Abstract
An ion-pair, reversed-phase, high-pressure liquid chromatographic method for the analysis of penicillin N ring expansion activity has been developed which allows simultaneous measurement of both substrate and product. The high-pressure liquid chromatography conditions were as follows: stationary phase, C18; flow rate, 2 ml/min; detection, 220 nm. The stationary phase was preconditioned with 4.5 mM tetrabutylammonium bromide in 0.05 M KH2PO4 (pH 4.0)-methanol (85:15, vol/vol) and then equilibrated with 0.06 mM tetrabutylammonium bromide in 0.05 M KH2PO4 (pH 4.0)-methanol (95:5, vol/vol) for analysis of reaction mixtures. These conditions separated authentic samples of penicillin N and desacetoxycephalosporin C and allowed cell-free studies of the ring expansion of penicillin N to desacetoxycephalosporin C by a partially purified enzyme from Streptomyces clavuligerus to be followed conveniently.
Full text
PDF
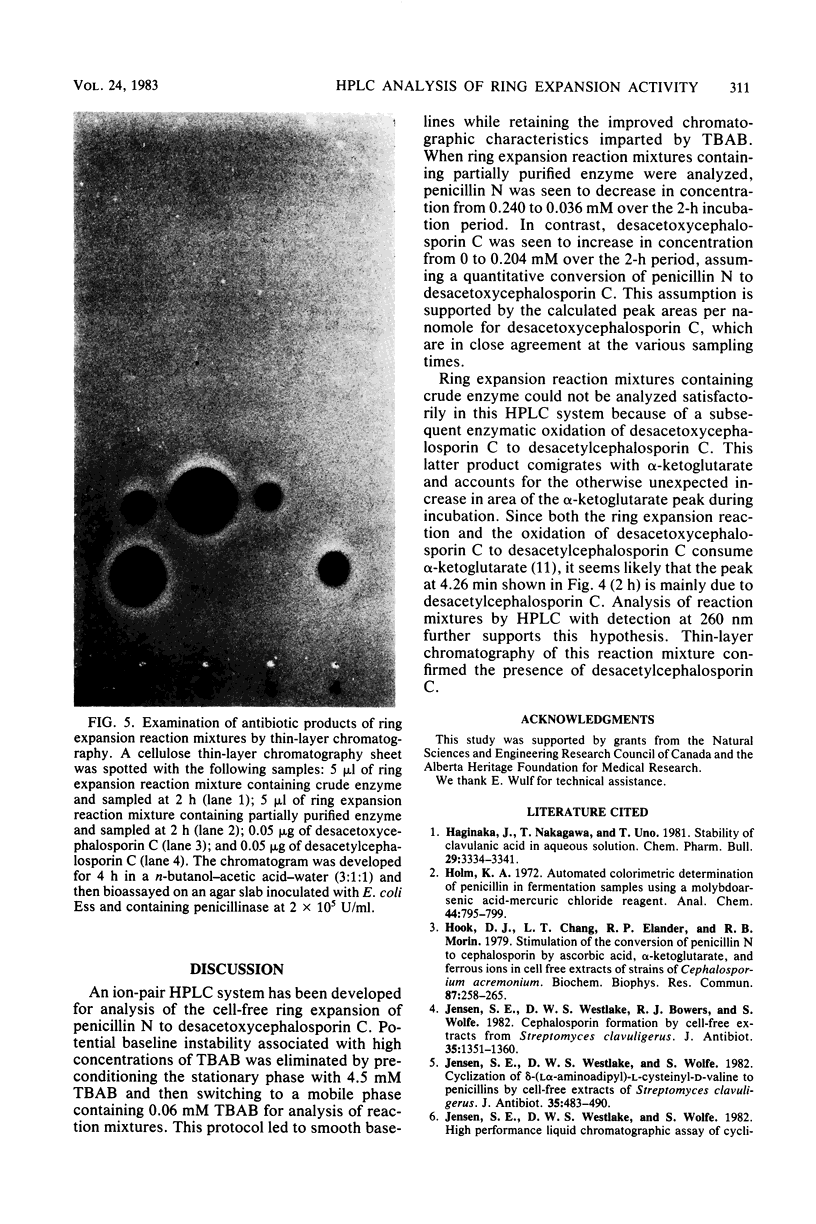

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Holm K. A. Automated colorimetric determination of penicillin in fermentation samples using a molybdoarsenic acid-mercuric chloride reagent. Anal Chem. 1972 Apr;44(4):796–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook D. J., Chang L. T., Elander R. P., Morin R. B. Stimulation of the conversion of penicillin N to cephalosporin by ascorbic acid, alpha-ketoglutarate, and ferrous ions in cell-free extracts of strains of Cephalosporium acremonium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Mar 15;87(1):258–265. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91674-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen S. E., Westlake D. W., Bowers R. J., Wolfe S. Cephalosporin formation by cell-free extracts from Streptomyces clavuligerus. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1982 Oct;35(10):1351–1360. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.35.1351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen S. E., Westlake D. W., Wolfe S. Cyclization of delta-(L-alpha-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine to penicillins by cell-free extracts of Streptomyces clavuligerus. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1982 Apr;35(4):483–490. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.35.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohsaka M., Demain A. L. Conversion of penicillin N to cephalosporin(s) by cell-free extracts of Cephalosporium acremonium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 17;70(2):465–473. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91069-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupka J., Shen Y. Q., Wolfe S., Demain A. L. Studies on the ring-cyclization and ring-expansion enzymes of beta-lactam biosynthesis in Cephalosporium acremonium. Can J Microbiol. 1983 May;29(5):488–496. doi: 10.1139/m83-078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. D., Huckstep L. L., McDermott J. P., Queener S. W., Kukolja S., Spry D. O., Elzey T. K., Lawrence S. M., Neuss N. High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) of natural products. IV. The use of HPLC in biosynthetic studies of cephalosporin C in the cell-free system. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1981 Aug;34(8):984–993. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.34.984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. D., Neuss N. High performance liquid chromatography of natural products. II. Direct biological correlation of components in the fermentation broth. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1978 Nov;31(11):1132–1136. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.31.1132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner M. K., Farthing J. E., Brewer S. J. The oxygenation of [3-methyl-3H]desacetoxycephalosporin C [7beta-(5-D-aminadipamido)-3-methylceph-3-em-4-carboxylic acid] to [3-hydroxymethyl-3H]desacetylcephalosporin C by 2-oxoglutarate-linked dioxygenases from Acremonium chrysogenum and Streptomyces clavuligerus. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 1;173(3):839–850. doi: 10.1042/bj1730839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]