Abstract
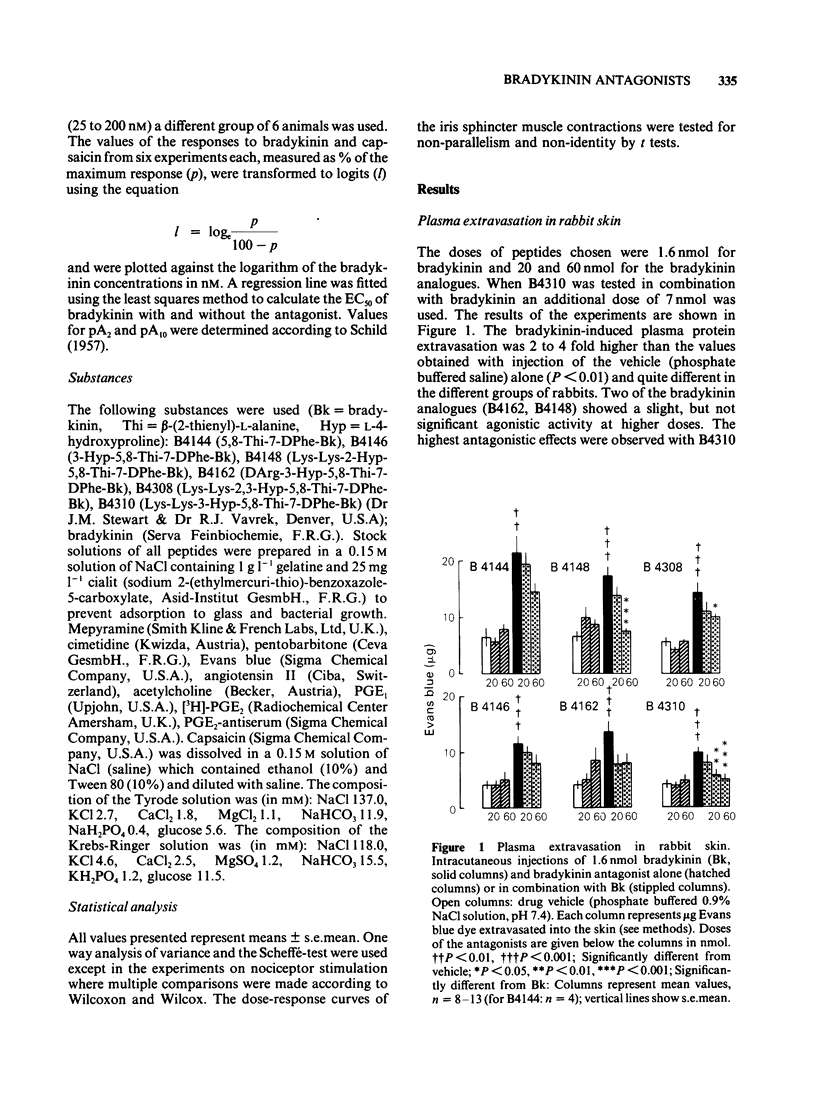
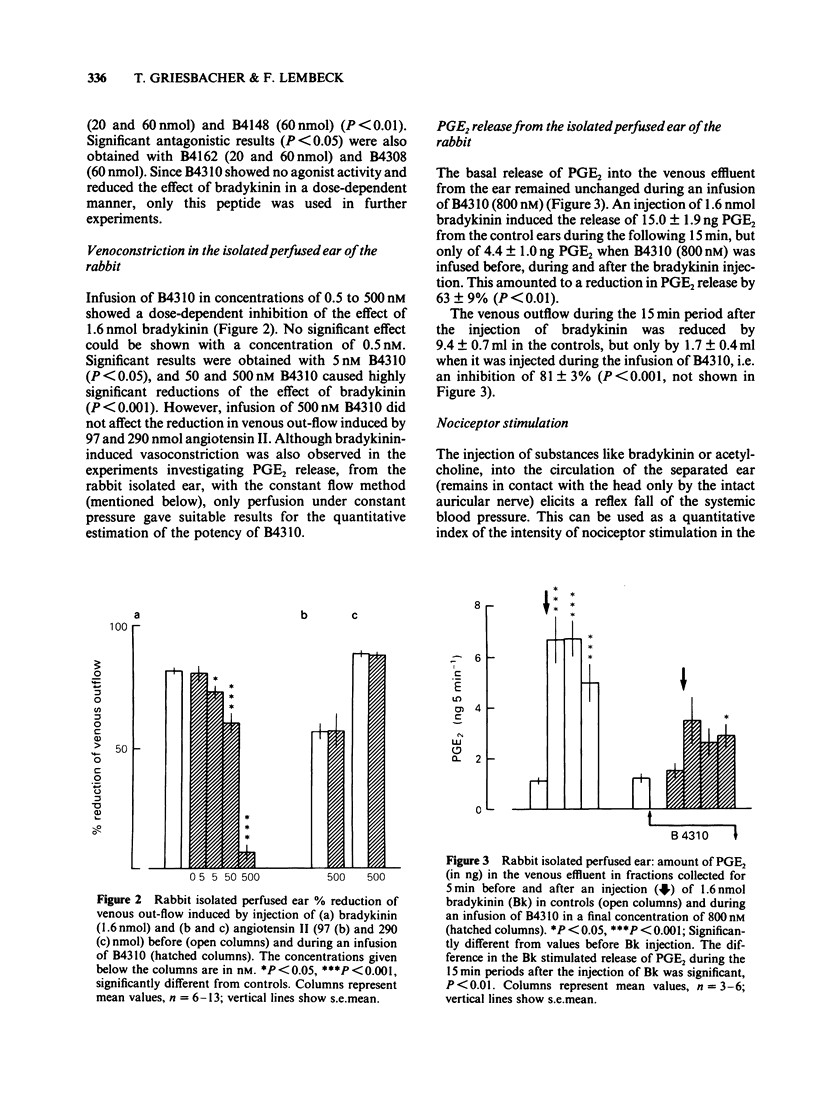
1 The inhibition of the bradykinin-induced plasma extravasation by six bradykinin (Bk) antagonists was tested on rabbit skin. All of them showed inhibitory effects without an agonistic action in the does used. B4310 (Lys-Lys-3-Hyp-5,8-Thi-7-DPhe-Bk) was the most active antagonist and was therefore used in the subsequent experiments. 2 B4310 (5-500 nM) antagonized the bradykinin-induced reduction of the venous outflow from the rabbit isolated ear in dose-dependent manner without affecting the arterial vasoconstriction induced by angiotensin II. 3 The bradykinin-induced release of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) from the perfused rabbit ear was reduced by 63% when B4310 (800 nM) was infused before, during and after the bradykinin injection. 4 Bradykinin was injected into the ear artery of anaesthetized rabbits and the reflex hypotensive response was used as indicator of the nociception. The response was antagonized by a local infusion of B4310 (50 and 500 nM). The antagonism was dose-dependent and reversible. The parallel shift of the dose-response curve to bradykinin suggests a competitive inhibition. However, B4310 did not antagonize acetylcholine-induced nociceptor stimulation. 5 B4310 inhibited bradykinin-induced stimulation of the trigeminal nerve which results in a substance P-mediated contraction of the iris sphincter muscle. A pA2 of 7.59 was calculated. B4310 did not inhibit capsaicin-induced contractions. 6 It is concluded that B4310 inhibits specifically five different actions of bradykinin which are related to its possible pathophysiological role.
