Abstract
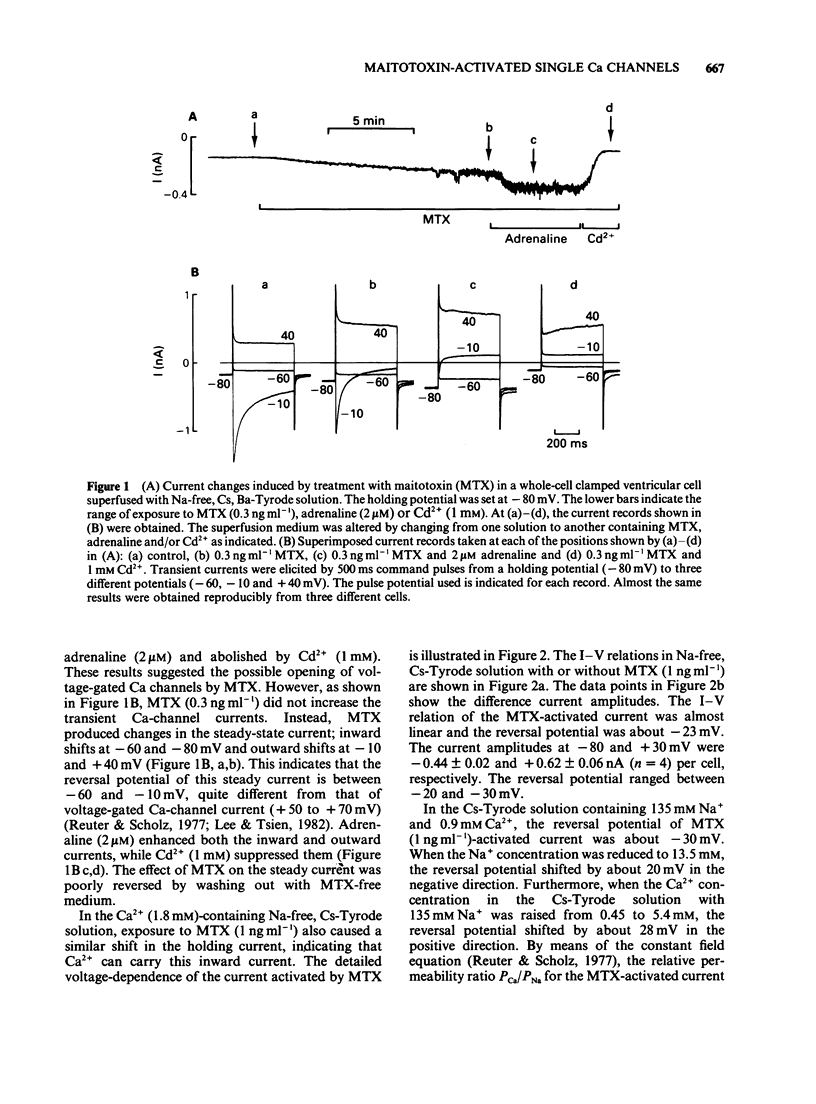
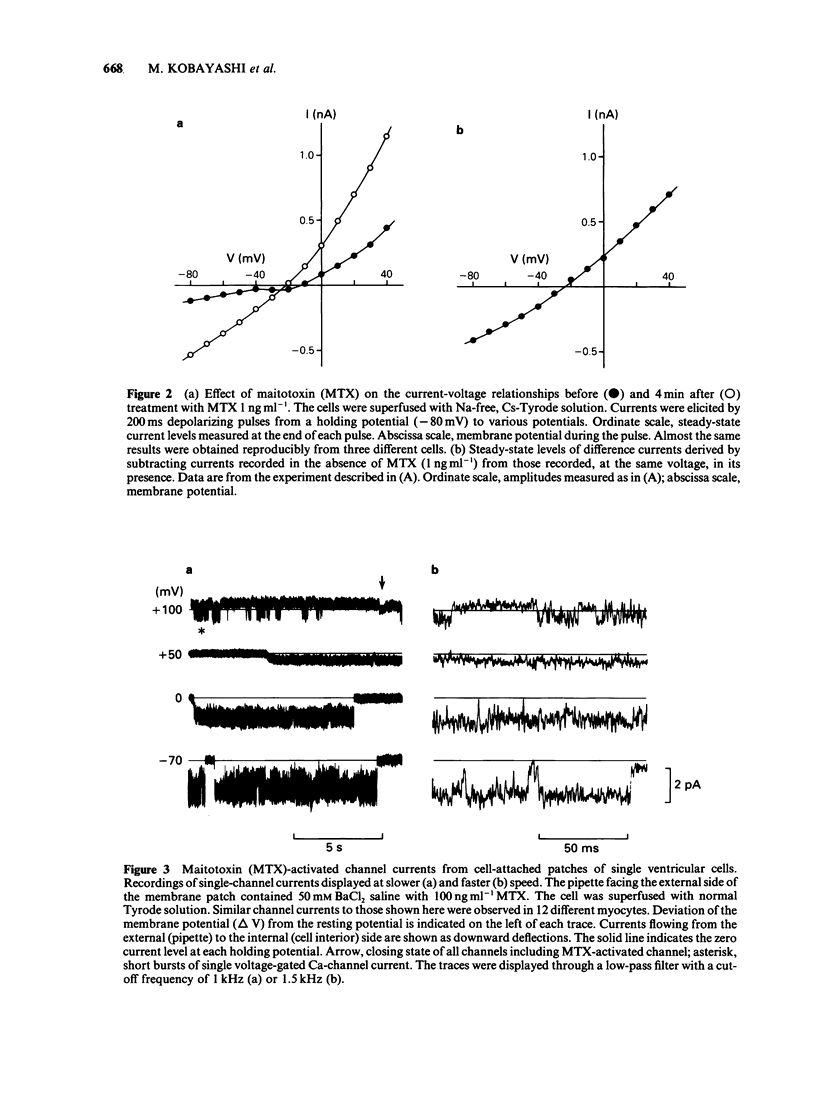
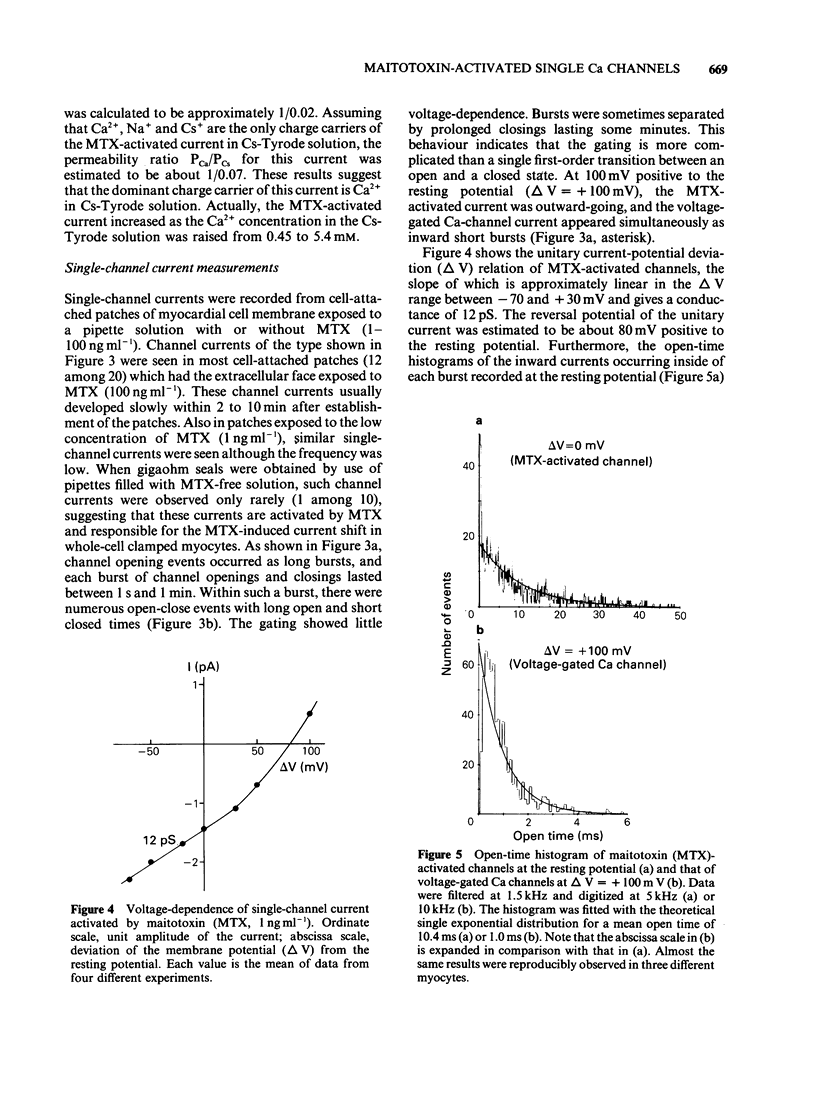
1. In order to clarify the mechanism of Ca-dependent excitatory action of maitotoxin (MTX), the most potent marine toxin known, patch-clamp techniques were used to analyse electrophysiological effects of MTX on guinea-pig isolated cardiac myocytes. 2. The whole-cell recordings showed that MTX (0.3 ng ml-1) produced a sustained inward current that was enhanced by adrenaline (2 microM) and abolished by Cd2+ (1 mM). 3. This current was predominantly carried by Ca2+ or Ba2+ and has an almost linear current-voltage relationship. 4. In cell-attached patches, MTX added to the pipette solution activated Ca channels with novel properties. The opening events of these channels occurred as long bursts, and the channel gating showed little voltage-dependence. 5. The unitary conductance was 12 pS in the presence of 50 mM Ba2+. Within a burst, the distribution of opening times was a single exponential with a mean open time of 10.4 ms. 6. The channel described here represents either a new class of voltage-independent Ca channel or an entirely modified form of voltage-gated Ca channel. This channel may account for the mechanism of enhanced Ca2+ influx through the cell membrane induced by MTX, and presumably regulates some ionic movements in myocardial cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albuquerque E. X., Daly J. W., Witkop B. Batrachotoxin: chemistry and pharmacology. Science. 1971 Jun 4;172(3987):995–1002. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3987.995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Molecular properties of voltage-sensitive sodium channels. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:953–985. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Neurotoxins that act on voltage-sensitive sodium channels in excitable membranes. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1980;20:15–43. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.20.040180.000311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalié A., Ochi R., Pelzer D., Trautwein W. Elementary currents through Ca2+ channels in guinea pig myocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Sep;398(4):284–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00657238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Neher E., Reuter H., Stevens C. F. Inward current channels activated by intracellular Ca in cultured cardiac cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):752–754. doi: 10.1038/294752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman S. B., Miller R. J., Miller D. M., Tindall D. R. Interactions of maitotoxin with voltage-sensitive calcium channels in cultured neuronal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4582–4585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honerjäger P. Cardioactive substances that prolong the open state of sodium channels. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1982;92:1–74. doi: 10.1007/BFb0030502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. I., Login I. S., Yasumoto T. Maitotoxin activates quantal transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction: evidence for elevated intraterminal Ca2+ in the motor nerve terminal. Brain Res. 1985 Nov 4;346(2):357–362. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90870-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Kondo S., Yasumoto T., Ohizumi Y. Cardiotoxic effects of maitotoxin, a principal toxin of seafood poisoning, on guinea pig and rat cardiac muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Sep;238(3):1077–1083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Miyakoda G., Nakamura T., Ohizumi Y. Ca-dependent arrhythmogenic effects of maitotoxin, the most potent marine toxin known, on isolated rat cardiac muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Apr 23;111(1):121–123. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Ohizumi Y., Yasumoto T. The mechanism of action of maitotoxin in relation to Ca2+ movements in guinea-pig and rat cardiac muscles. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Oct;86(2):385–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08907.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Tsien R. W. Reversal of current through calcium channels in dialysed single heart cells. Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):498–501. doi: 10.1038/297498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz M. D., Sutro J. B., Hille B. Voltage-dependent gating of veratridine-modified Na channels. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Jan;87(1):25–46. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemos J. R., Nordmann J. J., Cooke I. M., Stuenkel E. L. Single channels and ionic currents in peptidergic nerve terminals. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):410–412. doi: 10.1038/319410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Login I. S., Judd A. M., Cronin M. J., Koike K., Schettini G., Yasumoto T., MacLeod R. M. The effects of maitotoxin on 45Ca2+ flux and hormone release in GH3 rat pituitary cells. Endocrinology. 1985 Feb;116(2):622–627. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-2-622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama Y., Peterson O. H. Single-channel currents in isolated patches of plasma membrane from basal surface of pancreatic acini. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):159–161. doi: 10.1038/299159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto T., Ohizumi Y., Washio H., Yasumoto Y. Potent excitatory effect of maitotoxin on Ca channels in the insect skeletal muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Apr;400(4):439–441. doi: 10.1007/BF00587546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narahashi T. Chemicals as tools in the study of excitable membranes. Physiol Rev. 1974 Oct;54(4):813–889. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1974.54.4.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohizumi Y., Kajiwara A., Yasumoto T. Excitatory effect of the most potent marine toxin, maitotoxin, on the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Oct;227(1):199–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohizumi Y., Yasumoto T. Contractile response of the rabbit aorta to maitotoxin, the most potent marine toxin. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:711–721. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H., Scholz H. A study of the ion selectivity and the kinetic properties of the calcium dependent slow inward current in mammalian cardiac muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Jan;264(1):17–47. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schettini G., Koike K., Login I. S., Judd A. M., Cronin M. J., Yasumoto T., MacLeod R. M. Maitotoxin stimulates hormonal release and calcium flux in rat anterior pituitary cells in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1984 Oct;247(4 Pt 1):E520–E525. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.247.4.E520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutro J. B. Kinetics of veratridine action on Na channels of skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Jan;87(1):1–24. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Ohizumi Y., Yasumoto T. Maitotoxin, a Ca2+ channel activator candidate. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7287–7289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Tatsumi M., Ohizumi Y., Yasumoto T. Ca2+ channel activating function of maitotoxin, the most potent marine toxin known, in clonal rat pheochromocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):10944–10949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Tamura S., Fukushima N., Takagi H. Pertussis toxin (IAP) enhances maitotoxin (a putative Ca2+ channel agonist)-induced Ca2+ entry into synaptosomes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Apr 2;122(3):379–380. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90421-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G. Single Ca2+-activated nonselective cation channels in neuroblastoma. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):357–359. doi: 10.1038/296357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


