Abstract
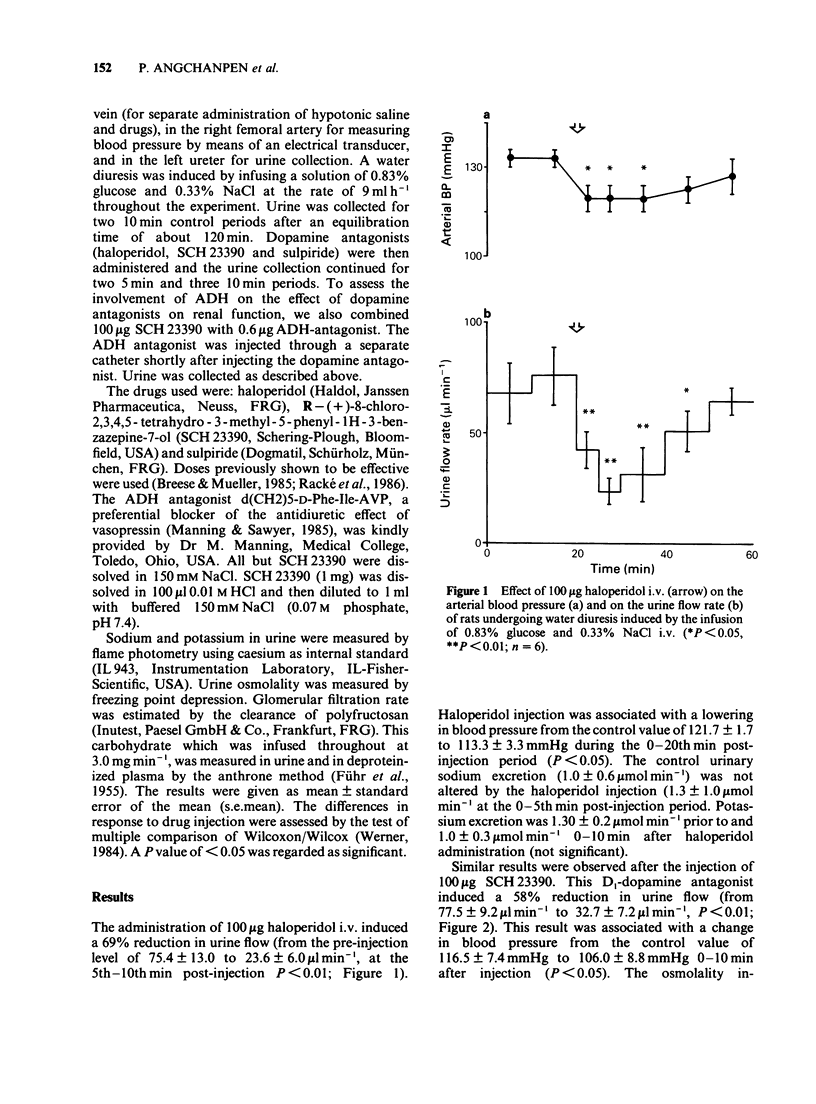
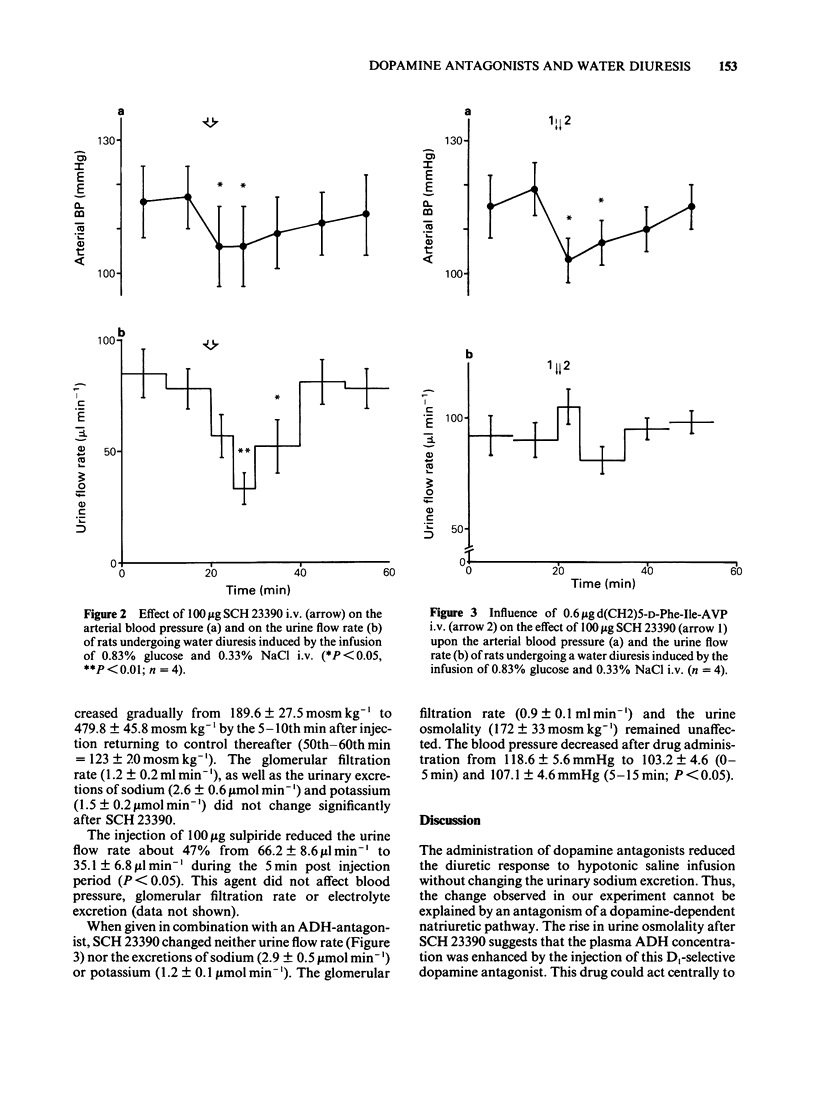
1. The probable involvement of dopamine in the regulation of water excretion was investigated by administering dopamine antagonists intravenously to barbiturate--anaesthetized rats undergoing a water diuresis induced by the infusion of 0.83% glucose with 0.3% NaCl at the rate of 9 ml h-1. 2. Administration of 100 micrograms of the D1-/D2-dopamine antagonist, haloperidol, reduced the enhanced urine flow of rats infused with the hypotonic solution by 69% (from 75.4 +/- 13.0 to 23.6 +/- 6.0 microliter min-1, P less than 0.01). Similarly, the D1-receptor antagonist, SCH 23390, reduced urine flow by 58% (from 77.5 +/- 9.2 to 32.7 +/- 7.2 microliters min-1, P less than 0.01) and the D2-receptor antagonist, sulpiride, by 47% (from 66.2 +/- 8.6 to 35.1 +/- 6.8 microliter min-1, P less than 0.05). 3. The injection of SCH 23390 increased the urine osmolality from 189.6 +/- 27.5 to 479.8 +/- 45.8 mosm kg-1 (P less than 0.05). There was no significant change in sodium and potassium excretion in any of the experiments. Blood pressure (BP) decreased after haloperidol and SCH 23390 injection from control values of 121.7 +/- 1.7 and 116.5 +/- 7.4 to 113.3 +/- 3.3 and 106.0 +/- 8.8 mmHg respectively (P less than 0.05). 4. To study whether the influence of dopamine antagonists on urine flow during water diuresis depends on antidiuretic hormone (ADH), we administered 0.6 micrograms d(CH2)5-D-Phe-Ile-AVP (an ADH antagonist) shortly after the injection of 100 micrograms SCH 23390.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arruda J. A., Sabatini S. Dopaminergic inhibition of vasopressin-stimulated water flow in the toad bladder: evidence for local formation of dopamine. J Membr Biol. 1982;68(2):89–96. doi: 10.1007/BF01872257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breese G. R., Mueller R. A. SCH-23390 antagonism of a D-2 dopamine agonist depends upon catecholaminergic neurons. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jul 11;113(1):109–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90349-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges T. E., Hillhouse E. W., Jones M. T. The effect of dopamine on neurohypophysial hormone release in vivo and from the rat neural lobe and hypothalamus in vitro. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;260(3):647–666. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman B. J., Horn N. M., Munday K. A., Robertson M. J. The actions of dopamine and of sulpiride on regional blood flows in the rat kidney. J Physiol. 1980 Jan;298:437–452. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUHR J., KACZMARCZYK J., KRUTTGEN C. D. Eine einfache colorimetrische Methode zur Inulinbestimmung für Nieren-Clearance-Untersuchungen bei Stoffwechselgesunden und Diabetikern. Klin Wochenschr. 