Abstract
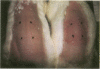
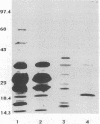
Erythema migrans (EM), persistent skin infection, and visceral dissemination can be induced reproducibly in the adult male New Zealand White rabbit by intradermal injection of as few as 10(3) Borrelia burgdorferi. EM was found to persist for 7 +/- 3 d. Skin culture positivity (infection) cleared within a mean of 6.7 +/- 1.4 wk after infection and similarly visceral infection was not demonstrated after 8 wk; infection-derived immunity to intradermal challenge was evident 5 mo after initial infection. The extent of the protection against EM and dermal infection induced by untreated infection was directly related to the extent of prior in vitro passage of the B31 strain. Initial infection with as few as 4 x 10(3) B31 passage 4 induced complete protection against EM and skin infection upon subsequent challenge with 4 x 10(7) B31, passage 4. Initial infection with B31 passage 27 led to partial protection against EM along with complete protection against skin infection. Initial infection with passage 47 led to partial protection against EM, but conferred no protection against skin infection. Using serum from rabbits fully immune to reinfection, we defined a set of B. burgdorferi proteins present in virulent B31, but absent in the avirulent American Type Culture Collection B31 strain, termed "va" for virulent strain associated. The va proteins of B31 passages 1, 27, and 47 differed strikingly, thus raising the possibility that these changes may relate in a causal way to the differences in induction of protective immunity observed.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Beck D. S., Hansen G. M., Terwilliger G. A., Moody K. D. Lyme borreliosis in selected strains and ages of laboratory mice. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):133–138. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Moody K. D., Terwilliger G. A., Duray P. H., Jacoby R. O., Steere A. C. Experimental Lyme arthritis in rats infected with Borrelia burgdorferi. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):842–846. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., de Souza M. S., Janotka J. L., Smith A. L., Persing D. H. Chronic Lyme borreliosis in the laboratory mouse. Am J Pathol. 1993 Sep;143(3):959–971. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duray P. H. Histopathology of clinical phases of human Lyme disease. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1989 Nov;15(4):691–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman J. L., Jurkovich P., Kodner C., Johnson R. C. Persistent cardiac and urinary tract infections with Borrelia burgdorferi in experimentally infected Syrian hamsters. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 May;29(5):894–896. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.5.894-896.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Marek N., Kodner C. Infection of Syrian hamsters with Lyme disease spirochetes. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1099–1101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1099-1101.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblatt A. N., Steere A. C., Brownstein D. G. Experimental Lyme disease in rabbits: spirochetes found in erythema migrans and blood. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):220–223. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.220-223.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krinsky W. L., Brown S. J., Askenase P. W. Ixodes dammini: induced skin lesions in guinea pigs and rabbits compared to erythema chronicum migrans in patients with lyme arthritis. Exp Parasitol. 1982 Jun;53(3):381–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(82)90081-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logigian E. L., Kaplan R. F., Steere A. C. Chronic neurologic manifestations of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1990 Nov 22;323(21):1438–1444. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199011223232102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody K. D., Barthold S. W., Terwilliger G. A., Beck D. S., Hansen G. M., Jacoby R. O. Experimental chronic Lyme borreliosis in Lewis rats. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1990 Feb;42(2):165–174. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1990.42.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody K. D., Barthold S. W., Terwilliger G. A. Lyme borreliosis in laboratory animals: effect of host species and in vitro passage of Borrelia burgdorferi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1990 Jul;43(1):87–92. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1990.43.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J., Carter C. J., Howell J. K., Barbour A. G. Low-passage-associated proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi B31: characterization and molecular cloning of OspD, a surface-exposed, plasmid-encoded lipoprotein. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4662–4672. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4662-4672.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipp M. T., Aydintug M. K., Bohm R. P., Jr, Cogswell F. B., Dennis V. A., Lanners H. N., Lowrie R. C., Jr, Roberts E. D., Conway M. D., Karaçorlu M. Early and early disseminated phases of Lyme disease in the rhesus monkey: a model for infection in humans. Infect Immun. 1993 Jul;61(7):3047–3059. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.7.3047-3059.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preac Mursic V., Patsouris E., Wilske B., Reinhardt S., Gross B., Mehraein P. Persistence of Borrelia burgdorferi and histopathological alterations in experimentally infected animals. A comparison with histopathological findings in human Lyme disease. Infection. 1990 Nov-Dec;18(6):332–341. doi: 10.1007/BF01646399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidli J., Hunziker T., Moesli P., Schaad U. B. Cultivation of Borrelia burgdorferi from joint fluid three months after treatment of facial palsy due to Lyme borreliosis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):905–906. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J. L., Schell R. F., Hejka A., England D. M., Konick L. Induction of lyme arthritis in LSH hamsters. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2336–2342. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2336-2342.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W., Garon C. F. Changes in infectivity and plasmid profile of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, as a result of in vitro cultivation. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1831–1836. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1831-1836.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W., Schrumpf M. E., Karstens R. H. The urinary bladder, a consistent source of Borrelia burgdorferi in experimentally infected white-footed mice (Peromyscus leucopus). J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):893–895. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.893-895.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnesyn S. W., Manivel J. C., Johnson R. C., Goodman J. L. A guinea pig model for Lyme disease. Infect Immun. 1993 Nov;61(11):4777–4784. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.11.4777-4784.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanek G., Klein J., Bittner R., Glogar D. Isolation of Borrelia burgdorferi from the myocardium of a patient with longstanding cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jan 25;322(4):249–252. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199001253220407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E., Hardin J. A., Ruddy S., Askenase W., Andiman W. A. Erythema chronicum migrans and Lyme arthritis. The enlarging clinical spectrum. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Jun;86(6):685–698. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-6-685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Göbel U. B., Graf B., Jauris S., Soutschek E., Schwab E., Zumstein G. An OspA serotyping system for Borrelia burgdorferi based on reactivity with monoclonal antibodies and OspA sequence analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Feb;31(2):340–350. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.2.340-350.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]