Abstract
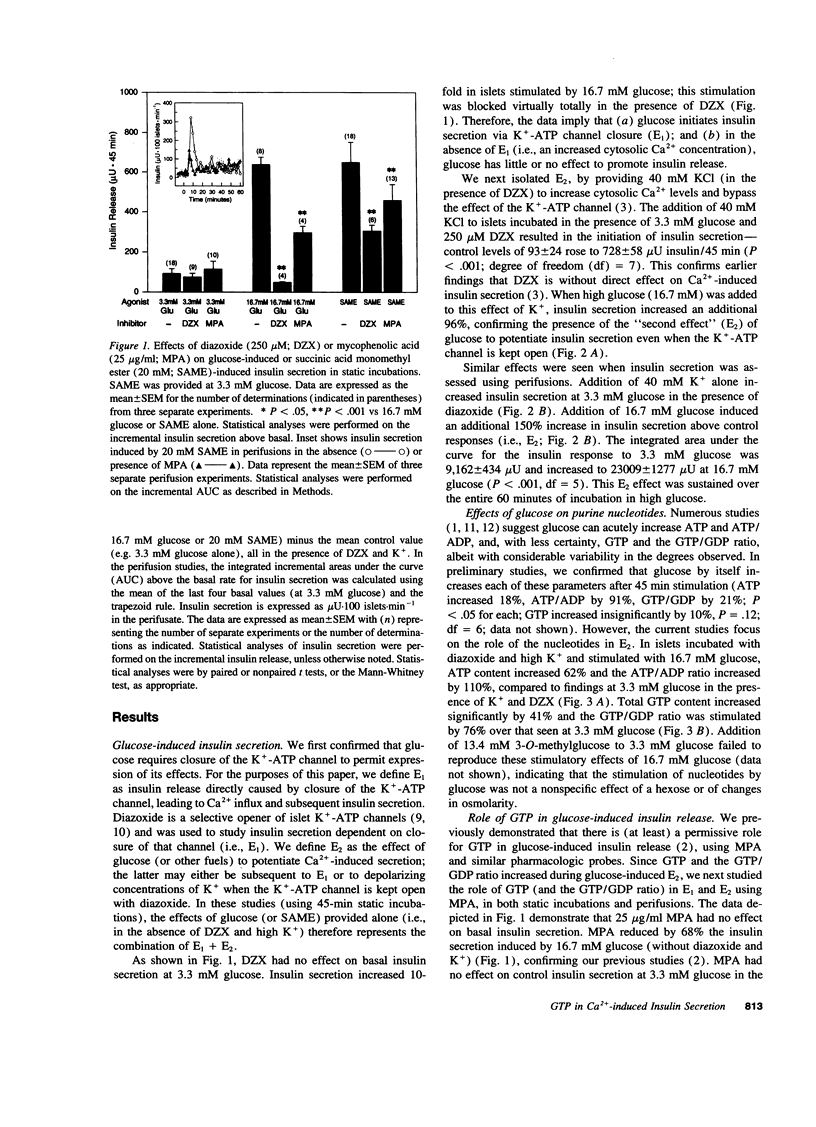
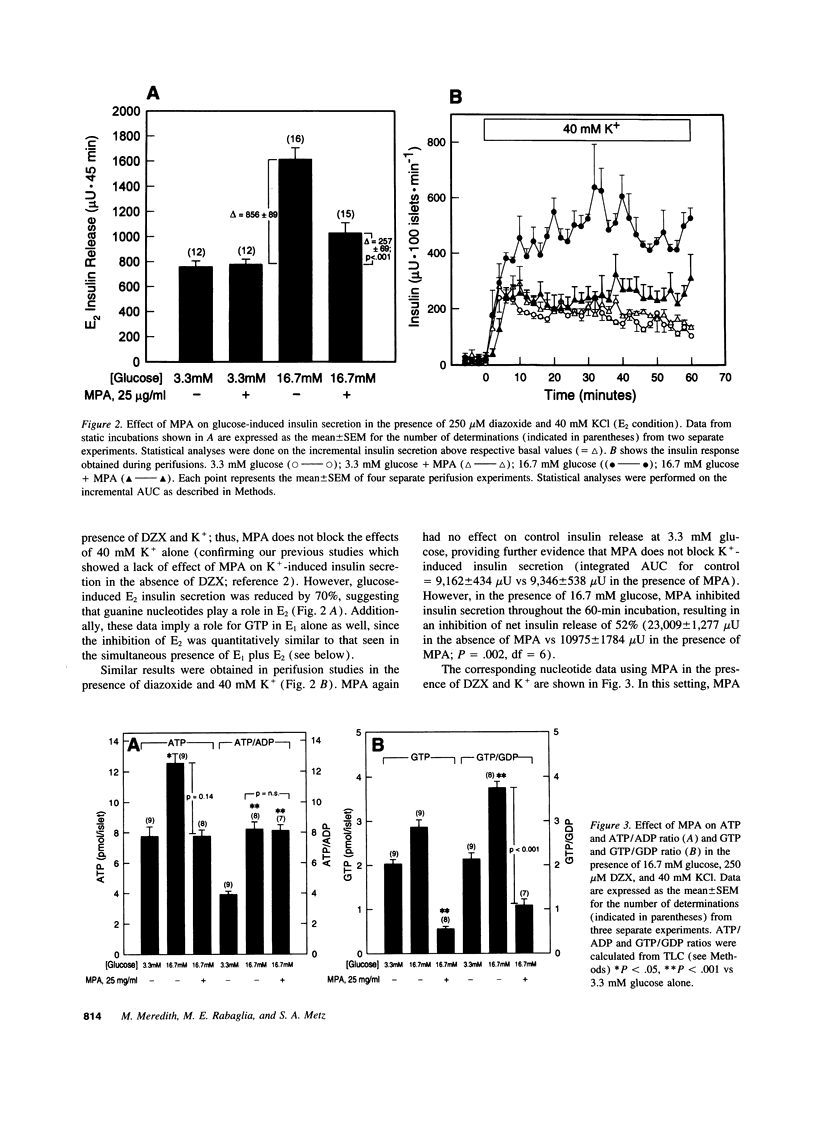
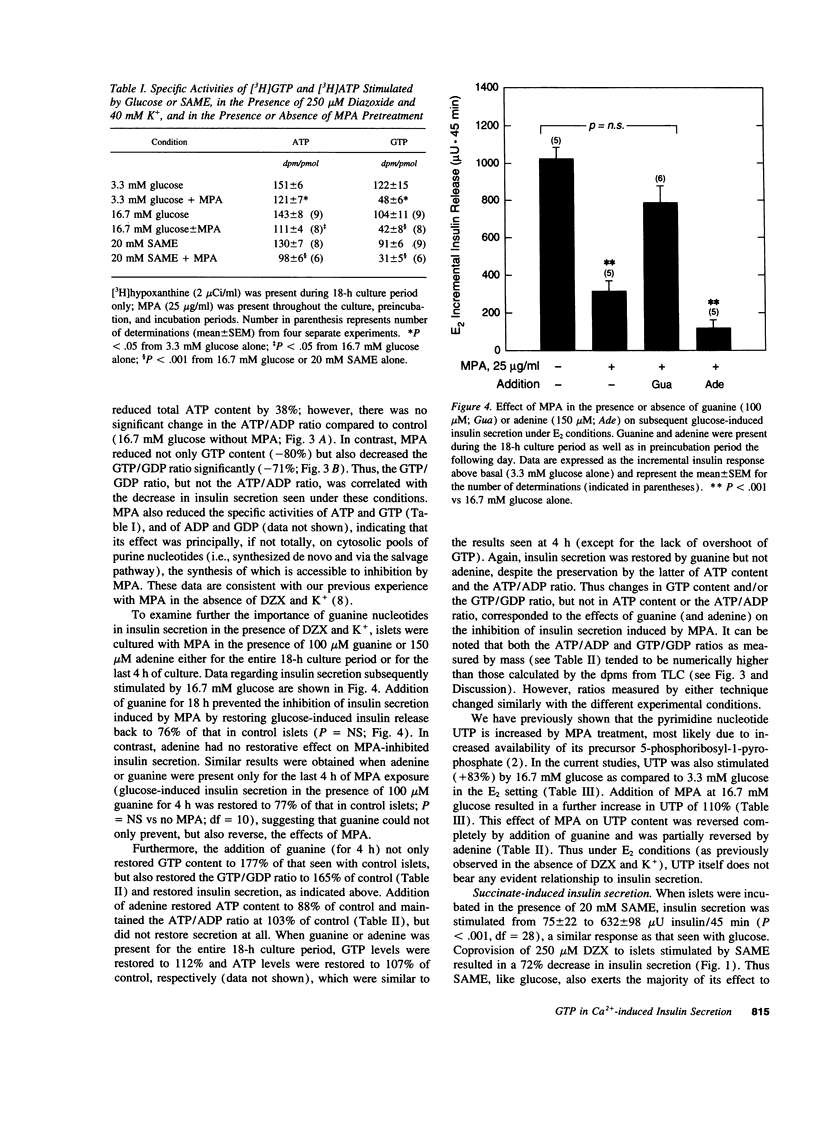
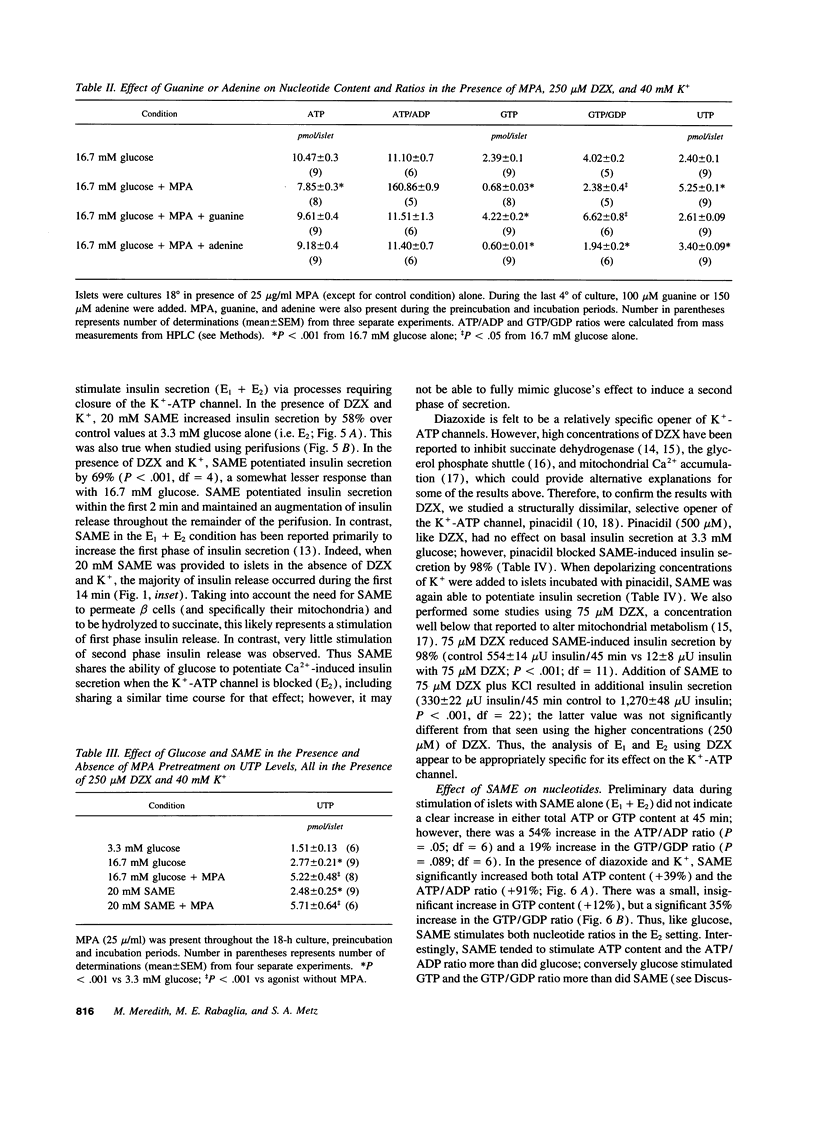
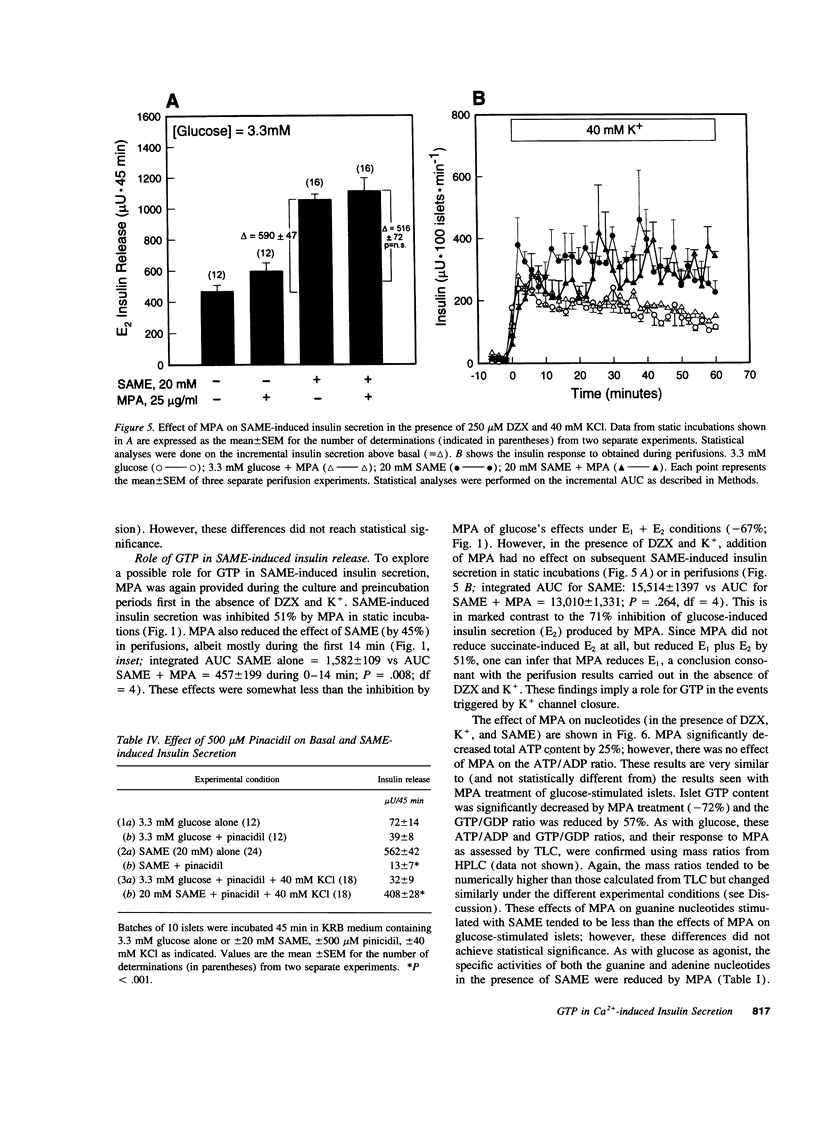
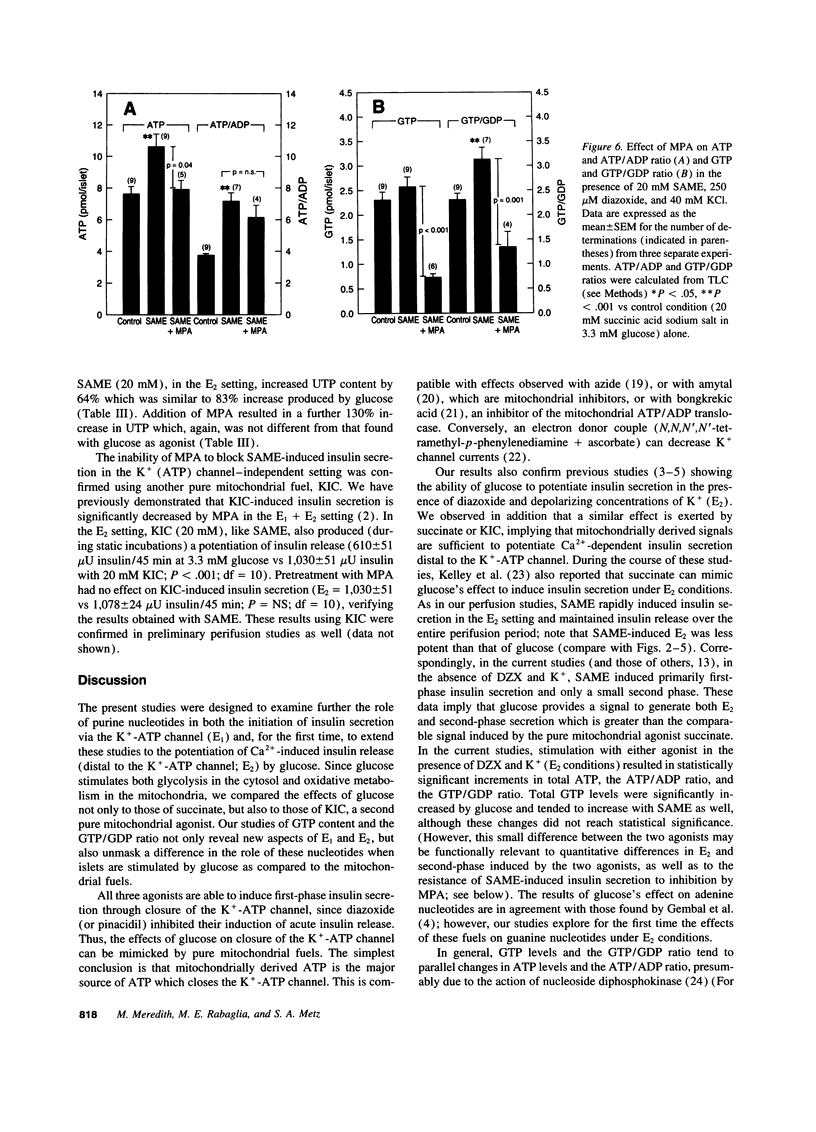
Glucose initiates insulin secretion by closing K(+)-ATP channels, leading to Ca2+ influx (E1); it also potentiates Ca(2+)-induced secretion (E2) when the K(+)-ATP channel is kept open using diazoxide and depolarizing concentrations of K+ are provided. To examine the roles of purine nucleotides in E2, we compared the effects of glucose to those of the mitochondrial fuel monomethylsuccinate. Either agonist could induce E2 accompanied by significant increases in ATP, ATP/ADP ratio, and GTP/GDP ratio; GTP increased significantly only with glucose. Mycophenolic acid (MPA), an inhibitor of cytosolic GTP synthesis, markedly inhibited glucose-induced E2 (either in perifusions or in static incubations) and decreased GTP and the GTP/GDP ratio, but did not alter the ATP/ADP ratio. Provision of guanine (but not adenine) reversed these changes pari passu. In contrast, MPA had no effect on succinate-induced E2, despite generally similar changes in nucleotides. A similar lack of effect of MPA on E2 was seen with a second mitochondrial fuel, alpha-ketoisocaproic acid (KIC). However, in the absence of diazoxide and K+, MPA blunted the secretory effects of either glucose, succinate, or KIC. These studies suggest that GTP plays a role in both glucose and succinate or KIC-induced insulin secretion at a step dependent on mitochondrial metabolism and the K(+)-ATP channel. In addition to mitochondrial effects, glucose appears to have extramitochondrial effects important to its potentiation of Ca(2+)-induced insulin secretion that are also dependent on GTP.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aizawa T., Sato Y., Ishihara F., Taguchi N., Komatsu M., Suzuki N., Hashizume K., Yamada T. ATP-sensitive K+ channel-independent glucose action in rat pancreatic beta-cell. Am J Physiol. 