Abstract
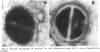
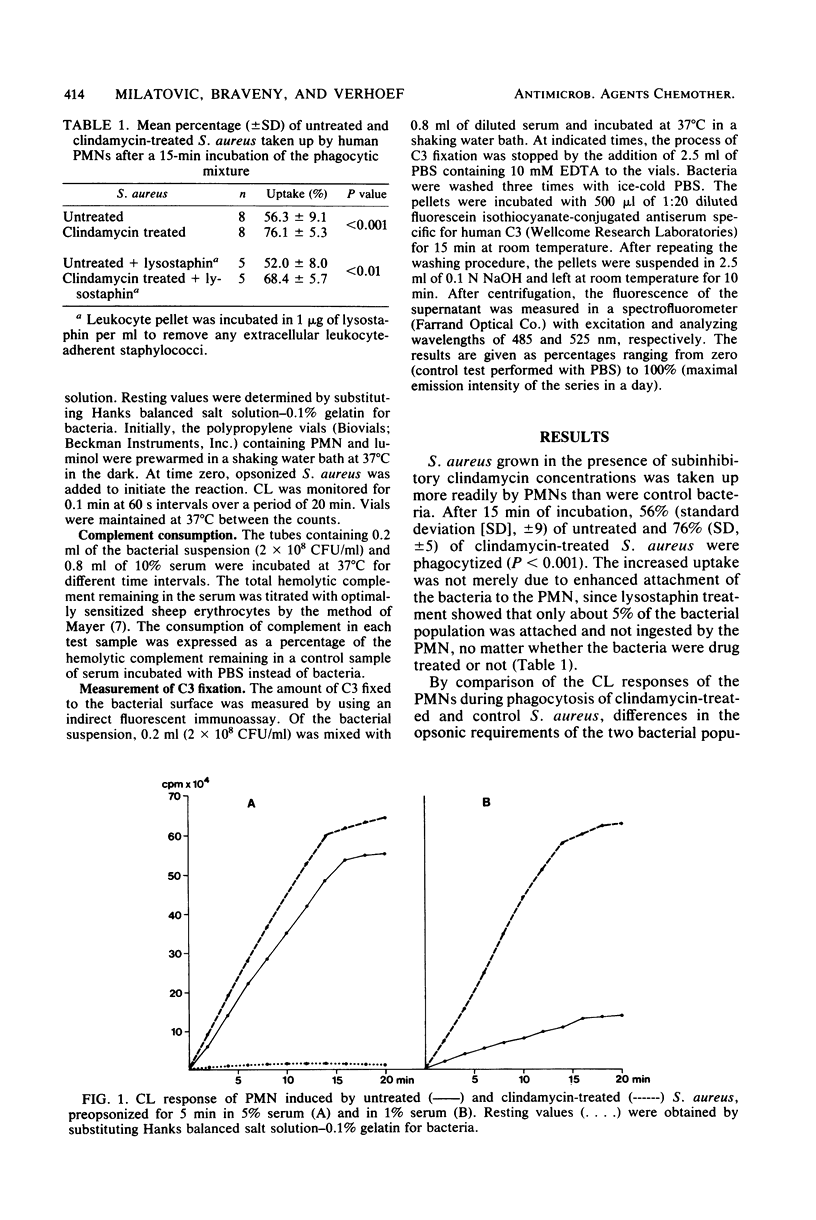
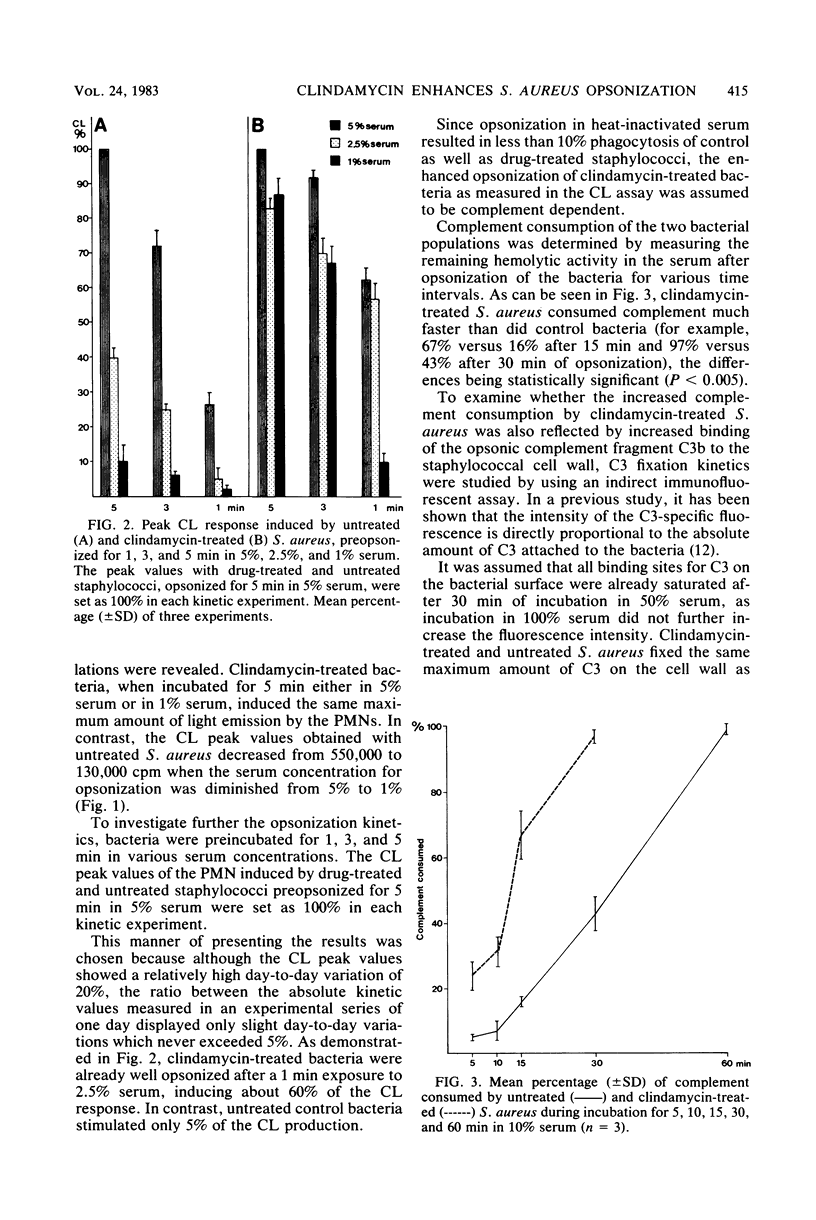
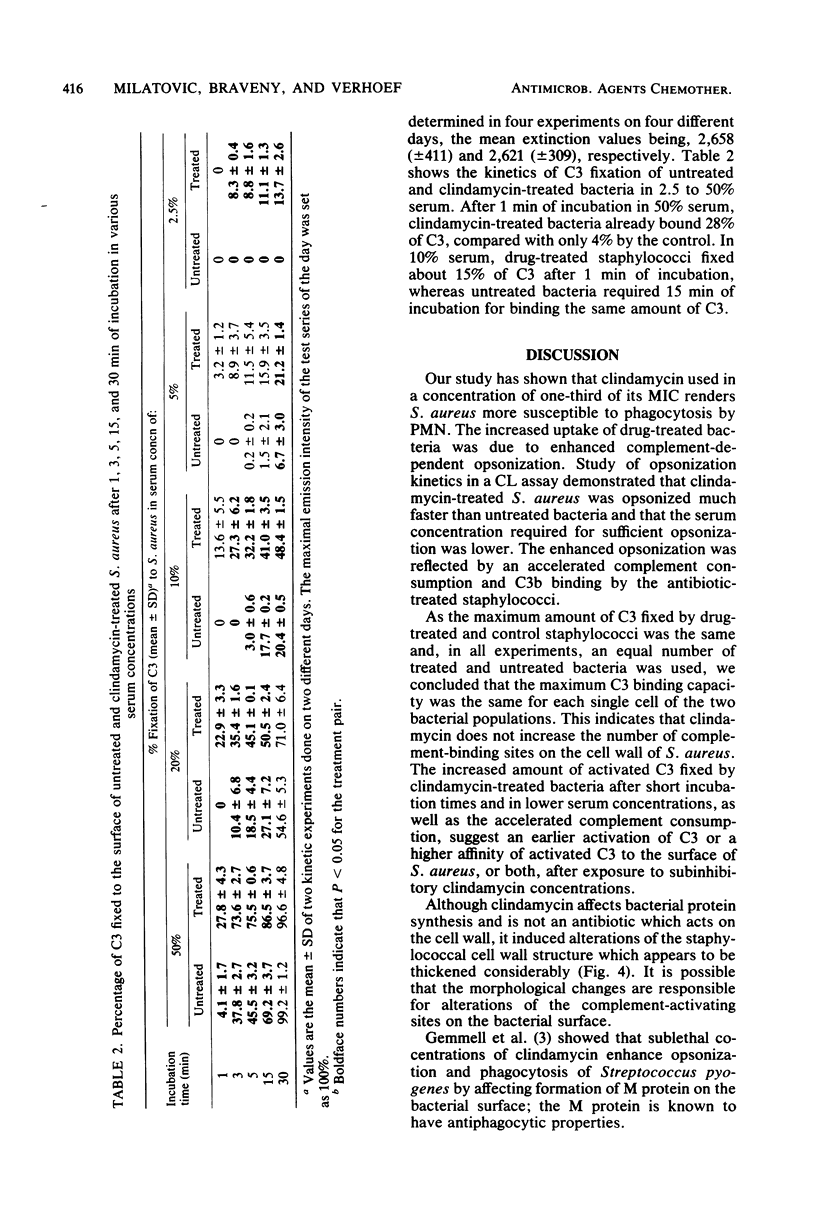
Staphylococcus aureus 502A was grown in the presence of one-third of the minimal inhibitory concentration of clindamycin. Phagocytosis of the antibiotic-treated bacteria by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes was significantly enhanced, compared with that of the untreated control (P less than 0.001). Study of opsonization kinetics by a chemiluminescence assay demonstrated that clindamycin-treated staphylococci were opsonized more rapidly than control bacteria and that the serum concentration required for sufficient opsonization was lower. Complement was consumed much faster, and the opsonic fragment C3b was fixed more rapidly to the bacterial surface when the staphylococci were preincubated with clindamycin. Electron micrographs showed an alteration of the staphylococcal cell wall after clindamycin treatment.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam D., Schaffert W., Marget W. Enhanced in vitro phagocytosis of Listeria monocytogenes by human monocytes in the presence of ampicillin, tetracycline, and chloramphenicol. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):811–814. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.811-814.