Full text
PDF

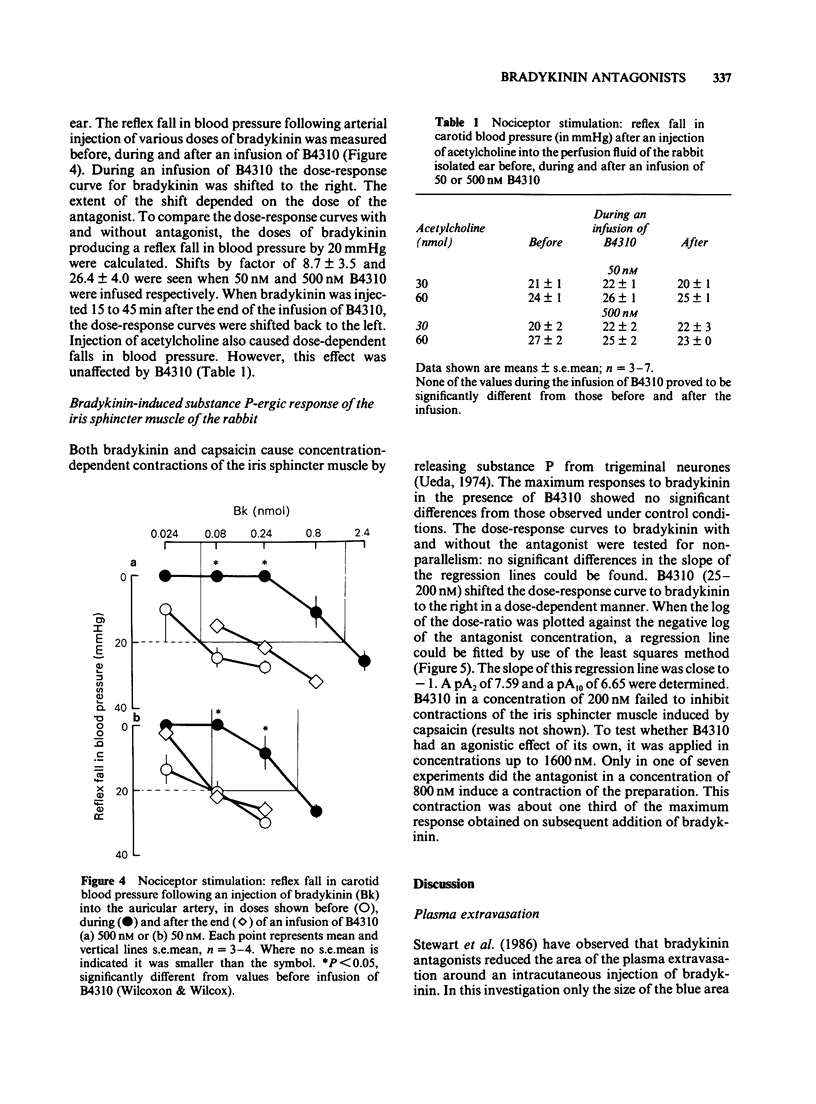


Selected References
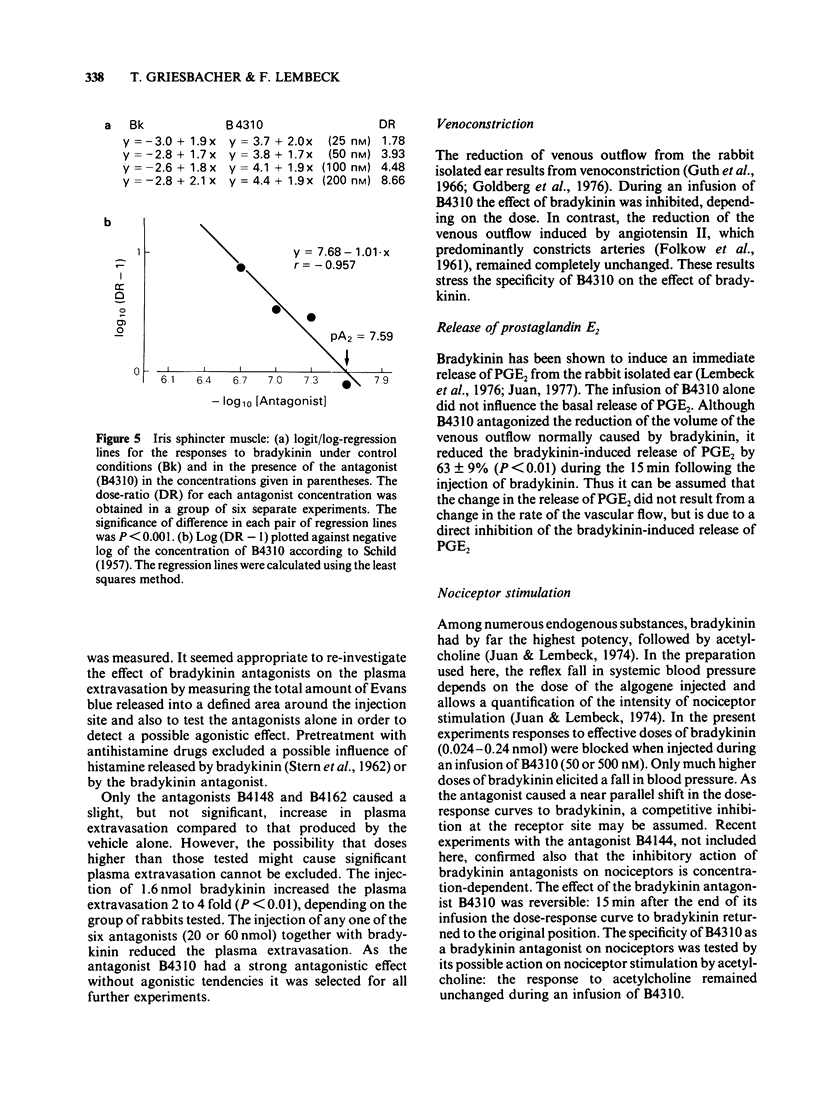
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Butler J. M., Hammond B. R. The effects of sensory denervation on the responses of the rabbit eye to prostaglandin E1, bradykinin and substance P. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Jul;69(3):495–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb07040.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chahl L. A. Interactions of bradykinin, prostaglandin E1, 5-hydroxytryptamine, histamine and adenosine-5'-triphosphate on the dry leakage response in rat skin. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1976 Oct;28(10):753–757. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1976.tb04041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLKOW B., JOHANSSON B., MELLANDER S. The comparative effects of angiotensin and noradrenaline on consecutive vascular sections. Acta Physiol Scand. 1961 Oct;53:99–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1961.tb02267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamse R., Holzer P., Lembeck F. Decrease of substance P in primary afferent neurones and impairment of neurogenic plasma extravasation by capsaicin. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Feb;68(2):207–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10409.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. R., Chapnick B. M., Joiner P. D., Hyman A. L., Kadowitz P. J. Influence of inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis on venoconstrictor responses to bradykinin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Aug;198(2):357–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juan H., Lembeck F. Action of peptides and other algesic agents on paravascular pain receptors of the isolated perfused rabbit ear. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1974;283(2):151–164. doi: 10.1007/BF00501142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juan H. Mechanism of action of bradykinin-induced release of prostaglandin E. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;300(1):77–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00505082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern R. Die adrenergischen Receptoren der intraoculären Muskeln des Menschen. Eine in vitro-Studie. Albrecht Von Graefes Arch Klin Exp Ophthalmol. 