Abstract
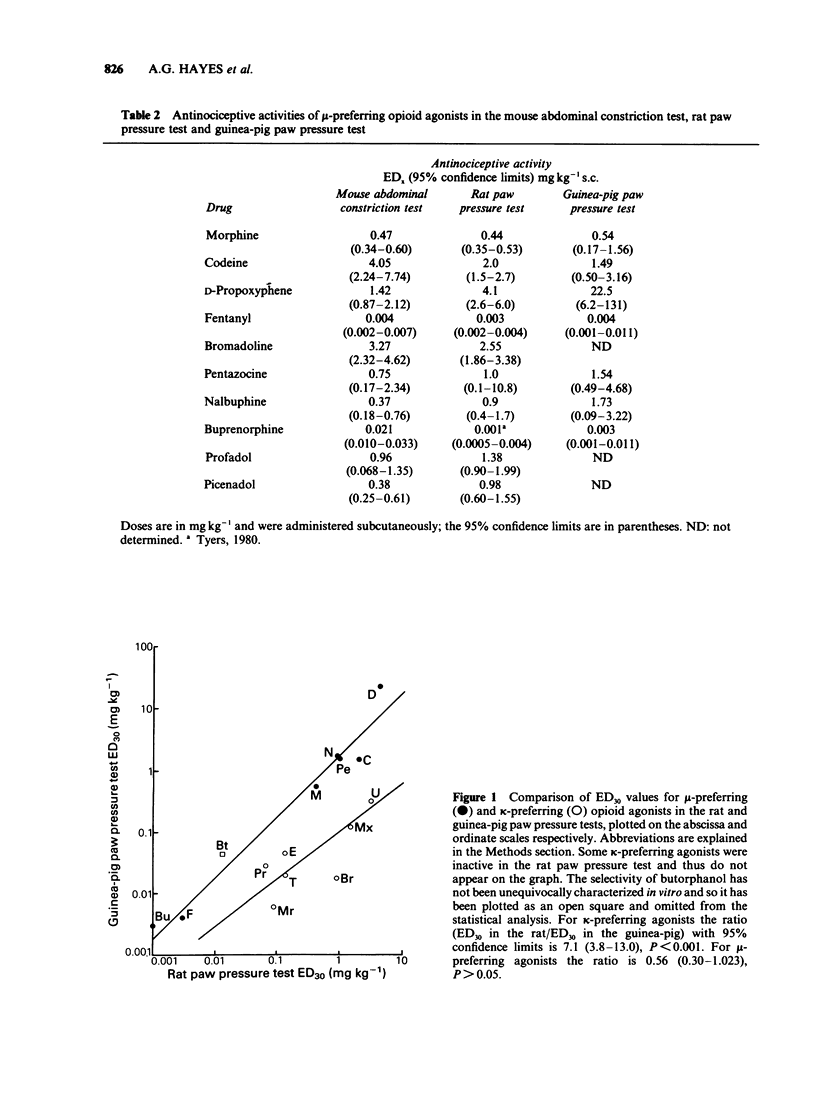
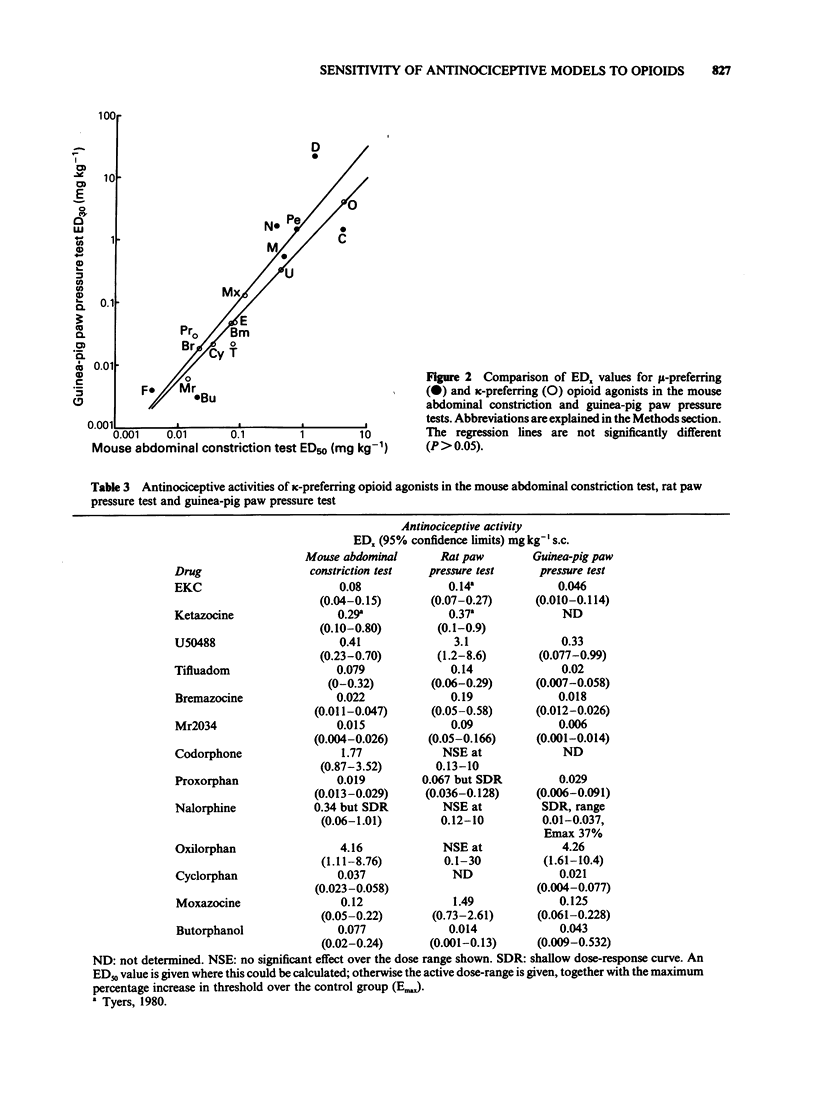
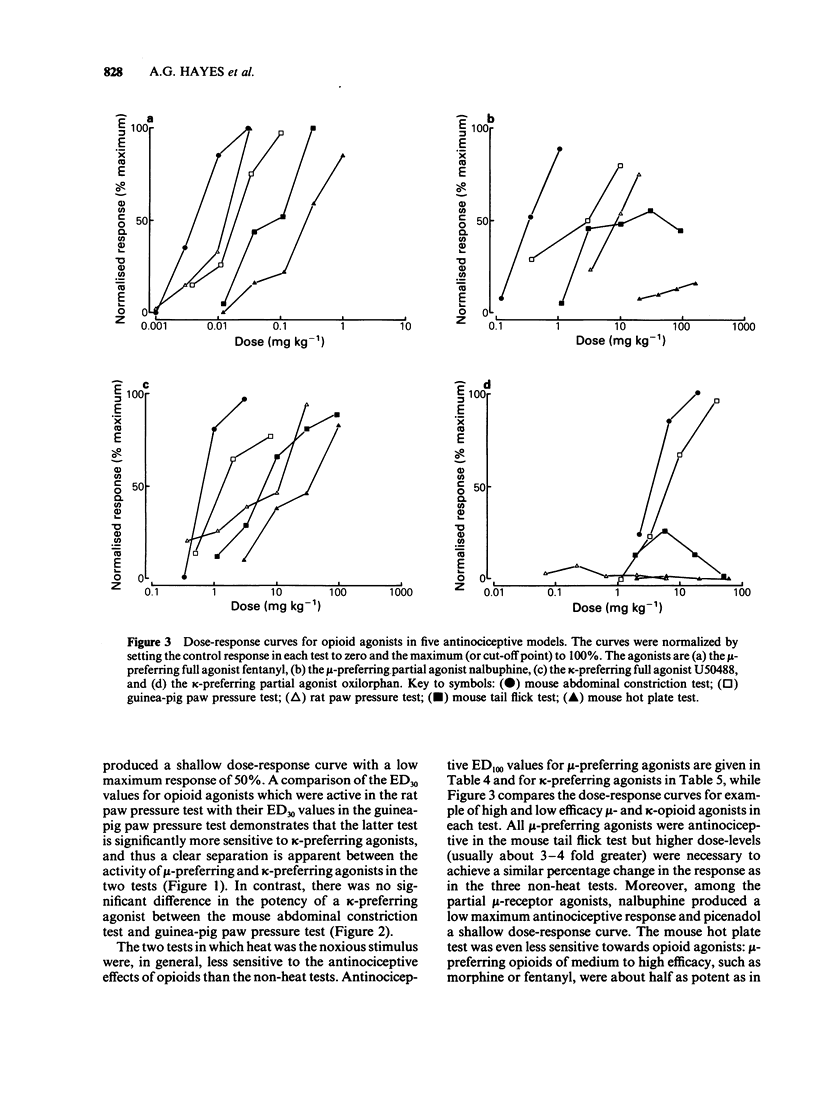
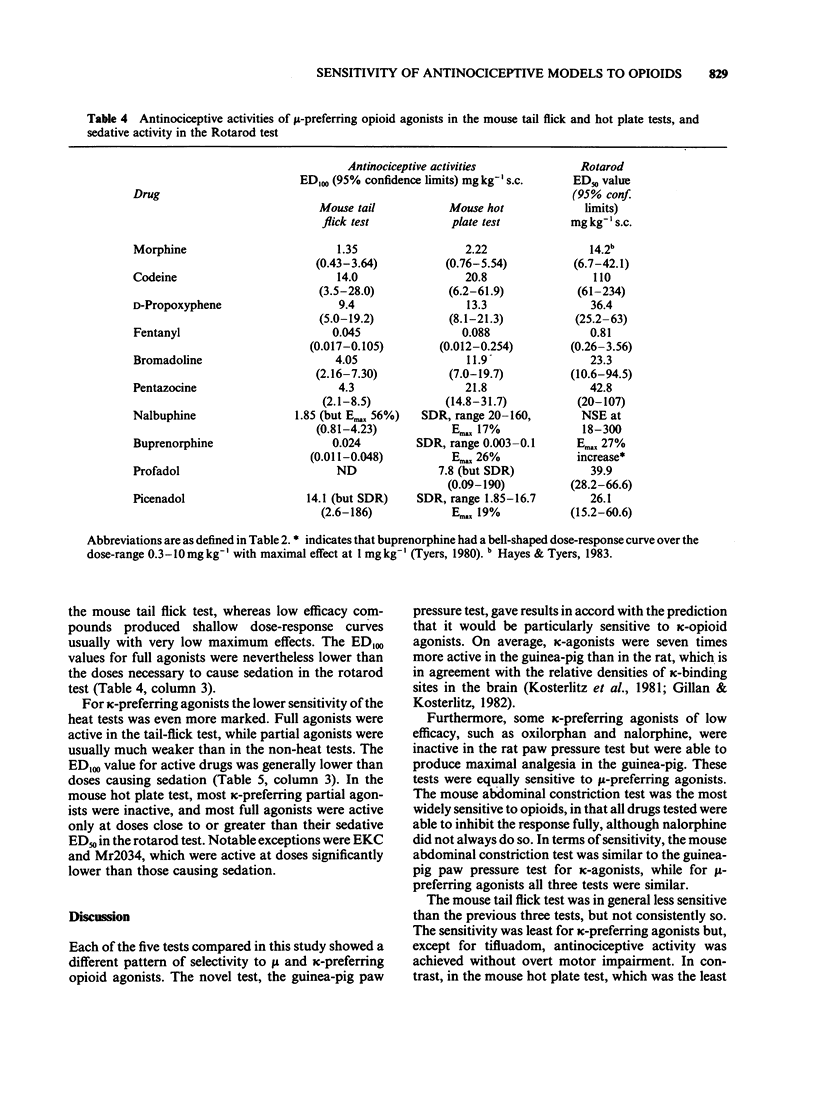
1 A range of opioid receptor agonists were tested for activity in five antinociceptive models: the acetylcholine-induced abdominal constriction, tail-flick and hot plate tests in the mouse and the paw pressure test in the rat and guinea-pig. 2 Agonists acting preferentially at the kappa-opioid receptor were significantly more potent in the guinea-pig than in the rat paw pressure test, whereas mu-receptor preferring agonists were equipotent in the two tests. The mouse abdominal constriction test was of equal sensitivity to the guinea-pig pressure test for both types of agonist. 3 The mouse tail-flick and hot plate tests were progressively less sensitive than the other three tests, particularly to kappa-receptor preferring agonists. 4 The efficacy of an agonist can also markedly affect its activity in antinociceptive tests. Thus, partial kappa-agonists were weak or inactive in the rat paw pressure test, and partial agonists at both mu- and kappa-opioid receptors were relatively weak in the tests in which heat was the noxious stimulus, particularly the mouse hot plate test. 5 The mouse abdominal constriction test is suggested as the most appropriate antinociceptive model for testing a broad range of opioid agonists, whilst the relative potency of a drug in the rat and guinea-pig paw pressure tests may indicate the degree to which it is selective for kappa-opioid receptors in vivo.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chaillet P., Coulaud A., Zajac J. M., Fournie-Zaluski M. C., Costentin J., Roques B. P. The mu rather than the delta subtype of opioid receptors appears to be involved in enkephalin-induced analgesia. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 May 18;101(1-2):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galligan J. J., Mosberg H. I., Hurst R., Hruby V. J., Burks T. F. Cerebral delta opioid receptors mediate analgesia but not the intestinal motility effects of intracerebroventricularly administered opioids. