neonatal mouse calvaria by parathyroid hormone, transforming growth factor-beta, and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Endocrinology. 1991 Mar;128(3):1511–1518. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-3-1511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linkhart T. A., Mohan S. Parathyroid hormone stimulates release of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF-II from neonatal mouse calvaria in organ culture. Endocrinology. 1989 Sep;125(3):1484–1491. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-3-1484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy T. L., Centrella M., Canalis E. Parathyroid hormone enhances the transcript and polypeptide levels of insulin-like growth factor I in osteoblast-enriched cultures from fetal rat bone. Endocrinology. 1989 Mar;124(3):1247–1253. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-3-1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. C., Nissley S. P., Short P. A., Rechler M. M., White R. M., Knight A. B., Higa O. Z. Increased levels of multiplication-stimulating activity, an insulin-like growth factor, in fetal rat serum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3649–3653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oursler M. J., Cortese C., Keeting P., Anderson M. A., Bonde S. K., Riggs B. L., Spelsberg T. C. Modulation of transforming growth factor-beta production in normal human osteoblast-like cells by 17 beta-estradiol and parathyroid hormone. Endocrinology. 1991 Dec;129(6):3313–3320. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-6-3313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overall C. M. A microtechnique for dialysis of small volume solutions with quantitative recoveries. Anal Biochem. 1987 Aug 15;165(1):208–214. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90221-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve J., Davies U. M., Hesp R., McNally E., Katz D. Treatment of osteoporosis with human parathyroid peptide and observations on effect of sodium fluoride. BMJ. 1990 Aug 11;301(6747):314–318. doi: 10.1136/bmj.301.6747.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve J., Hesp R., Williams D., Hulme P., Klenerman L., Zanelli J. M., Darby A. J., Tregear G. W., Parsons J. A. Anabolic effect of low doses of a fragment of human parathyroid hormone on the skeleton in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Lancet. 1976 May 15;1(7968):1035–1038. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92216-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve J., Meunier P. J., Parsons J. A., Bernat M., Bijvoet O. L., Courpron P., Edouard C., Klenerman L., Neer R. M., Renier J. C. Anabolic effect of human parathyroid hormone fragment on trabecular bone in involutional osteoporosis: a multicentre trial. Br Med J. 1980 Jun 7;280(6228):1340–1344. doi: 10.1136/bmj.280.6228.1340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson L., Zioncheck T. F., Amento E. P., Deguzman L., Lee W. P., Xu Y., Beck L. S. Characterization of radioiodinated recombinant human TGF-beta 1 binding to bone matrix within rabbit skull defects. J Bone Miner Res. 1993 Nov;8(11):1407–1414. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650081115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivero F., Goya L., Pascual-Leone A. M. Comparison of extraction methods for insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins prior to measurement of insulin-like growth factor-I in undernourished neonatal and adult rat serum. J Endocrinol. 1994 Feb;140(2):257–263. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1400257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slovik D. M., Rosenthal D. I., Doppelt S. H., Potts J. T., Jr, Daly M. A., Campbell J. A., Neer R. M. Restoration of spinal bone in osteoporotic men by treatment with human parathyroid hormone (1-34) and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D. J Bone Miner Res. 1986 Aug;1(4):377–381. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650010411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontag W. Age-dependent morphometric change in the lumbar vertebrae of male and female rats: comparison with the femur. Bone. 1994 Nov-Dec;15(6):593–601. doi: 10.1016/8756-3282(94)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi Y., Kodama Y., Matsumoto T. Bone matrix decorin binds transforming growth factor-beta and enhances its bioactivity. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 23;269(51):32634–32638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam C. S., Heersche J. N., Murray T. M., Parsons J. A. Parathyroid hormone stimulates the bone apposition rate independently of its resorptive action: differential effects of intermittent and continuous administration. Endocrinology. 1982 Feb;110(2):506–512. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-2-506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapanainen J., Rönnberg L., Martikainen H., Reinilä M., Koistinen R., Seppälä M. Short and long term effects of growth hormone on circulating levels of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), IGF-binding protein-1, and insulin: a placebo-controlled study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Jul;73(1):71–74. doi: 10.1210/jcem-73-1-71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triffitt J. T., Gebauer U., Ashton B. A., Owen M. E., Reynolds J. J. Origin of plasma alpha2HS-glycoprotein and its accumulation in bone. Nature. 1976 Jul 15;262(5565):226–227. doi: 10.1038/262226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker R. F., Shipley G. D., Moses H. L., Holley R. W. Growth inhibitor from BSC-1 cells closely related to platelet type beta transforming growth factor. Science. 1984 Nov 9;226(4675):705–707. doi: 10.1126/science.6093254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOESSNER J. F., Jr The determination of hydroxyproline in tissue and protein samples containing small proportions of this imino acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 May;93:440–447. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90291-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