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman H., Warren G. H. Enhanced susceptibility of penicillin-resistant staphylococci to phagocytosis after in vitro incubation with low doses of nafcillin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Jul;146(3):707–711. doi: 10.3181/00379727-146-38177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemmell C. G., Peterson P. K., Schmeling D., Kim Y., Mathews J., Wannamaker L., Quie P. G. Potentiation of opsonization and phagocytosis of Streptococcus pyogenes following growth in the presence of clindamycin. J Clin Invest. 1981 May;67(5):1249–1256. doi: 10.1172/JCI110152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser W. E., Jr, Remington J. S. Effect of antibiotics on the immune response. Am J Med. 1982 May;72(5):711–716. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90534-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne D., Tomasz A. Hypersusceptibility of penicillin-treated group B streptococci to bactericidal activity of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):745–753. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell L. A. Effects of antimicrobial and antineoplastic drugs on the phagocytic and microbicidal function of the polymorphonuclear leukocyte. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 May-Jun;4(3):683–697. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.3.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald P. J., Wetherall B. L., Pruul H. Postantibiotic leukocyte enhancement: increased susceptibility of bacteria pretreated with antibiotics to activity of leukocytes. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Jan-Feb;3(1):38–44. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milatovic D., Braveny I. Wechselwirkungen zwischen Antibiotika und Phagozytose. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1982 Dec 24;107(51-52):1975–1979. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1070244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milatović D. Effect of subinhibitory antibiotic concentrations on the phagocytosis of Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;1(2):97–101. doi: 10.1007/BF02014199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Isturiz R., Molavi A., Metcalf J. A., Malech H. L. Interactions between antibiotics and human neutrophils in the killing of staphylococci. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jan;67(1):247–259. doi: 10.1172/JCI110020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., van Dijk W. C., van Erne M. E., Peters R., Peterson P. K., Verhoef J. Quantitation of the third component of human complement attached to the surface of opsonized bacteria: opsonin-deficient sera and phagocytosis-resistant strains. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):808–814. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.808-814.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef J., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G. Kinetics of staphylococcal opsonization, attachment, ingestion and killing by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: a quantitative assay using [3H]thymidine labeled bacteria. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(3-4):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]