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Jun;229(3):641–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillan M. G., Kosterlitz H. W. Spectrum of the mu, delta- and kappa-binding sites in homogenates of rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;77(3):461–469. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes A. G., Sheehan M. J., Tyers M. B. Determination of the receptor selectivity of opioid agonists in the guinea-pig ileum and mouse vas deferens by use of beta-funaltrexamine. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Dec;86(4):899–904. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb11112.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes A. G., Tyers M. B. Determination of receptors that mediate opiate side effects in the mouse. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jul;79(3):731–736. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10011.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes A., Kelly A. Profile of activity of kappa receptor agonists in the rabbit vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Apr 16;110(3):317–322. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90558-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson M., Kosterlitz H. W., Leslie F. M., Waterfield A. A. Assessment in the guinea-pig ileum and mouse vas deferens of benzomorphans which have strong antinociceptive activity but do not substitute for morphine in the dependent monkey. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Dec;55(4):541–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07430.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Paterson S. J., Robson L. E. Characterization of the kappa-subtype of the opiate receptor in the guinea-pig brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Aug;73(4):939–949. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb08749.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leander J. D. A kappa opioid effect: increased urination in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jan;224(1):89–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leander J. D. Evidence that nalorphine, butorphanol and oxilorphan are partial agonists at a kappa-opioid receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan 21;86(3-4):467–470. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90198-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnan J., Paterson S. J., Tavani A., Kosterlitz H. W. The binding spectrum of narcotic analgesic drugs with different agonist and antagonist properties. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 Jun;319(3):197–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00495865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. R., Eades C. G., Thompson J. A., Huppler R. E., Gilbert P. E. The effects of morphine- and nalorphine- like drugs in the nondependent and morphine-dependent chronic spinal dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jun;197(3):517–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L., Shaw J. S. Characterisation of the delta-opioid receptor on the hamster vas deferens. Neuropeptides. 1985 Dec;6(6):531–536. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(85)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka T., Negishi K., Suda M., Matsumiya T., Inazu T., Ueki M. Rabbit vas deferens: a specific bioassay for opioid kappa-receptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 17;73(2-3):235–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90098-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Adler B. A., Rodriguez J. Characterization of the opioid receptor binding and animal pharmacology of meptazinol. Postgrad Med J. 1985;61 (Suppl 2):5–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearl J., Aceto M. D., Fitzgerald J. J. Differences in antiwrithing activity of morphine and nalorphine over time and in slopes of the dose-response lines. Psychopharmacologia. 