Abstract
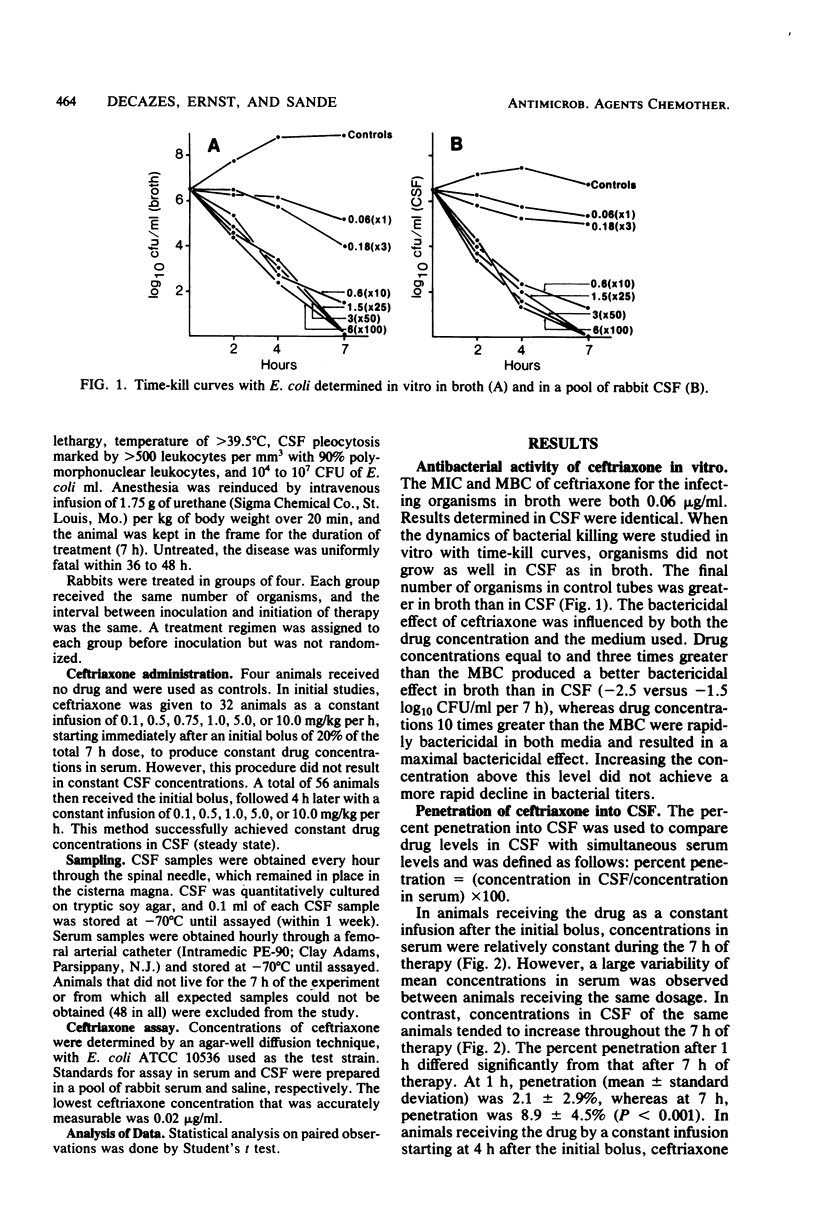
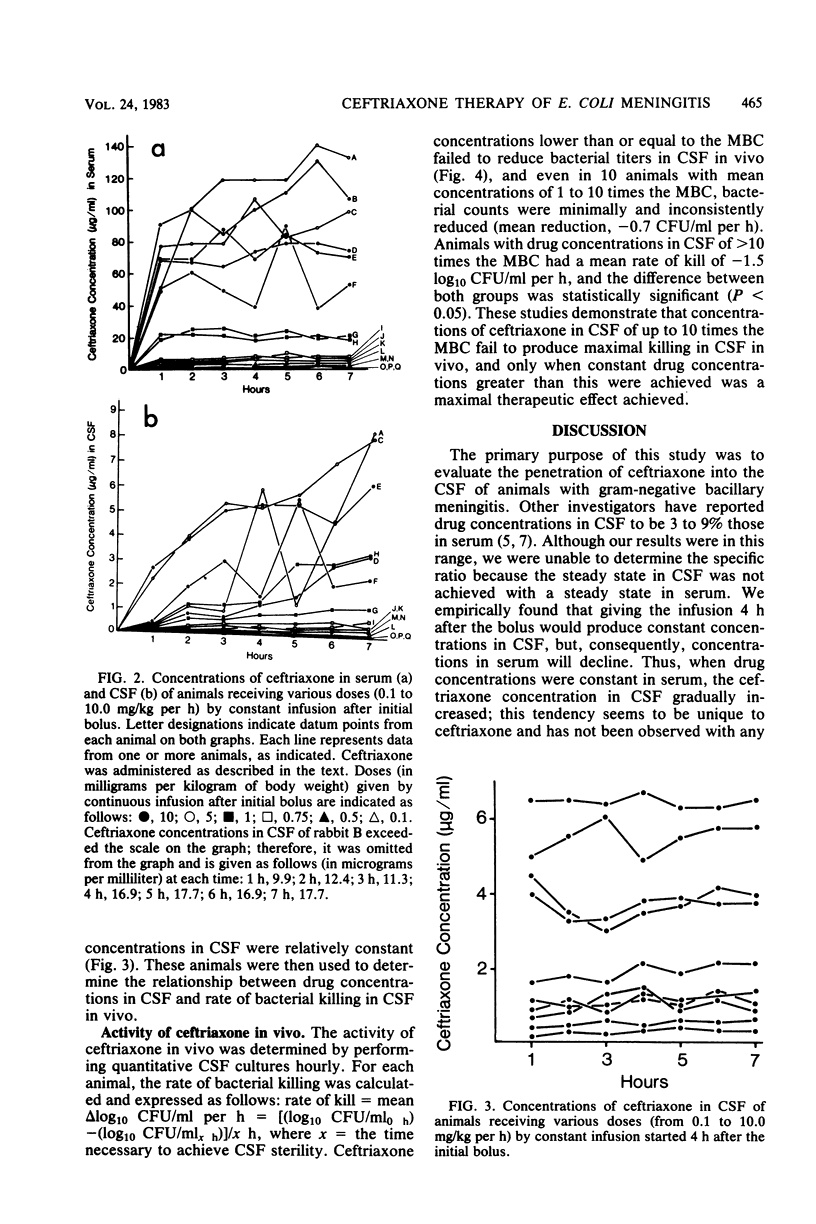
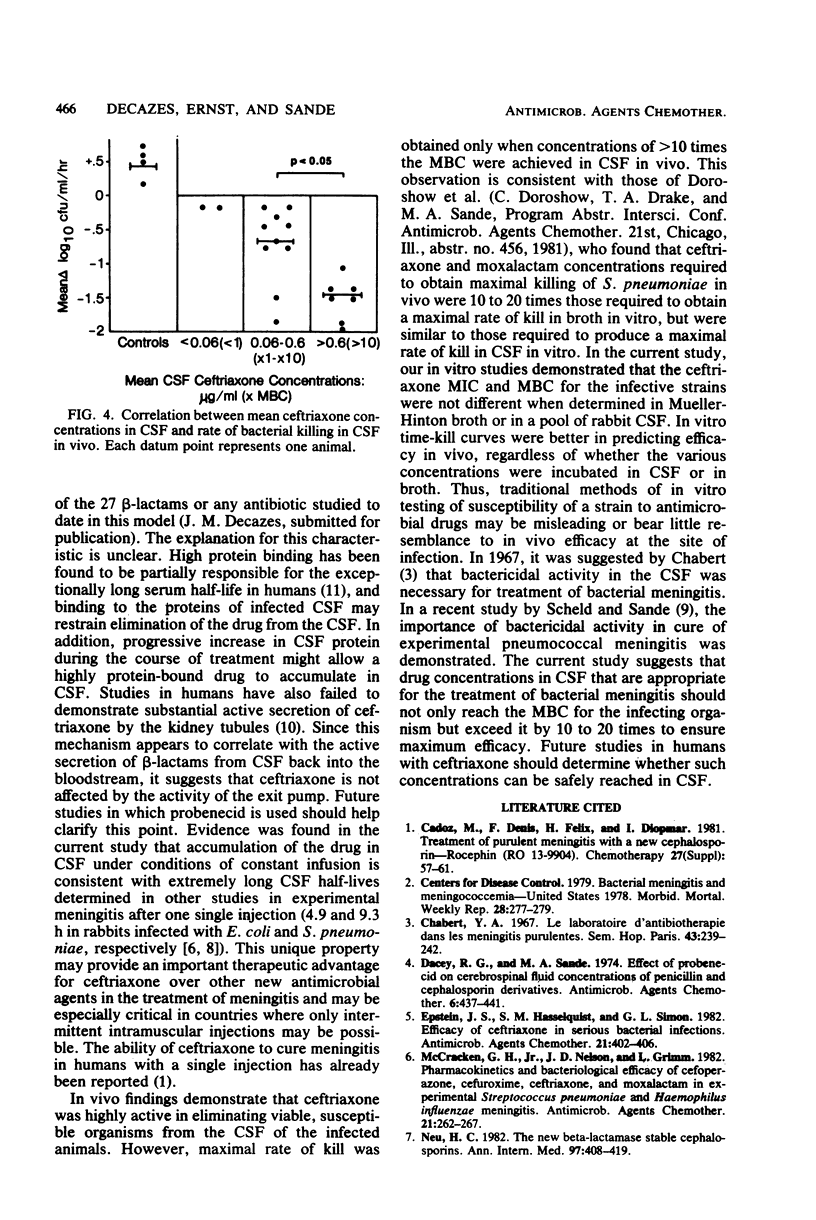
Ceftriaxone was highly active in eliminating Escherichia coli from the cerebrospinal fluid of rabbits infected with experimental meningitis. However, concentrations equal to or greater than 10 times the minimal bactericidal concentration had to be achieved to ensure optimal efficacy (rate of kill, 1.5 log10 CFU/ml per h). In contrast to other beta-lactams studied in this model, ceftriaxone concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid progressively increased, whereas serum steady state was obtained by constant infusion. The percent penetration was 2.1% after 1 h of therapy, in contrast to 8.9% after 7 h (P less than 0.001). In vitro time-kill curves done in cerebrospinal fluid or broth more closely predicted the drug concentrations required for a maximum cidal effect in vivo than that predicted by determinations of minimal inhibitory or bactericidal concentrations.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cadoz M., Denis F., Félix H., Diop Mar I. Treatment of purulent meningitis with a new cephalosporin-Rocephin (Ro 13-9904). Clinical, bacteriological and pharmacological observations in 24 cases. Chemotherapy. 