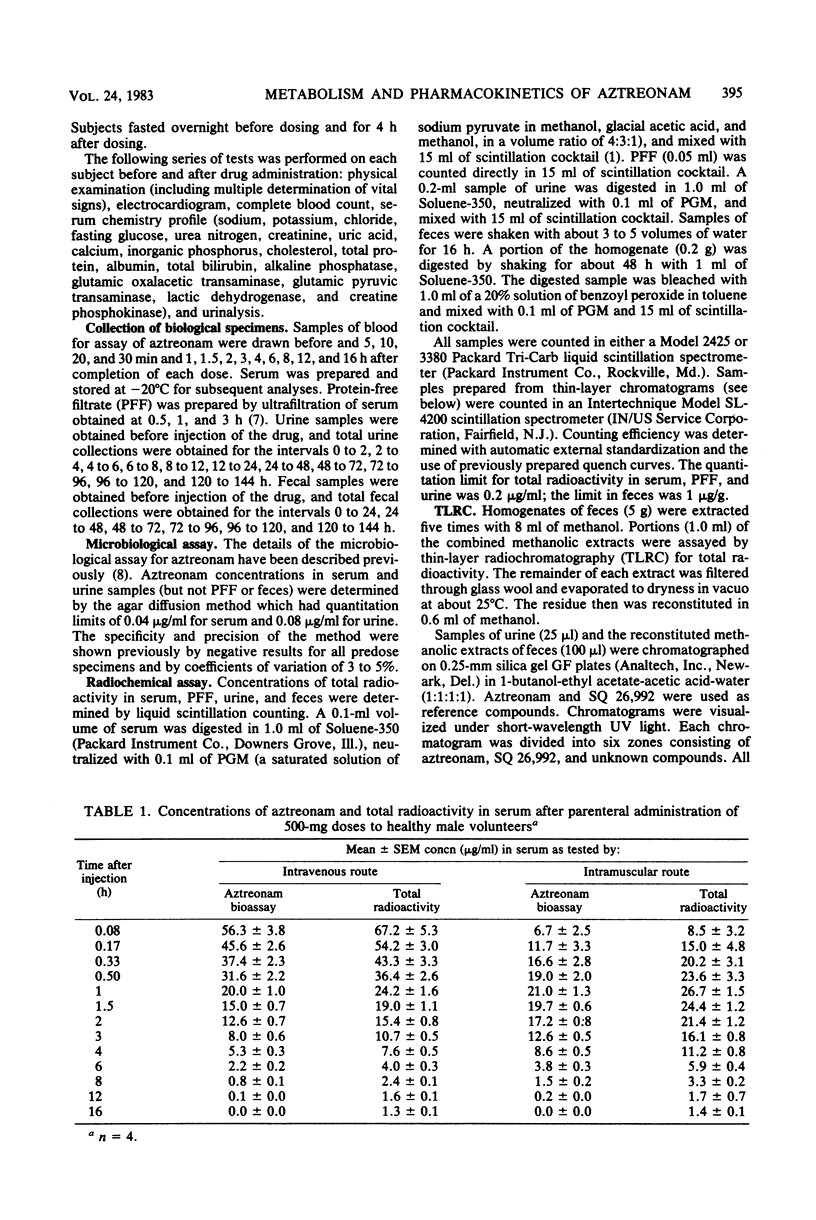
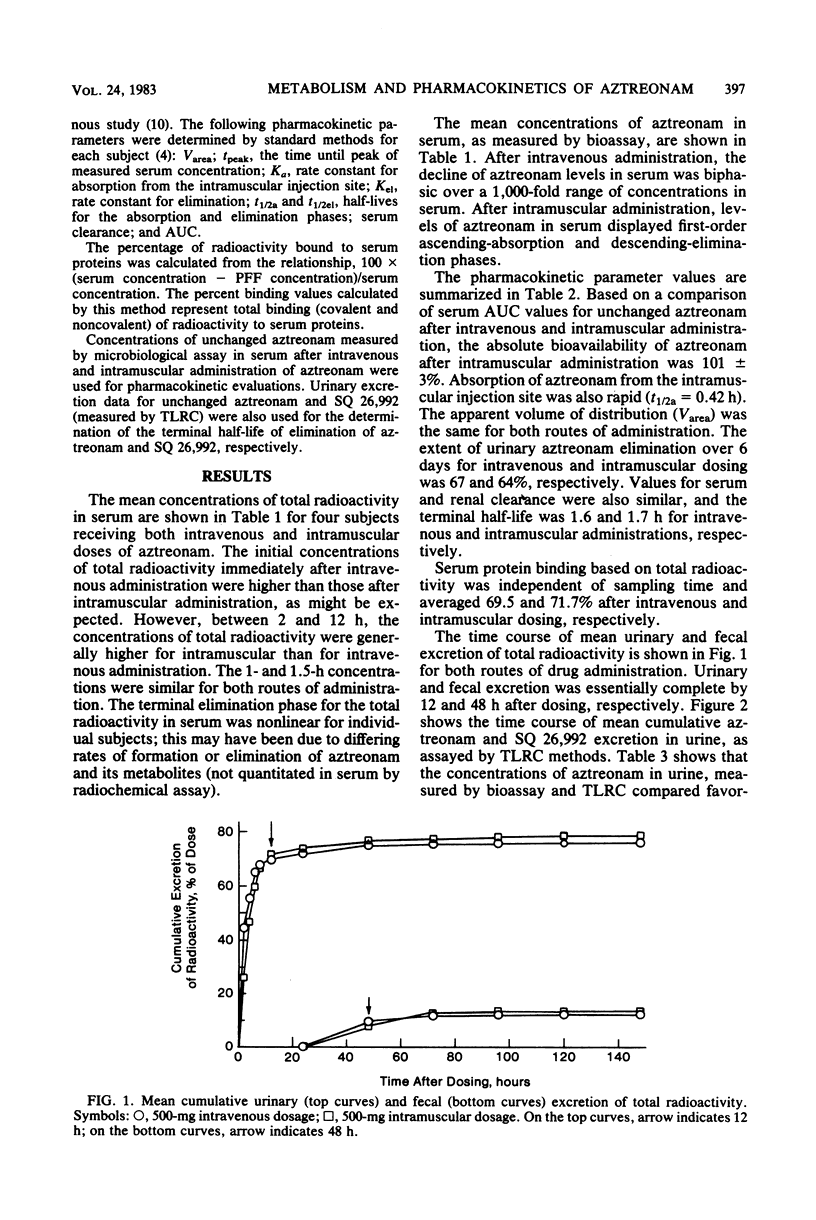
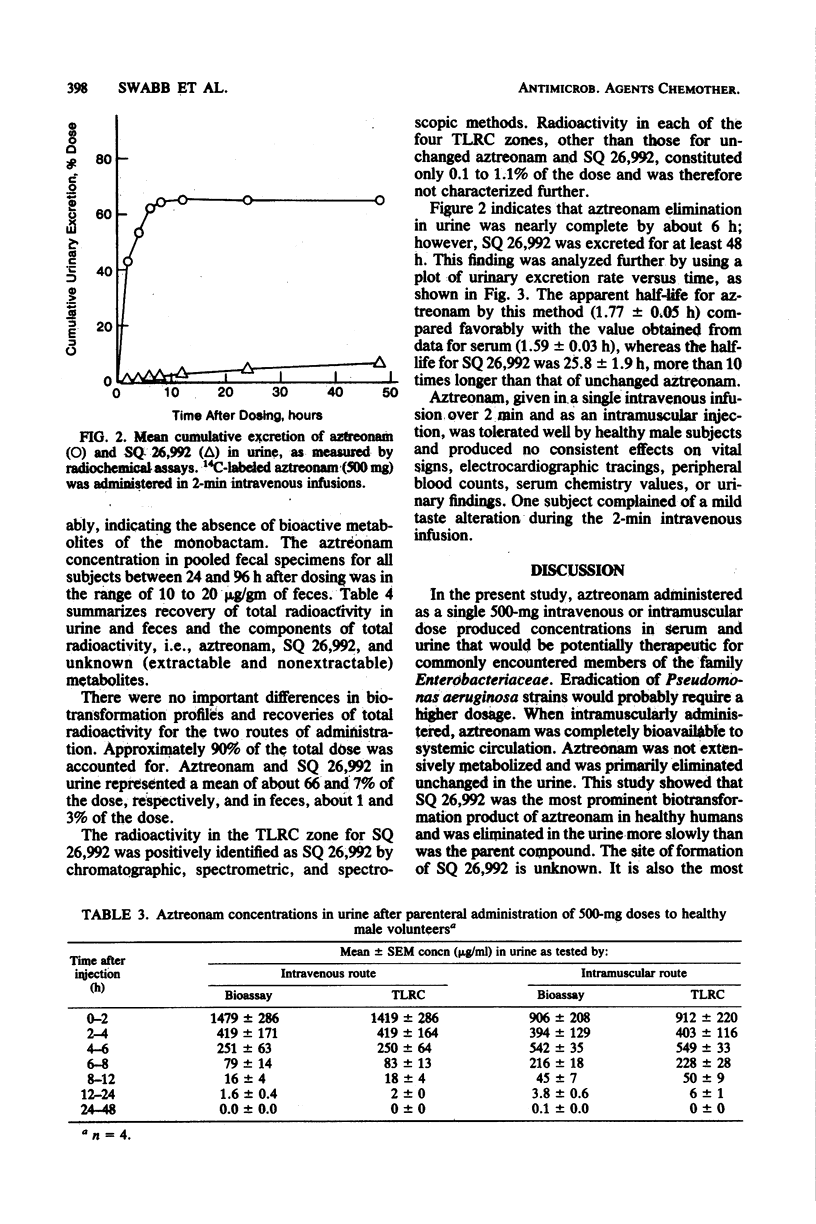
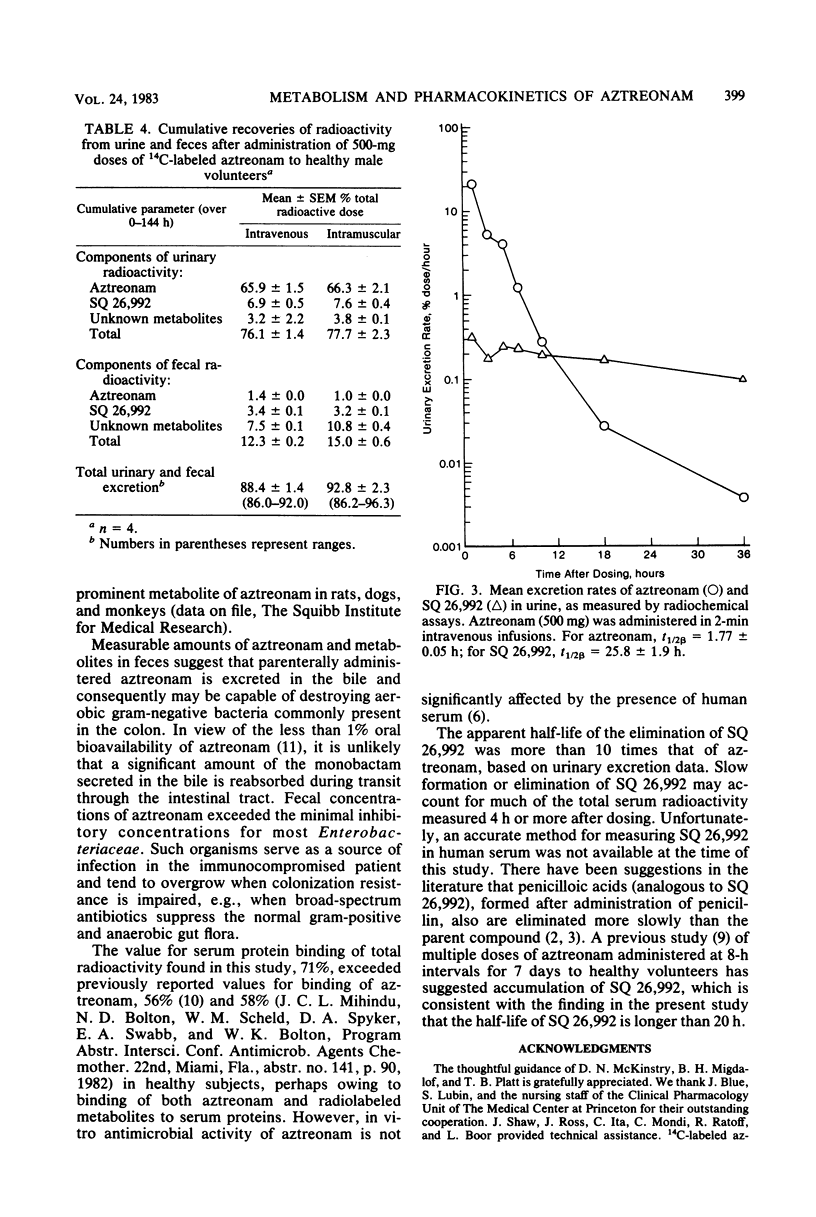
Abstract
The metabolism and pharmacokinetics of aztreonam (SQ 26,776) were studied in four healthy male volunteers, each of whom received single 500-mg intravenous and intramuscular doses of 14C-labeled drug according to a two-way crossover design. Serial samples of serum, urine, and feces were assayed for aztreonam and metabolites. Serum pharmacokinetics of aztreonam administered intravenously were described by an open, linear, two-compartment kinetic model. Kinetics of intramuscular aztreonam followed a one-compartment model with first-order absorption and elimination. Intramuscular bioavailability was 100%. After either intravenous or intramuscular administration, aztreonam was eliminated primarily by urinary excretion of unchanged drug (about 66% of dose), whereas only 1% of the dose