1968;13(4):341–345. doi: 10.1007/BF00414345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan M. J., Hayes A. G., Tyers M. B. Pharmacology of delta-opioid receptors in the hamster vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Oct 14;130(1-2):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90183-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skingle M., Hayes A. G., Tyers M. B. Effects of opiates on urine output in the water-loaded rat and reversal by beta-funaltrexamine. Neuropeptides. 1985 Feb;5(4-6):433–436. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(85)90047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. F., Rance M. J. Opiate receptors in the rat vas deferens. Life Sci. 1983;33 (Suppl 1):327–330. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90509-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam S. W. (+)-[3H]SKF 10,047, (+)-[3H]ethylketocyclazocine, mu, kappa, delta and phencyclidine binding sites in guinea pig brain membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb 12;109(1):33–41. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90536-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyers M. B. A classification of opiate receptors that mediate antinociception in animals. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Jul;69(3):503–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb07041.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upton N., Sewell R. D., Spencer P. S. Differentiation of potent mu and kappa-opiate agonists using heat and pressure antinociceptive profiles and combined potency analysis. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Mar 26;78(4):421–429. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90484-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S. J., Takemori A. E. Relative involvement of mu, kappa and delta receptor mechanisms in opiate-mediated antinociception in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Mar;224(3):525–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


