Abstract
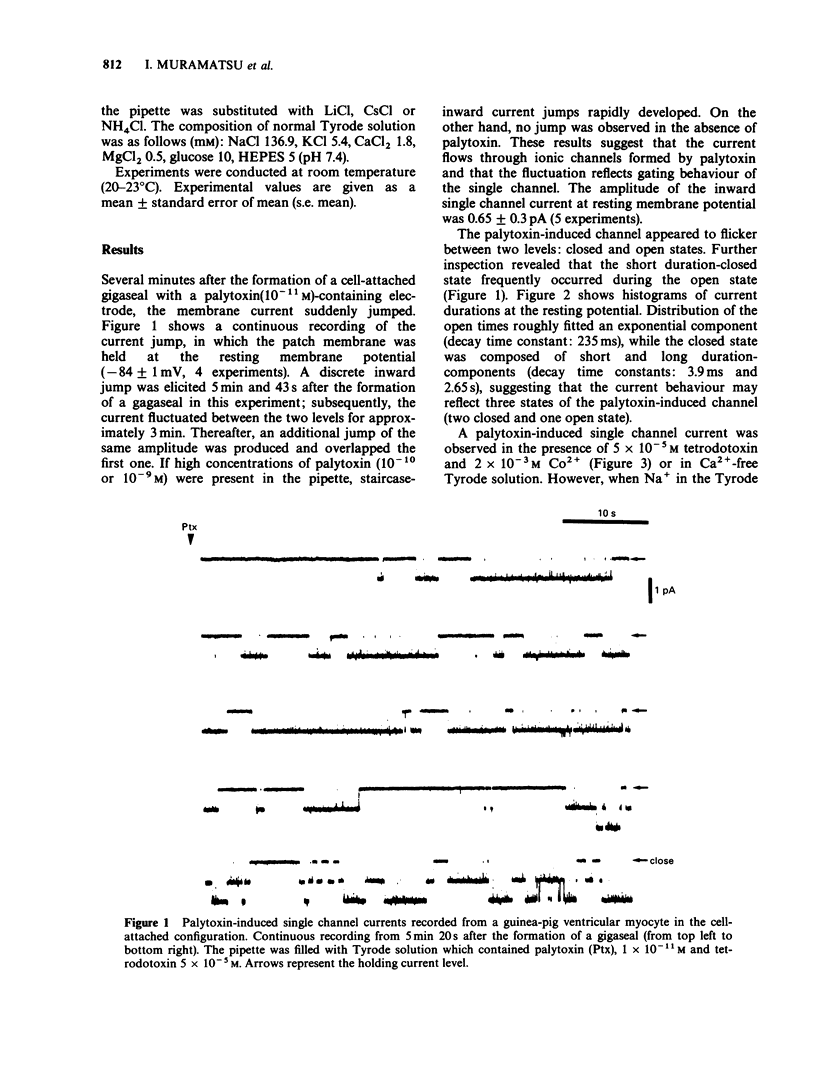
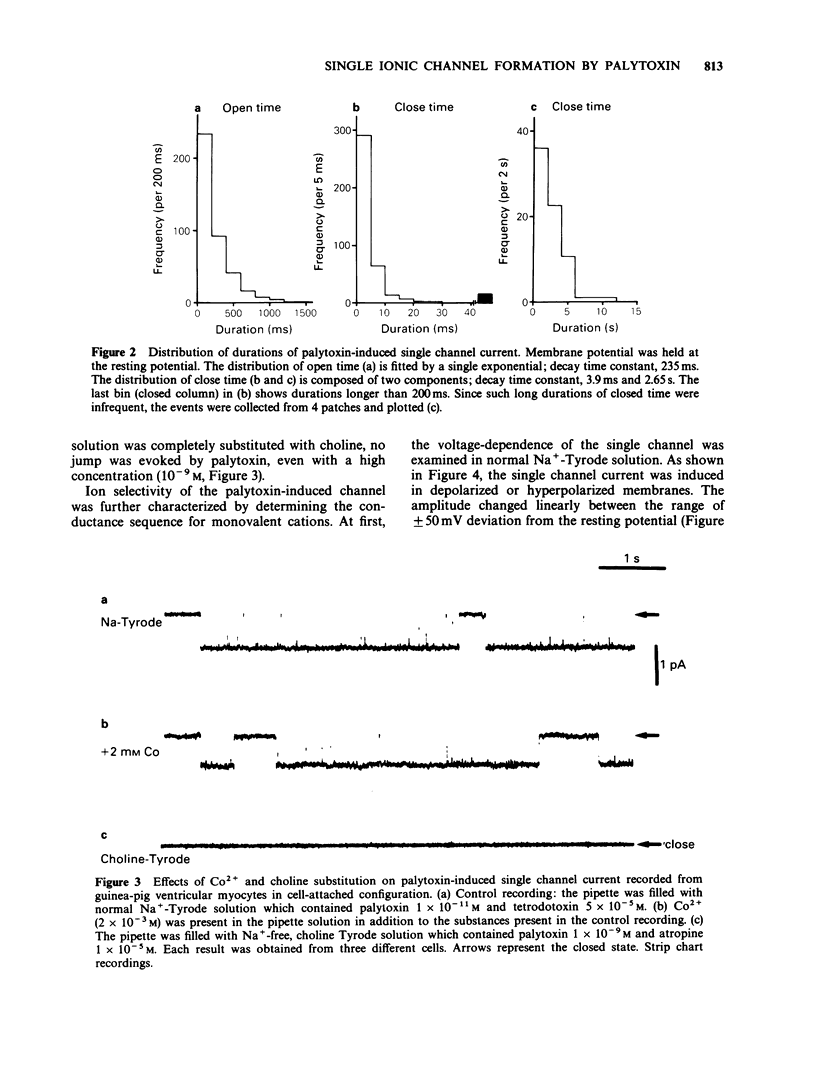
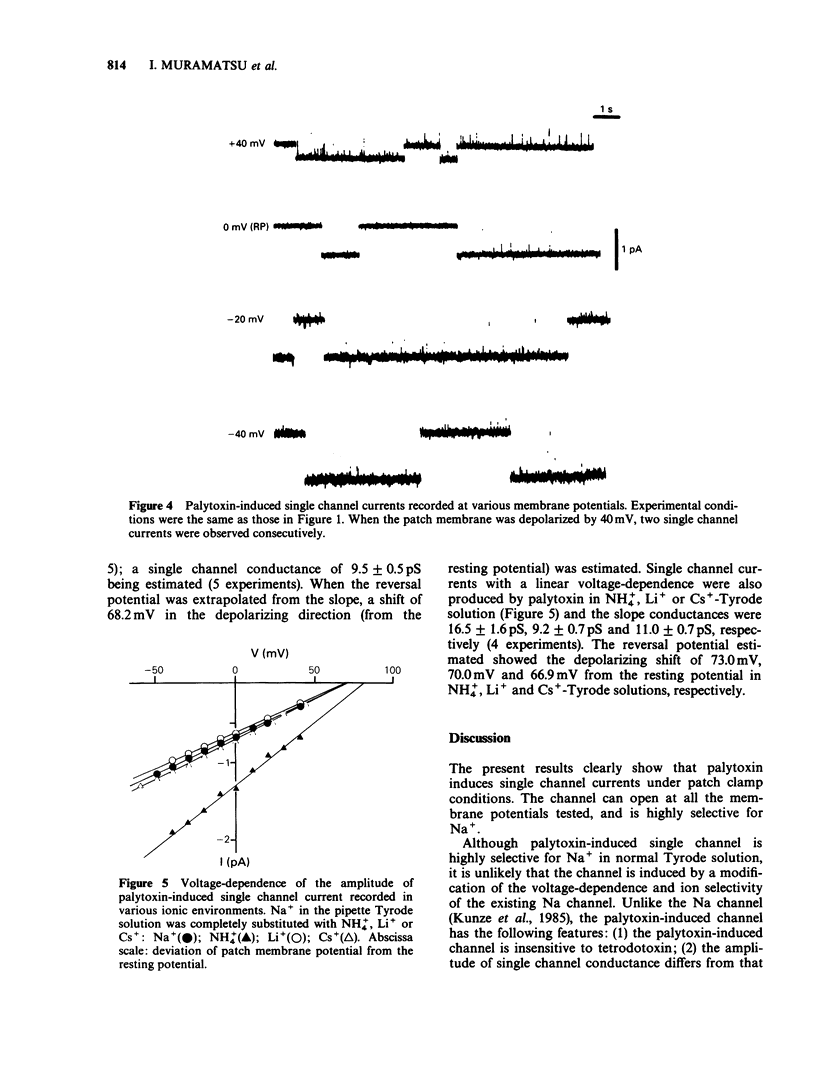
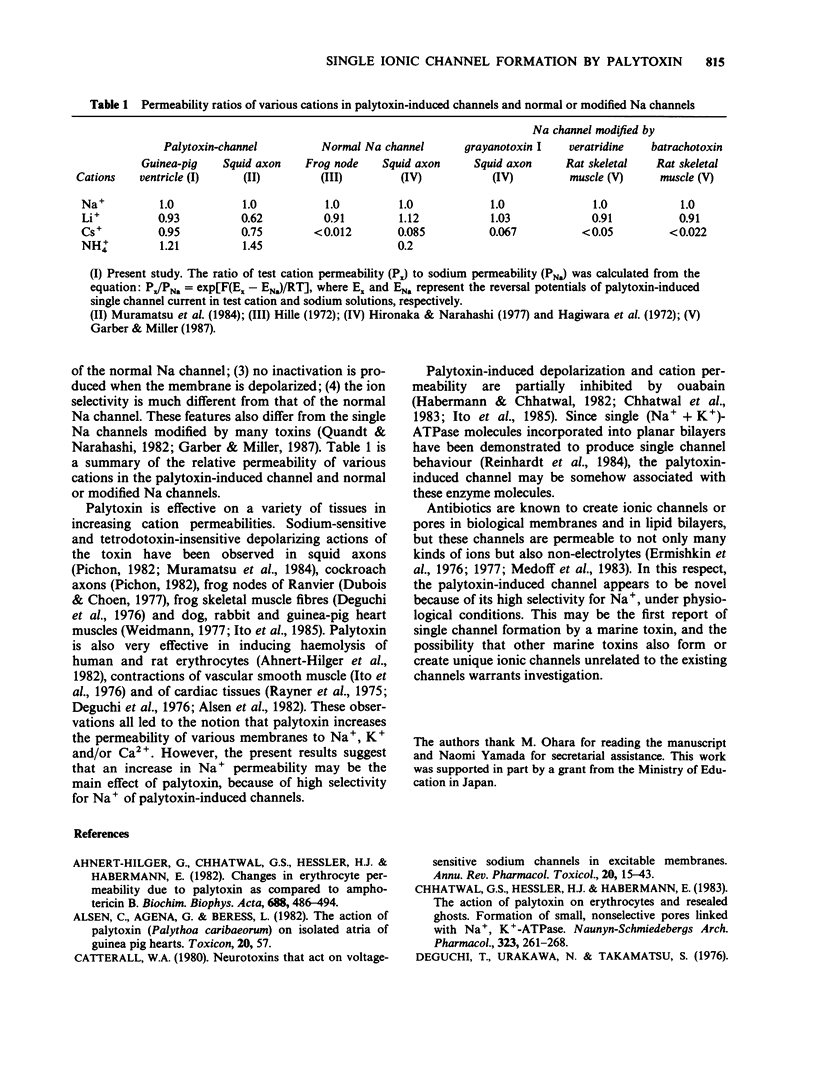
1. Mechanisms of palytoxin-induced ion permeability were examined in isolated single ventricular cells of guinea-pig under whole-cell-attached patch clamp conditions. 2. Palytoxin (1-2 x 10(-11) M, dissolved in Tyrode solution and put in the patch electrode) induced an elementary current flowing through single channels. Direction of the current was inward and the amplitude was 0.65 +/- 0.03 pA (mean +/- s.e. mean) at the resting membrane potential. The amplitude increased linearly with membrane hyperpolarization and decreased with depolarization; the single channel conductance was 9.5 +/- 0.5 pS. 3. Palytoxin-induced single channel current was resistant to tetrodotoxin (5 x 10(-5) M) or cobalt ions (2 x 10(-3) M) and was observed under Ca-free conditions. However, no channel current was induced by palytoxin (10(-11) - 10(-9) M) dissolved in Na+-free, choline-Tyrode solution. 4. Palytoxin also induced single channel currents in Na+-free, NH4+-, Li+- or Cs+-Tyrode solution, and the slope conductances were 16.5 +/- 1.6 pS, 9.2 +/- 0.7 pS and 11.0 +/- 0.7 pS, respectively. 5. These results indicate that palytoxin forms a new type of ionic channel with unique ion selectivity and gating behaviour.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahnert-Hilger G., Chhatwal G. S., Hessler H. J., Habermann E. Changes in erythrocyte permeability due to palytoxin as compared to amphotericin B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 14;688(2):486–494. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90360-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Neurotoxins that act on voltage-sensitive sodium channels in excitable membranes. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1980;20:15–43. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.20.040180.000311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chhatwal G. S., Hessler H. J., Habermann E. The action of palytoxin on erythrocytes and resealed ghosts. Formation of small, nonselective pores linked with Na+, K+-ATPase. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1983 Jul;323(3):261–268. doi: 10.1007/BF00497672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois J. M., Cohen J. B. Effect of palytoxin on membrane and potential and current of frog myelinated fibers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Apr;201(1):148–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ermishkin L. N., Kasumov K. M., Potseluyev V. M. Properties of amphotericin B channels in a lipid bilayer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 1;470(3):357–367. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90127-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ermishkin L. N., Kasumov K. M., Potzeluyev V. M. Single ionic channels induced in lipid bilayers by polyene antibiotics amphotericin B and nystatine. Nature. 1976 Aug 19;262(5570):698–699. doi: 10.1038/262698a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber S. S., Miller C. Single Na+ channels activated by veratridine and batrachotoxin. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Mar;89(3):459–480. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.3.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E., Chhatwal G. S. Ouabain inhibits the increase due to palytoxin of cation permeability of erythrocytes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 May;319(2):101–107. doi: 10.1007/BF00503920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Eaton D. C., Stuart A. E., Rosenthal N. P. Cation selectivity of the resting membrane of squid axon. J Membr Biol. 1972;9(4):373–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The permeability of the sodium channel to metal cations in myelinated nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Jun;59(6):637–658. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.6.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hironaka T., Narahashi T. Cation permeability ratios of sodium channels in normal and grayanotoxin-treated squid axon membranes. J Membr Biol. 1977 Mar 23;31(4):359–381. doi: 10.1007/BF01869413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honerjäger P. Cardioactive substances that prolong the open state of sodium channels. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1982;92:1–74. doi: 10.1007/BFb0030502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Karaki H., Ishida Y., Urakawa N., Deguchi T. Effects of palytoxin on isolated intestinal and vascular smooth muscles. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1976 Dec;26(6):683–692. doi: 10.1254/jjp.26.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Saruwatari N., Mitani K., Enomoto Y. Characterization of depolarization induced by palytoxin and grayanotoxin-I in isolated cardiac tissues from dogs and guinea pigs. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Jul;330(1):67–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00586711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunze D. L., Lacerda A. E., Wilson D. L., Brown A. M. Cardiac Na currents and the inactivating, reopening, and waiting properties of single cardiac Na channels. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Nov;86(5):691–719. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.5.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medoff G., Brajtburg J., Kobayashi G. S., Bolard J. Antifungal agents useful in therapy of systemic fungal infections. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1983;23:303–330. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.23.040183.001511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. E., Scheuer P. J. Palytoxin: a new marine toxin from a coelenterate. Science. 1971 Apr 30;172(3982):495–498. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3982.