1955 Aug 1;33(29-30):729–730. doi: 10.1007/BF01473295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsling M. L., Lightman S. L. Effect of L-dopa on vasopressin secretion in man [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:64P–65P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzbauer M., Sharman D. F., Godden U., Mann S. P., Stephens D. B. Effect of water and salt intake on pituitary catecholamines in the rat and domestic pig. Neuroscience. 1980;5(11):1959–1968. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzbauer M., Sharman D. F., Godden U. Observations on the function of the dopaminergic nerves innervating the pituitary gland. Neuroscience. 1978;3(12):1251–1262. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna G. G., Danovitch G. M., Beck F. W., Sowers J. R. Dopaminergic mediation of the natriuretic response to volume expansion. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Feb;105(2):214–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightman S. L., Iversen L. L., Forsling M. L. Dopamine and [D-ALA2, D-Leu5]enkephalin inhibit the electrically stimulated neurohypophyseal release of vasopressin in vitro: evidence for calcium-dependent opiate action. J Neurosci. 1982 Jan;2(1):78–81. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-01-00078.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marin-Grez M., Angchanpen P., Gambaro G., Schnermann J., Schubert G., Briggs J. P. Evidence for an involvement of dopamine receptors in the natriuretic response to atrial natriuretic peptide. Klin Wochenschr. 1987;65 (Suppl 8):97–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marin-Grez M., Briggs J. P., Schubert G., Schnermann J. Dopamine receptor antagonists inhibit the natriuretic response to atrial natriuretic factor (ANF). Life Sci. 1985 Jun 3;36(22):2171–2176. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90314-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClanahan M., Sowers J. R., Beck F. W., Mohanty P. K., McKenzie T. Dopaminergic regulation of natriuretic response to acute volume expansion in dogs. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Mar;68(3):263–269. doi: 10.1042/cs0680263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto S., Tabei K., Asano Y., Imai M. Dopaminergic inhibition of the action of vasopressin on the cortical collecting tubule. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Aug 27;114(3):393–397. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90386-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racké K., Meuresch J., Trapp B., Muscholl E. Modulation by fenoldopam (SKF 82526) and bromocriptine of the electrically evoked release of vasopressin from the rat neurohypophysis. Effects of dopamine depletion. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;332(4):332–337. doi: 10.1007/BF00500083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson G. L. The regulation of vasopressin function in health and disease. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1976;33:333–385. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571133-3.50015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