was found as unchanged drug in the feces, presumably owing to biliary secretion. The average elimination half-life of aztreonam was 1.6 and 1.7 h, respectively, for intravenous and intramuscular administration. Aztreonam did not undergo extensive metabolism; the most prominent biotransformation product of aztreonam was SQ 26,992, the compound resulting from the hydrolytic opening of the beta-lactam ring. Urinary and fecal SQ 26,992 constituted 7 and 3% of the administered dose, respectively. SQ 26,992 was eliminated at a considerably slower rate than was aztreonam.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson L. E., McClure W. O. An improved scintillation cocktail of high-solubilizing power. Anal Biochem. 1973 Jan;51(1):173–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90465-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birner J. Determination of phenoxymethyl penicilloic acid and phenoxyethyl penicilloic acid in urine in the presence of the parent penicillins. J Pharm Sci. 1970 Jun;59(6):757–760. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600590606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M., Kenig M. D., Hewitt V. A. Metabolism of penicillins to penicilloic acids and 6-aminopenicillanic acid in man and its significance in assessing penicillin absorption. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Apr;3(4):463–468. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.4.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Labthavikul P. Antibacterial activity of a monocyclic beta-lactam SQ 26,776. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):111–122. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swabb E. A., Leitz M. A., Pilkiewicz F. G., Sugerman A. A. Pharmacokinetics of the monobactam SQ 26,776 after single intravenous doses in healthy subjects. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):131–140. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swabb E. A., Sugerman A. A., McKinstry D. N. Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of the monobactam azthreonam (SQ 26,776) in healthy subjects. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jan;23(1):125–132. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swabb E. A., Sugerman A. A., Platt T. B., Pilkiewicz F. G., Frantz M. Single-dose pharmacokinetics of the monobactam azthreonam (SQ 26,776) in healthy subjects. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jun;21(6):944–949. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.6.944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swabb E. A., Sugerman A. A., Stern M. Oral bioavailability of the monobactam aztreonam (SQ 26,776) in healthy subjects. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Apr;23(4):548–550. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.4.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