1970;180(3):231–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00411532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lembeck F., Holzer P. Substance P as neurogenic mediator of antidromic vasodilation and neurogenic plasma extravasation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Dec;310(2):175–183. doi: 10.1007/BF00500282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lembeck F., Popper H., Juan H. Release of prostaglandins by bradykinin as an intrinsic mechanism of its algesic effect. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1976 Jul;294(1):69–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00692786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILES A. A., MILES E. M. Vascular reactions to histamine, histamine-liberator and leukotaxine in the skin of guinea-pigs. J Physiol. 1952 Oct;118(2):228–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marceau F., Knap M., Regoli D. Pharmacological characterization of the vascular permeability enhancing effects of kinins in the rabbit skin. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;59(9):921–926. doi: 10.1139/y81-142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWLEY D. A. VENOUS CONSTRICTION AS THE CAUSE OF INCREASED VASCULAR PERMEABILITY PRODUCED BY 5-HYDROXYTRYPTAMINE, HISTAMINE, BRADYKININ AND 48/80 IN THE RAT. Br J Exp Pathol. 1964 Feb;45:56–67. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Barabé J. Pharmacology of bradykinin and related kinins. Pharmacol Rev. 1980 Mar;32(1):1–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Drapeau G., Rovero P., Dion S., D'Orléans-Juste P., Barabé J. The actions of kinin antagonists on B1 and B2 receptor systems. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Apr 9;123(1):61–65. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90687-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILD H. O. Drug antagonism and pAx. Pharmacol Rev. 1957 Jun;9(2):242–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERN P., NIKULIN A., FERLUGA J. The role of histamine and bradykinin in the inflammatory process. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1962 Dec 1;140:528–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda N., Muramatsu I., Fujiwara M. Capsaicin and bradykinin-induced substance P-ergic responses in the iris sphincter muscle of the rabbit. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Aug;230(2):469–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vavrek R. J., Stewart J. M. Competitive antagonists of bradykinin. Peptides. 1985 Mar-Apr;6(2):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