1994 Mar;266(3 Pt 1):C622–C627. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.266.3.C622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corkey B. E., Tornheim K., Deeney J. T., Glennon M. C., Parker J. C., Matschinsky F. M., Ruderman N. B., Prentki M. Linked oscillations of free Ca2+ and the ATP/ADP ratio in permeabilized RINm5F insulinoma cells supplemented with a glycolyzing cell-free muscle extract. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4254–4258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detimary P., Gilon P., Nenquin M., Henquin J. C. Two sites of glucose control of insulin release with distinct dependence on the energy state in pancreatic B-cells. Biochem J. 1994 Feb 1;297(Pt 3):455–461. doi: 10.1042/bj2970455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchen M. R., Smith P. A., Ashcroft F. M. Substrate-dependent changes in mitochondrial function, intracellular free calcium concentration and membrane channels in pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem J. 1993 Aug 15;294(Pt 1):35–42. doi: 10.1042/bj2940035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dukes I. D., McIntyre M. S., Mertz R. J., Philipson L. H., Roe M. W., Spencer B., Worley J. F., 3rd Dependence on NADH produced during glycolysis for beta-cell glucose signaling. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):10979–10982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dukes I. D., McIntyre M. S., Mertz R. J., Philipson L. H., Roe M. W., Spencer B., Worley J. F., 3rd Dependence on NADH produced during glycolysis for beta-cell glucose signaling. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):10979–10982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erecińska M., Bryła J., Michalik M., Meglasson M. D., Nelson D. Energy metabolism in islets of Langerhans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Aug 7;1101(3):273–295. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(92)90084-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrino M. G., Plant T. D., Henquin J. C. Effects of putative activators of K+ channels in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):957–965. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14626.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gembal M., Detimary P., Gilon P., Gao Z. Y., Henquin J. C. Mechanisms by which glucose can control insulin release independently from its action on adenosine triphosphate-sensitive K+ channels in mouse B cells. J Clin Invest. 1993 Mar;91(3):871–880. doi: 10.1172/JCI116308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gembal M., Gilon P., Henquin J. C. Evidence that glucose can control insulin release independently from its action on ATP-sensitive K+ channels in mouse B cells. J Clin Invest. 1992 Apr;89(4):1288–1295. doi: 10.1172/JCI115714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German M. S. Glucose sensing in pancreatic islet beta cells: the key role of glucokinase and the glycolytic intermediates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1781–1785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haney S. A., Broach J. R. Cdc25p, the guanine nucleotide exchange factor for the Ras proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, promotes exchange by stabilizing Ras in a nucleotide-free state. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 17;269(24):16541–16548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Charles S., Nenquin M., Mathot F., Tamagawa T. Diazoxide and D600 inhibition of insulin release. Distinct mechanisms explain the specificity for different stimuli. Diabetes. 1982 Sep;31(9):776–783. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.9.776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoenig M., Matschinsky F. M. HPLC analysis of nucleotide profiles in glucose-stimulated perifused rat islets. Metabolism. 