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu I., Fujiwara M., Miura A., Narahashi T. Effects of Goniopora toxin on crayfish giant axons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Aug;234(2):307–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu I., Uemura D., Fujiwara M., Narahashi T. Characteristics of palytoxin-induced depolarization in squid axons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Dec;231(3):488–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narahashi T. Chemicals as tools in the study of excitable membranes. Physiol Rev. 1974 Oct;54(4):813–889. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1974.54.4.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishio M., Kigoshi S., Muramatsu I. Ryanodine has no effect on the Ca current in single ventricular cells of guinea-pig. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 May 27;124(3):353–356. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90239-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichon Y. Effects of palytoxin on sodium and potassium permeabilities in unmyelinated axons. Toxicon. 1982;20(1):41–47. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(82)90141-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quandt F. N., Narahashi T. Modification of single Na+ channels by batrachotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6732–6736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayner M. D., Sanders B. J., Harris S. M., Lin Y. C., Morton B. E. Palytoxin: effects on contractility and 45Ca2+ uptake in isolated ventricle strips. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1975 May;11(1):55–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhardt R., Lindemann B., Anner B. M. Leakage-channel conductance of single (Na+ + K+)-ATPase molecules incorporated into planar bilayers by fusion of liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jul 11;774(1):147–150. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90285-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidmann S. Effects of palytoxin on the electrical activity of dog and rabbit heart. Experientia. 1977 Nov 15;33(11):1487–1489. doi: 10.1007/BF01918825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


