Abstract
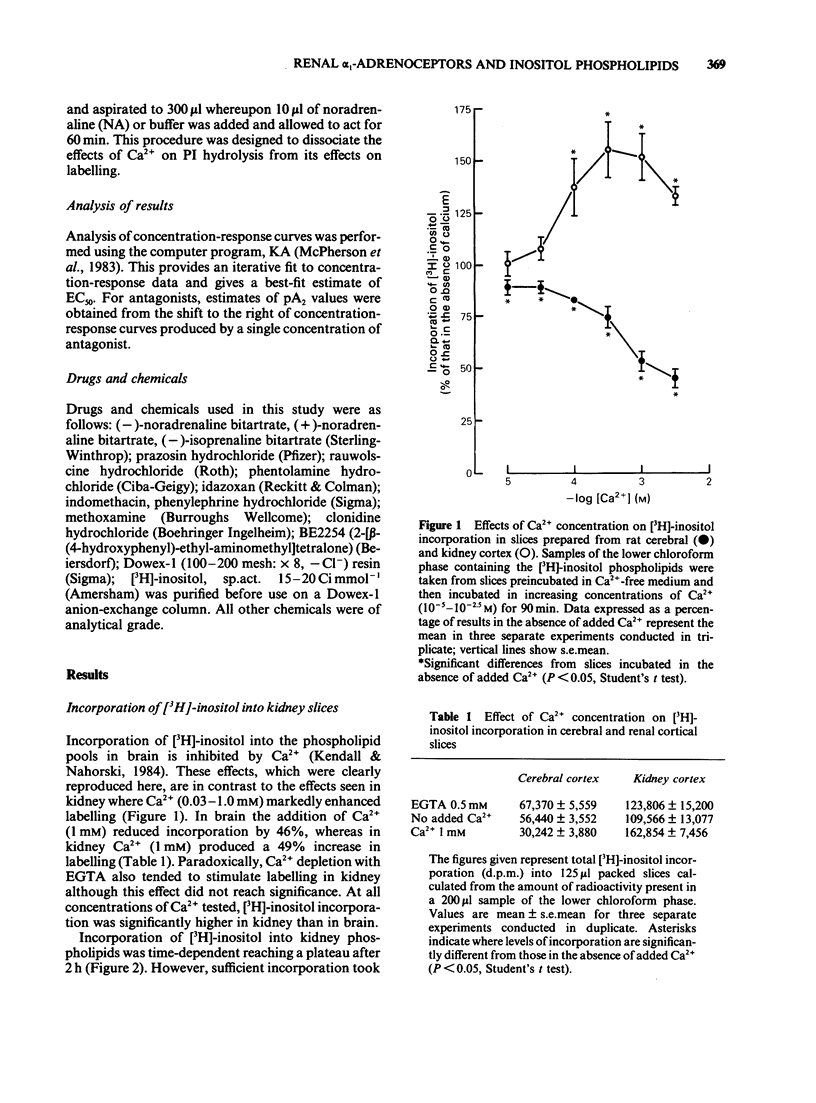
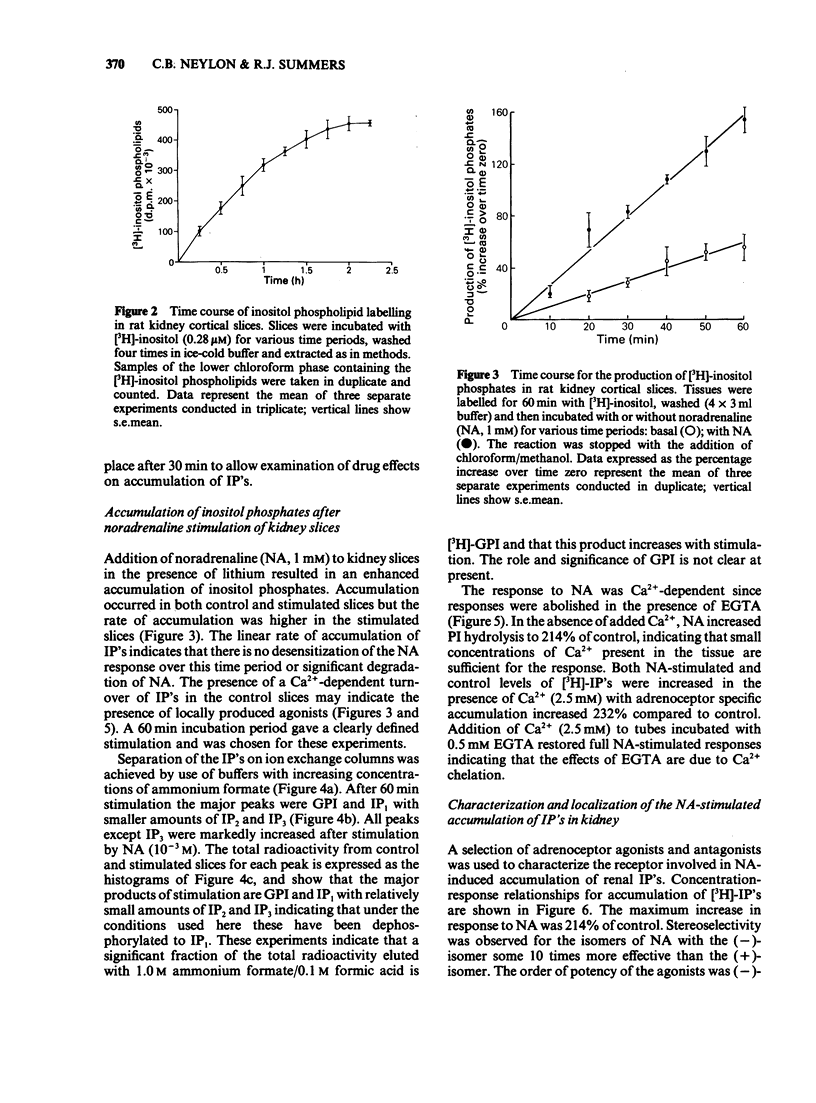
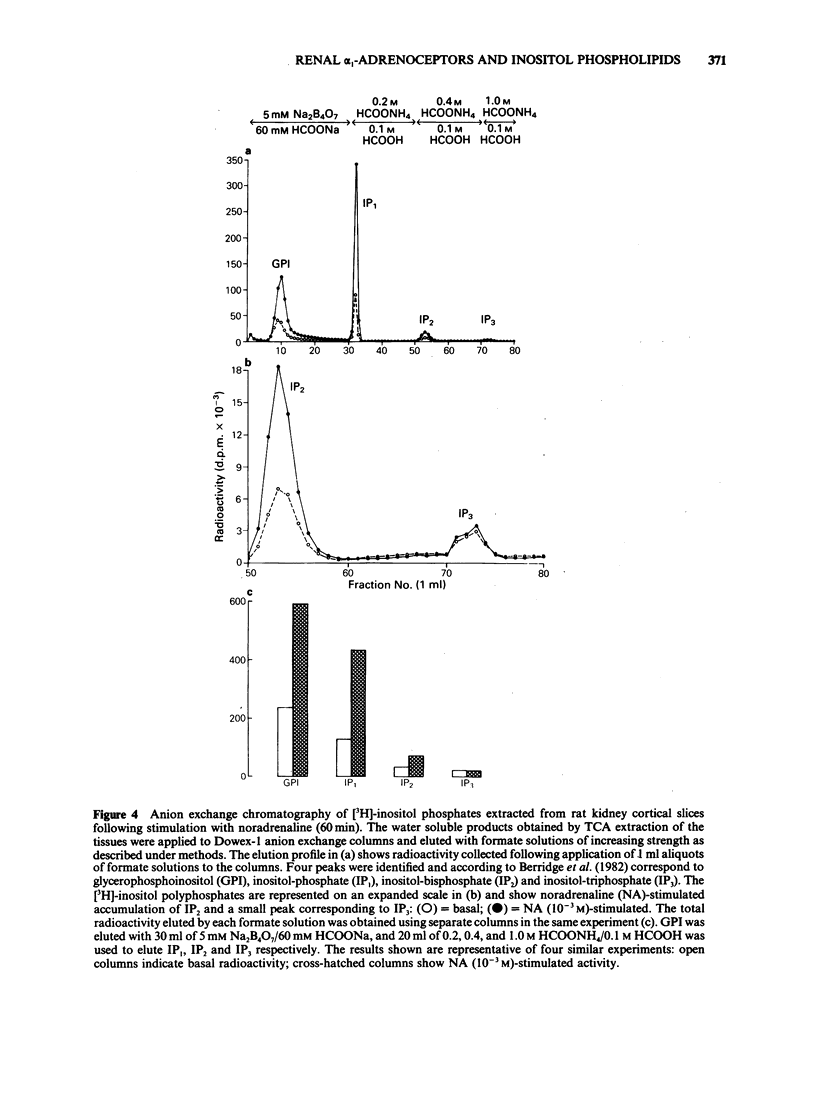
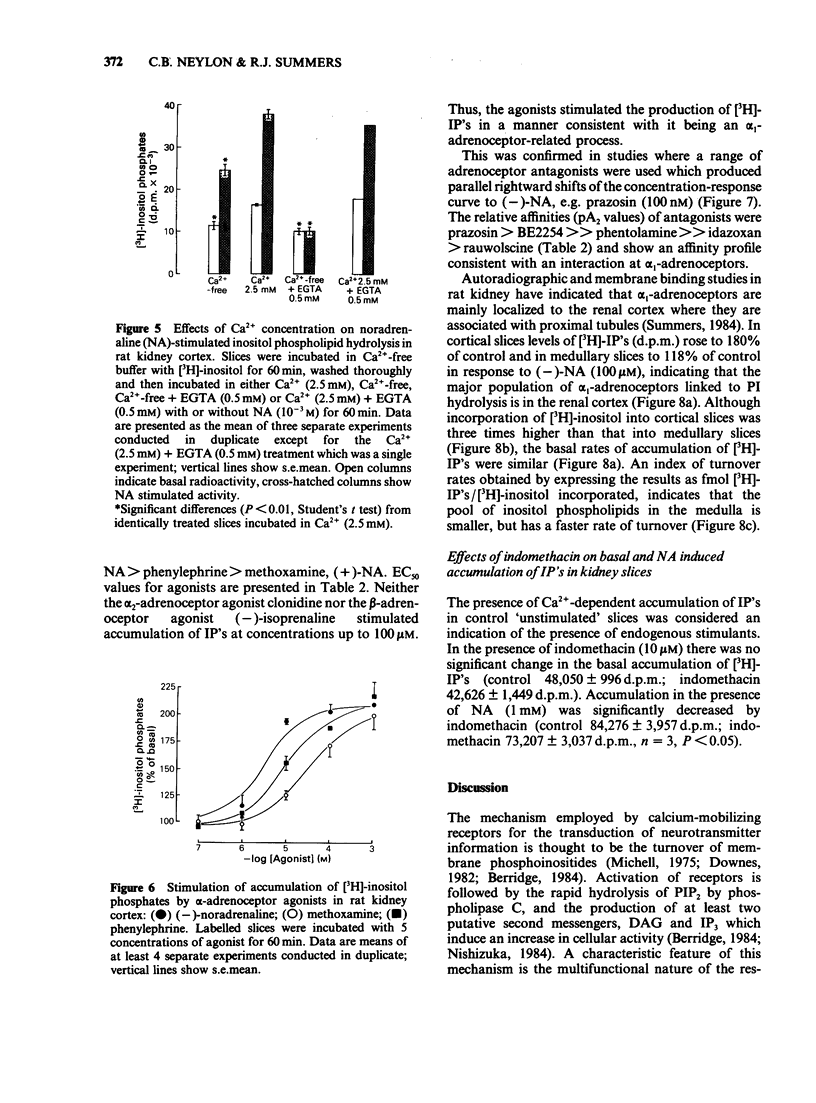
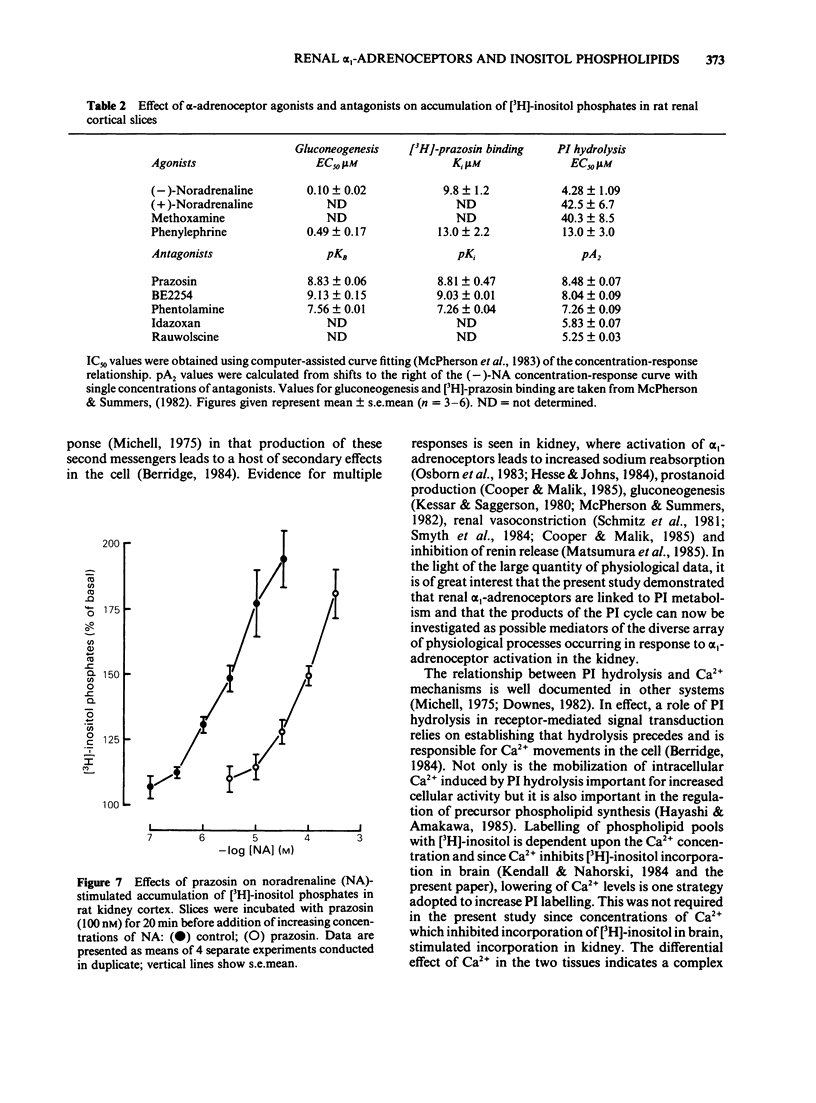
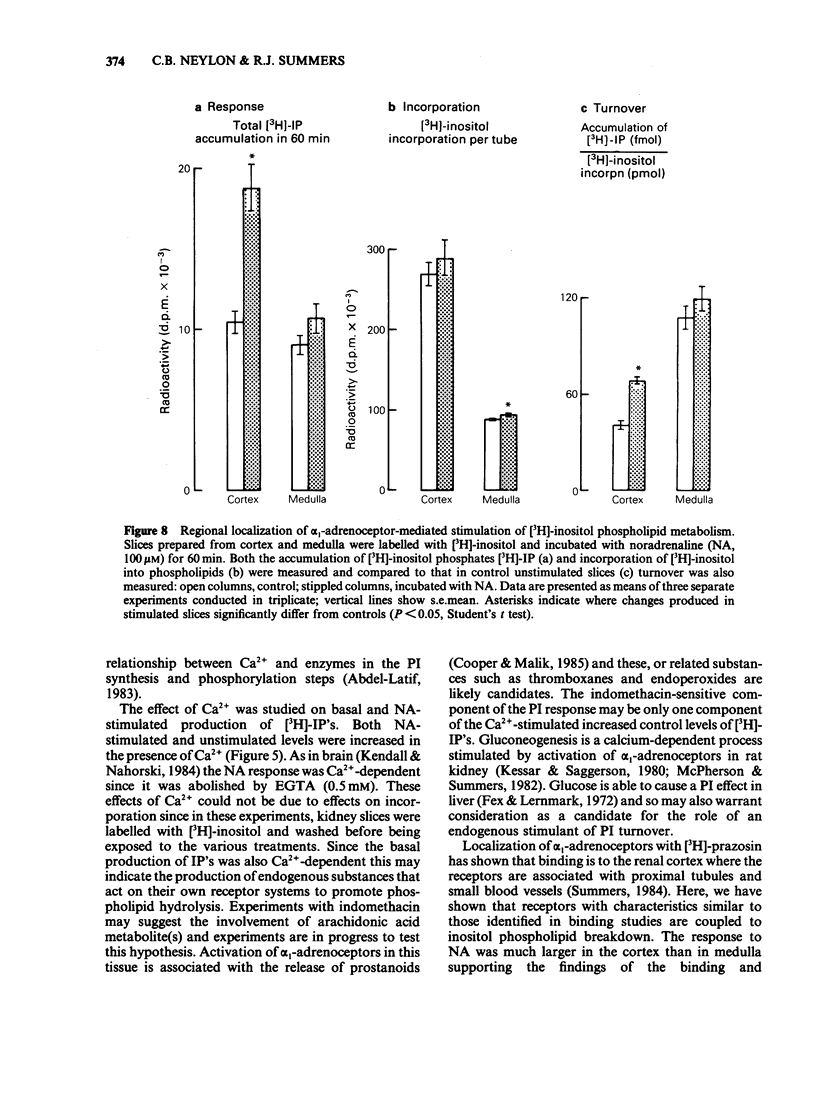
The molecular events which follow activation of alpha 1-adrenoceptors in rat kidney were investigated by measuring inositol phospholipid hydrolysis. Slices were labelled with [3H]-inositol (0.25 microM) and the accumulation of [3H]-inositol phosphates ([3H]-IP's) was measured after stimulation with alpha-adrenoceptor agonists. Phospholipid labelling was both time- and Ca2+-dependent. In kidney, Ca2+ (1 mM) increased the incorporation of [3H]-inositol by 49% and in cerebral cortex reduced it by 46%. Following addition of noradrenaline (NA, 1 mM), accumulation of [3H]-IP's increased linearly for at least 60 min. In Ca2+-free buffers a 2.1 fold increase in [3H]-IP accumulation was observed and further increases in stimulated and control levels were produced in the presence of Ca2+ (2.5 mM). These responses were attenuated by the inclusion of indomethacin (10 microM) and abolished in the presence of EGTA (0.5 mM). Responses to (-)-NA were more than 4 fold higher in the renal cortex than in the medulla. Separation of the IP's which accumulate after alpha-adrenoceptor agonists showed that after 60 min stimulation the major products were glycerophosphoinositol and inositol-phosphate with smaller amounts of inositol-bisphosphate and inositol-trisphosphate. The most effective agonists tested for stimulation of accumulation of [3H]-IP's were (-)-NA greater than phenylephrine greater than methoxamine, (+)-NA. Clonidine and (-)-isoprenaline were ineffective at concentrations up to 100 microM. The