1981;27 (Suppl 1):57–61. doi: 10.1159/000238030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabbert Y. A. Le laboratoire d'antibiothérapie dans les méningites purulentes. Sem Hop. 1967 Jan 20;43(4):239–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dacey R. G., Sande M. A. Effect of probenecid on cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of penicillin and cephalosporin derivatives. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Oct;6(4):437–441. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.4.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein J. S., Hasselquist S. M., Simon G. L. Efficacy of ceftriaxone in serious bacterial infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Mar;21(3):402–406. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.3.402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr, Nelson J. D., Grimm L. Pharmacokinetics and bacteriological efficacy of cefoperazone, ceftriaxone, and moxalactam in experimental Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae meningitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):262–267. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. The new beta-lactamase-stable cephalosporins. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Sep;97(3):408–419. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-3-408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaad U. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Loock C. A., Thomas M. L. Pharmacokinetics and bacteriologic efficacy of moxalactam, cefotaxime, cefoperazone, and rocephin in experimental bacterial meningitis. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):156–163. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheld W. M., Sande M. A. Bactericidal versus bacteriostatic antibiotic therapy of experimental pneumococcal meningitis in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):411–419. doi: 10.1172/JCI110785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seddon M., Wise R., Gillett A. P., Livingston R. Pharmacokinetics of Ro 13-9904, a broad-spectrum cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Aug;18(2):240–242. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.2.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckel K., McNamara P. J., Brandt R., Plozza-Nottebrock H., Ziegler W. H. Effects of concentration-dependent plasma protein binding on ceftriaxone kinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 May;29(5):650–657. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbist L., Verhaegen J. In vitro activity of Ro 13-9904, a new beta-lactamase-stable cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Feb;19(2):222–225. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.2.222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