1987 Mar;36(3):295–301. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(87)90192-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. C., Molday R. S. Glucose metabolism in photoreceptor outer segments. Its role in phototransduction and in NADPH-requiring reactions. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 8;269(27):17954–17959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas J. C., Li G., Palmer M., Weller U., Wollheim C. B. Dynamics of Ca2+ and guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate action on insulin secretion from alpha-toxin-permeabilized HIT-T15 cells. Biochem J. 1994 Jul 15;301(Pt 2):523–529. doi: 10.1042/bj3010523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley G. G., Zawalich K. C., Zawalich W. S. Calcium and a mitochondrial signal interact to stimulate phosphoinositide hydrolysis and insulin secretion in rat islets. Endocrinology. 1994 Apr;134(4):1648–1654. doi: 10.1210/endo.134.4.8137727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiranadi B., Bangham J. A., Smith P. A. Inhibition of electrical activity in mouse pancreatic beta-cells by the ATP/ADP translocase inhibitor, bongkrekic acid. FEBS Lett. 1991 May 20;283(1):93–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80561-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowluru A., Metz S. A. Characterization of nucleoside diphosphokinase activity in human and rodent pancreatic beta cells: evidence for its role in the formation of guanosine triphosphate, a permissive factor for nutrient-induced insulin secretion. Biochemistry. 1994 Oct 18;33(41):12495–12503. doi: 10.1021/bi00207a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauquin G. J., Villiers C., Michejda J. W., Hryniewiecka L. V., Vignais P. V. Adenine nucleotide transport in sonic submitochondrial particles. Kinetic properties and binding of specific inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 11;460(2):331–345. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrun P., Devreux V., Hermann M., Herchuelz A. Similarities between the effects of pinacidil and diazoxide on ionic and secretory events in rat pancreatic islets. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Sep;250(3):1011–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclercq-Meyer V., Malaisse W. J. Enhancement by succinic acid dimethyl ester of insulin release evoked by D-glucose and glimepiride in the perfused pancreas of normoglycemic and hyperglycemic rats. Biochem Pharmacol. 1994 Apr 29;47(9):1519–1524. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(94)90526-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitner J. W., Sussman K. E., Vatter A. E., Schneider F. H. Adenine nucleotides in the secretory granule fraction of rat islets. Endocrinology. 1975 Mar;96(3):662–677. doi: 10.1210/endo-96-3-662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenzen S., Panten U. Characterization of succinate dehydrogenase and alpha-glycerophosphate dehydrogenase in pancreatic islets. Biochem Med. 1983 Dec;30(3):349–356. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(83)90027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. J. Elusive proximal signals of beta-cells for insulin secretion. Diabetes. 1990 Dec;39(12):1461–1466. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.12.1461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. J., Fahien L. A. Glyceraldehyde phosphate and methyl esters of succinic acid. Two "new" potent insulin secretagogues. Diabetes. 1988 Jul;37(7):997–999. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.7.997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. J. High content of mitochondrial glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in pancreatic islets and its inhibition by diazoxide. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8287–8290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. J. The use of calcium uptake by small amounts of mitochondria from pancreatic islets to study mitochondrial respiration: the effects of diazoxide and sodium. Biochem Int. 1984 Jun;8(6):771–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meglasson M. D., Nelson J., Nelson D., Erecinska M. Bioenergetic response of pancreatic islets to stimulation by fuel molecules. Metabolism. 1989 Dec;38(12):1188–1195. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(89)90158-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meglasson M. D., Smith K. M., Nelson D., Erecinska M. alpha-Glycerophosphate shuttle in a clonal beta-cell line. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jan;256(1 Pt 1):E173–E178. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.256.1.E173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz S. A. Exogenous arachidonic acid promotes insulin release from intact or permeabilized rat islets by dual mechanisms. Putative activation of Ca2+ mobilization and protein kinase C. Diabetes. 1988 Nov;37(11):1453–1469. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.11.1453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz S. A., Meredith M., Rabaglia M. E., Kowluru A. Small elevations of glucose concentration redirect and amplify the synthesis of guanosine 5'-triphosphate in rat islets. J Clin Invest. 1993 Aug;92(2):872–882. doi: 10.1172/JCI116662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz S. A., Rabaglia M. E., Pintar T. J. Selective inhibitors of GTP synthesis impede exocytotic insulin release from intact rat islets. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12517–12527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta M., Nelson D., Nelson J., Meglasson M. D., Erecińska M. Oxygen and temperature dependence of stimulated insulin secretion in isolated rat islets of Langerhans. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17525–17532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimers H. J., Mustard J. F., Packham M. A. Transfer of adenine nucleotides between the releasable and nonreleasable compartments of rabbit blood platelets. J Cell Biol. 1975 Oct;67(1):61–71. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwanstecher C., Dickel C., Panten U. Interaction of tolbutamide and cytosolic nucleotides in controlling the ATP-sensitive K+ channel in mouse beta-cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jan;111(1):302–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14060.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer G., Portenhauser R., Trolp R. Inhibition of mitochondrial metabolism by the diabetogenic thiadiazine diazoxide. I. Action on succinate dehydrogenase and TCA-cycle oxidations. Biochem Pharmacol. 1971 Jun;20(6):1271–1280. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(71)90358-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallar L., Biden T. J., Wollheim C. B. Guanine nucleotides induce Ca2+-independent insulin secretion from permeabilized RINm5F cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5049–5056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waygood E. B., Sanwal B. D. The control of pyruvate kinases of Escherichia coli. I. Physicochemical and regulatory properties of the enzyme activated by fructose 1,6-diphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):265–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidemann M. J., Erdelt H., Klingenberg M. Adenine nucleotide translocation of mitochondria. Identification of carrier sites. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Oct;16(2):313–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01086.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawalich W. S., Zawalich K. C., Cline G., Shulman G., Rasmussen H. Comparative effects of monomethylsuccinate and glucose on insulin secretion from perifused rat islets. Diabetes. 1993 Jun;42(6):843–850. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.6.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


