Abstract
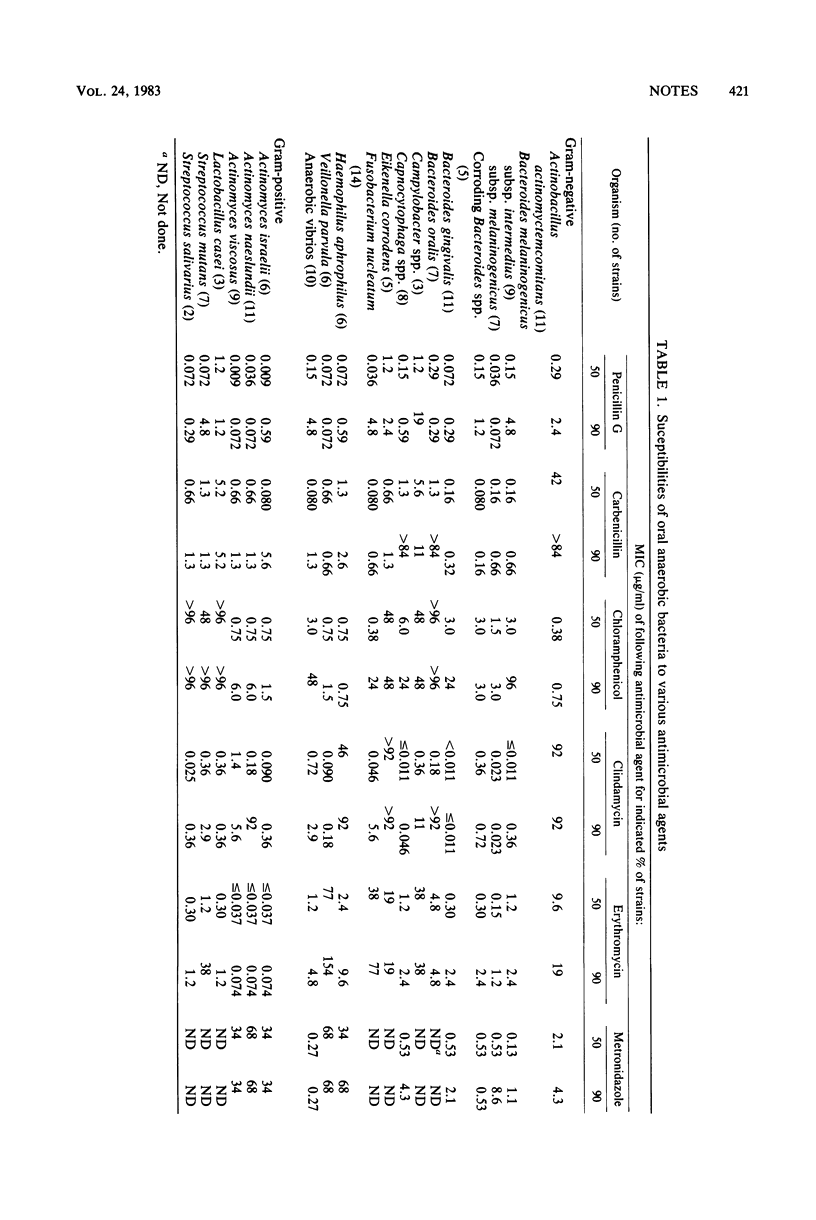
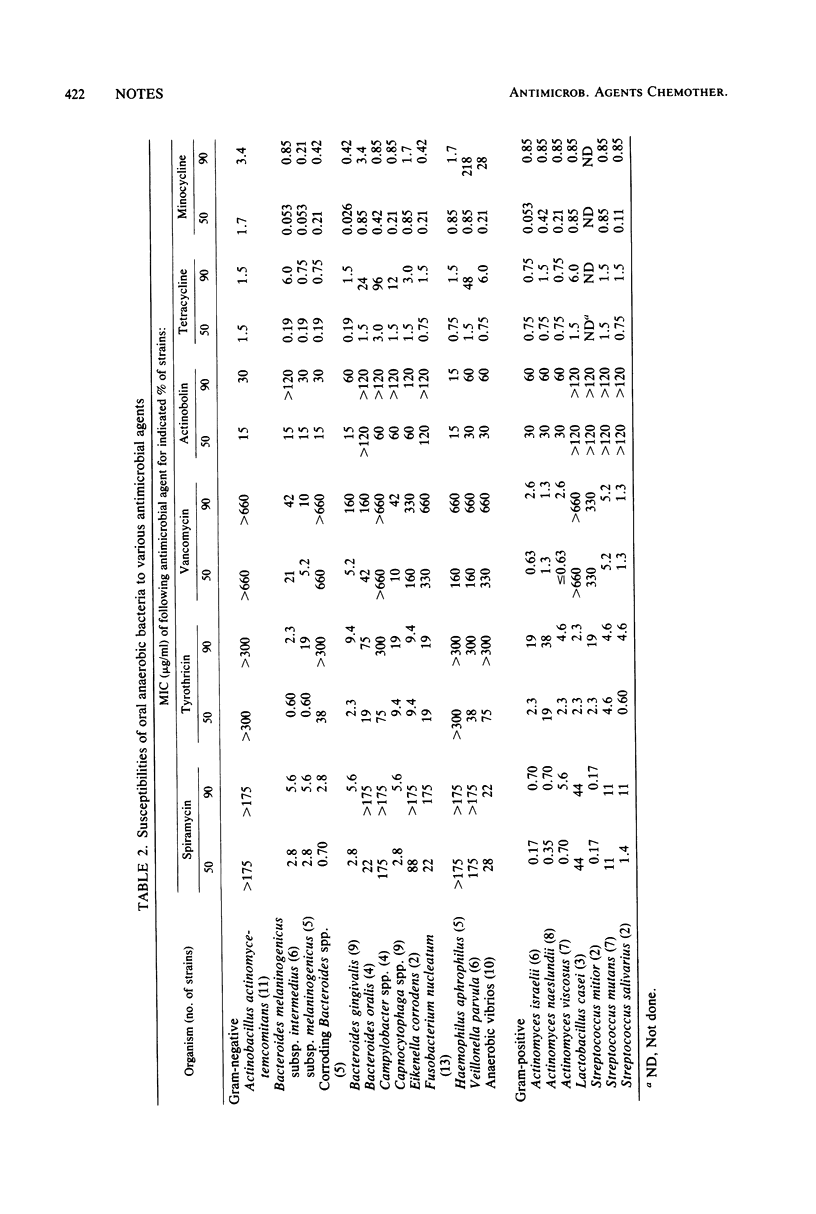
The minimal inhibitory concentrations of a series of antimicrobial agents for human oral organisms were determined under anaerobic growth conditions by an agar dilution assay. With the exception of black-pigmented Bacteroides spp., minimal inhibitory concentrations for oral isolates were similar to those for non-oral isolates of organisms of the same or closely related species.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appelbaum P. C., Chatterton S. A. Susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria to ten antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):371–376. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. N., Thornsberry C. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Streptococcus mutans isolated from patients with endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):268–271. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., O'Keefe P. The bacteriology of perimandibular space infections. J Oral Surg. 1979 Jun;37(6):407–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. J., Waatti P. E. Susceptibility testing of clinically isolated anaerobic bacteria by an agar dilution technique. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Apr;17(4):629–635. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.4.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow A. W., Patten V., Guze L. B. Comparative susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria to minocycline, doxycycline, and tetracycline. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jan;7(1):46–49. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow A. W., Roser S. M., Brady F. A. Orofacial odontogenic infections. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Mar;88(3):392–402. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-3-392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forlenza S. W., Newman M. G., Horikoshi A. L., Blachman U. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Capnocytophaga. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jan;19(1):144–146. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forlenza S. W., Newman M. G., Lipsey A. I., Siegel S. E., Blachman U. Capnocytophaga sepsis: a newly recognised clinical entity in granulocytopenic patients. Lancet. 1980 Mar 15;1(8168 Pt 1):567–568. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91057-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilligan P. H., McCarthy L. R., Bissett B. K. Capnocytophaga ochracea septicemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):643–645. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.643-645.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein E. J., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Susceptibility of Eikenella corrodens to ten cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Oct;14(4):639–641. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.4.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg K., Nord C. E., Dornbusch K. Antimicrobial in vitro susceptibility of actinomyces israelii and arachnia propionica. Scand J Infect Dis. 1977;9(1):40–45. doi: 10.3109/inf.1977.9.issue-1.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höffler U., Niederau W., Pulverer G. Susceptibility of Bacterium actinomycetem comitans to 45 antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):943–946. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner P. I. Susceptibility of pathogenic actinomycetes to antimicrobial compounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):302–309. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. J., Gardner M., Washington J. A., 2nd In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria isolated from clinical specimens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Feb;1(2):148–158. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.2.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. R., Rosenblatt J. E. Penicillin resistance and penicillinase production in clinical isolates of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):605–608. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. G., Hulem C., Colgate J., Anselmo C. Antibacterial susceptibility of plaque bacteria. J Dent Res. 1979 Jul;58(7):1722–1732. doi: 10.1177/00220345790580071401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. G. The role of Bacteroides melaninogenicus and other anaerobes in periodontal infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Mar-Apr;1(2):313–324. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.2.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page M. I., King E. O. Infection due to Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and Haemophilus aphrophilus. N Engl J Med. 1966 Jul 28;275(4):181–188. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196607282750403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. V., James A. L. In vitro susceptibility of Bacteroides corrodens and Eikenella corrodens to ten chemotherapeutic agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Nov;6(5):543–546. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.5.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Evans R. T., Lobbins P. M., Genco R. J. In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jul;18(1):9–12. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Reynolds H. S., Genco R. J. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human periodontal disease: a cross-sectional microbiological investigation. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1013–1020. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1013-1020.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J. Subgingival microflora and periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol. 1979 Oct;6(5):351–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1979.tb01935.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staneck J. L., Washington J. A., 2nd Antimicrobial susceptibilities of anaerobic bacteria: recent clinical isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Sep;6(3):311–315. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.3.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria to 23 antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):736–752. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Pyeatt D., Kwok Y. Y. In vitro susceptibility of Capnocytophaga strains to 18 antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Aug;20(2):270–271. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.2.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C. B., Gordon J. M., McQuilkin S. J., Niebloom T. A., Socransky S. S. Tetracycline: levels of achievable in gingival crevice fluid and in vitro effect on subgingival organisms. Part II. Susceptibilities of periodontal bacteria. J Periodontol. 1981 Oct;52(10):613–616. doi: 10.1902/jop.1981.52.10.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C. B., Niebloom T. A., Socransky S. S. Agar medium for use in susceptibility testing of bacteria from human periodontal pockets. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Oct;16(4):452–457. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.4.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins T. D., Chalgren S. Medium for use in antibiotic susceptibility testing of anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Dec;10(6):926–928. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.6.926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