order of effectiveness of alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists was prazosin greater than BE2254 greater than phentolamine greater than idazoxan greater than rauwolscine. The results indicate that alpha 1-adrenoceptors in rat kidney are linked to phosphoinositide hydrolysis and that this response is localized mainly to the renal cortex.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell R. L., Kennerly D. A., Stanford N., Majerus P. W. Diglyceride lipase: a pathway for arachidonate release from human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3238–3241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Downes C. P., Hanley M. R. Lithium amplifies agonist-dependent phosphatidylinositol responses in brain and salivary glands. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):587–595. doi: 10.1042/bj2060587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G., Cuatrecasas P. Phospholipase A2 and phospholipase C activities of platelets. Differential substrate specificity, Ca2+ requirement, pH dependence, and cellular localization. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10227–10231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E., Kendall D. A., Nahorski S. R. Inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in rat cerebral cortical slices: I. Receptor characterisation. J Neurochem. 1984 May;42(5):1379–1387. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb02798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns C. P., Rozengurt E. Serum, platelet-derived growth factor, vasopressin and phorbol esters increase intracellular pH in Swiss 3T3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Nov 15;116(3):931–938. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B., U'Prichard D. C. Characterization of alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1983;24:343–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabardès D., Montégut M., Imbert-Teboul M., Morel F. Inhibition of alpha 2-adrenergic agonists on AVP-induced cAMP accumulation in isolated collecting tubule of the rat kidney. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1984 Oct;37(3):263–275. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(84)90096-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper C. L., Malik K. U. Prostaglandin synthesis and renal vasoconstriction elicited by adrenergic stimuli are linked to activation of alpha-1 adrenergic receptors in the isolated rat kidney. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Apr;233(1):24–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P. Receptor-stimulated inositol phospholipid metabolism in the central nervous system. Cell Calcium. 1982 Oct;3(4-5):413–428. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(82)90027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N., García-Sáinz J. A. Role of phosphatidylinositol turnover in alpha 1 and of adenylate cyclase inhibition in alpha 2 effects of catecholamines. Life Sci. 1980 Apr 14;26(15):1183–1194. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fex G., Lernmark A. Effect of D-glucose on the incorporation of 32P into phospholipids of mouse pancreatic islets. FEBS Lett. 1972 Sep 15;25(2):287–291. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80505-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Sáinz J. A., Hasler A. K., Fain J. N. Alpha1-adrenergic activation of phosphatidylinositol labeling in isolated brown fat cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Dec;29(24):3330–3333. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90313-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington C. A., Eichberg J. Norepinephrine causes alpha 1-adrenergic receptor-mediated decrease of phosphatidylinositol in isolated rat liver plasma membranes supplemented with cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2087–2090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi F., Amakawa T. Calcium- and calmodulin-dependent phosphorylation of diphosphoinositide in acetylcholine receptor-rich membranes from electroplax of Narke japonica. J Neurochem. 1985 Jul;45(1):124–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb05483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse I. F., Johns E. J. The subtype of alpha-adrenoceptor involved in the neural control of renal tubular sodium reabsorption in the rabbit. J Physiol. 1984 Jul;352:527–538. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall D. A., Nahorski S. R. Inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in rat cerebral cortical slices: II. Calcium requirement. J Neurochem. 1984 May;42(5):1388–1394. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb02799.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessar P., Saggerson E. D. Evidence that catecholamines stimulate renal gluconeogenesis through an alpha 1-type of adrenoceptor. Biochem J. 1980 Jul 15;190(1):119–123. doi: 10.1042/bj1900119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus-Friedmann N. Hormonal regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis. Physiol Rev. 1984 Jan;64(1):170–259. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.1.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura Y., Miyawaki N., Sasaki Y., Morimoto S. Inhibitory effects of norepinephrine, methoxamine and phenylephrine on renin release from rat kidney cortical slices. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Jun;233(3):782–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A., Molenaar P., Raper C., Malta E. Analysis of dose-response curves and calculation of agonist dissociation constants using a weighted nonlinear curve fitting program. J Pharmacol Methods. 1983 Dec;10(4):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(83)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A., Summers R. J. A study of alpha 1-adrenoceptors in rat renal cortex: comparison of [3H]-prazosin binding with the alpha 1-adrenoceptor modulating gluconeogenesis under physiological conditions. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;77(1):177–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09284.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minneman K. P., Johnson R. D. Characterization of alpha-1 adrenergic receptors linked to [3H]inositol metabolism in rat cerebral cortex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Aug;230(2):317–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. L., Holdaas H., Thames M. D., DiBona G. F. Renal adrenoceptor mediation of antinatriuretic and renin secretion responses to low frequency renal nerve stimulation in the dog. Circ Res. 1983 Sep;53(3):298–305. doi: 10.1161/01.res.53.3.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J. M., Graham R. M., Sagalowsky A., Pettinger W. A. Renal alpha-1 and alpha-2 adrenergic receptors: biochemical and pharmacological correlations. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Nov;219(2):400–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva P., Ross B., Spokes K. Competition between sodium reabsorption and gluconeogenesis in kidneys of steroid-treated rats. Am J Physiol. 1980 Apr;238(4):F290–F295. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.238.4.F290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth D. D., Umemura S., Pettinger W. A. Alpha-1 adrenoceptor selectivity of phenoxybenzamine in the rat kidney. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Aug;230(2):387–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Alpha-adrenoceptor subclassification. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1981;88:199–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Schulz I. Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):67–69. doi: 10.1038/306067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers R. J. Renal alpha adrenoceptors. Fed Proc. 1984 Nov;43(14):2917–2922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzumaki H., Muraki T., Kato R. Involvement of alpha 1-adrenergic receptors in stimulation of phosphatidylinositol metabolism by catecholamines in mouse thyroids. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 1;31(13):2237–2241. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villalobos-Molina R., Uc M., Hong E., García-Sáinz J. A. Correlation between phosphatidylinositol labeling and contraction in rabbit aorta: effect of alpha-1 adrenergic activation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Jul;222(1):258–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock E. A., Johnston C. I. Characterization of adenylate cyclase-coupled alpha 2-adrenergic receptors in rat renal cortex using [3H]yohimbine. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;22(3):589–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


